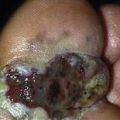
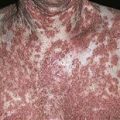
32
Cystic acne
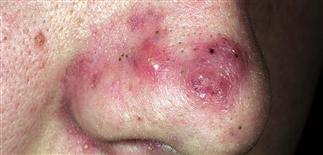
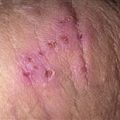
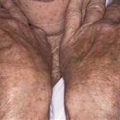
Cysts are larger, deeper, and last longer than papules and pustules. They may be painful and always scar.
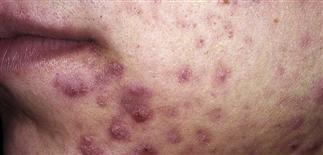
Moderate cystic acne. Scars from previous lesions are evident.
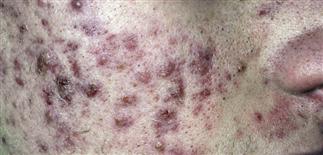
Severe cystic acne. Some cysts have become confluent. The disease is long-lasting, the scarring severe.
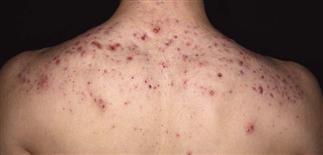
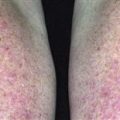
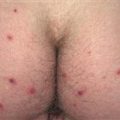
The back, chest, and upper arms are frequently affected. Cysts may become confluent and create very large, painful lesions.
DESCRIPTION
Most likely form of acne to cause scars. Must treat early with oral medications to avoid scars.
HISTORY
• Starts with cysts or evolves from papulopustular acne. • Lasts for months or decades. • May require repeated courses of isotretinoin.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
• Deep, inflamed cysts occur on the face, chest, back and shoulders. • Distribution and severity highly variable.
TREATMENT
• Moderate: same approach as for moderate and severe papulopustular acne. • Severe: May try brief trial of medications used to treat moderate and severe papulopustular acne. • Isotretinoin (Claravis, Amnesteem, Sotret) 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg. Start with low dosage (e.g. 10–40 mg q.d.) to avoid acne flare. Dose of 1–2 mg/kg/day is most effective for severe cystic acne, given over a total of 4–5 months. • Short course of prednisone is sometimes used. • Inject triamcinolone 2.5–5 mg/mL into painful inflammed cysts. • Oral contraceptives (e.g. Ortho Tri-Cyclen, Alesse) may be beneficial. • Spironolactone 50–100 mg b.i.d. may be helpful for women. Isotretinoin is highly teratogenic and its use is restricted in the USA to patients and their physicians who participate in the iPLEDGE registry program.