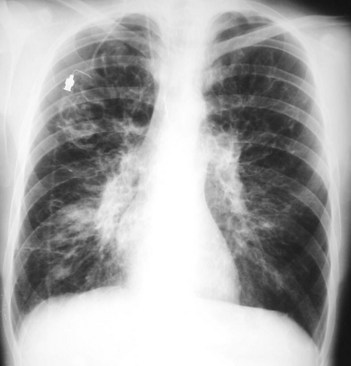
105 Cystic fibrosis
Salient features
Questions
What are the chances of this male patient having a child?
Males are sterile through the failure of development of the vas deferens and epididymis.
What are the clinical manifestations of this condition?
• Neonates: recurrent chest infections, failure to thrive, meconium ileus and rectal prolapse
• In childhood and young adults:
Advanced-level questions
If this patient requires lung transplantation, which type of transplantation is the treatment of choice?
What are the new methods of treatment available for cystic fibrosis?
• High-dose ibuprofen in patients with mild disease (FEV1 of at least 60% of the predicted value), taken consistently for 4 years, significantly slows the progression of lung disease without serious adverse effects.
• Aerosolized recombinant human DNAse (dornase-alpha), which is capable of degrading DNA in the bronchial secretion, has been shown to improve FEV1 by 20% when given by aerosol.
• Gene therapy: the gene is transferred in a ‘carrier’ (either in a cationic lipid envelope known as a liposome, or in an adenovirus). On transferring the gene for cystic fibrosis to the nasal epithelium using a cationic liposome, the deficit has been partly removed without provoking a local inflammatory response.
• Inhalation of hypertonic saline produces a sustained acceleration of mucus clearance and improved lung function. This treatment may protect the lung from insults that reduce mucus clearance and produce lung disease.
What advice would you give a patient with cystic fibrosis who wishes to become pregnant?
• The couple will be offered genetic counselling and the man will be offered testing to determine his genetic status. If he is a carrier, chorionic villous sampling will be considered, as the risk of the couple conceiving an infant with cystic fibrosis is 1 in 2 and they may wish to consider selective termination in the first trimester. The hazards of general anaesthesia (as lung function is impaired) for termination of pregnancy will be brought to their attention. Termination of pregnancy either with spinal anaesthesia or medications is an alternative.
• Women with severe disease will be informed that they may be unable to complete pregnancy and that their premature demise may leave a motherless child.
• In women with an FEV1 <60% of the predicted value there is an increased risk of premature delivery, an increased rate of caesarean section, some loss of lung function and risk of respiratory complications, and early death of the mother.
• Pregnancy after heart–lung transplantation offers better health and increased longevity in the mother, but the risk of organ rejection and exposure of the fetus to potentially teratogenic immunosuppressants means that pregnancy should not be attempted by women with transplants.