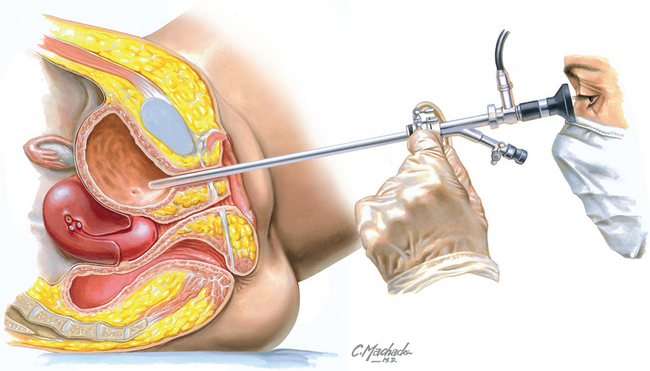
Chapter 240 Cystourethroscopy
REQUIRED EQUIPMENT
Gilmour DT, Das S, Flowerdew G. Rates of urinary tract injury from gynecologic surgery and the role of intraoperative cystoscopy. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107:1366.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The role of cystourethroscopy in the generalist obstetrician–gynecologist practice. ACOG Committee Opinion 372. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110:221.
Cundiff GW, Bent AE. Endoscopic evaluation of the lower urinary tract. In: Walters MD, Karram MM, editors. Urogynecology and reconstructive pelvic surgery. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier; 2007:114.
Dajani AS, Taubert KA, Wilson W, et al. Prevention of bacterial endocarditis. Recommendations by the American Heart Association. JAMA. 1997;277:1794.
Olson ES, Cookson BD. Do antimicrobials have a role in preventing septicemia following instrumentation of the urinary tract? J Hosp Infect. 2000;45:85.