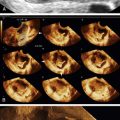
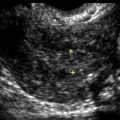
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Synonyms/Description
One of the epithelial-stromal tumors containing mucoid material
Etiology
Most mucinous cystadenomas are benign tumors, although 20% can be borderline (low malignant potential) or malignant. Benign mucinous cystadenomas represent 20% to 25% of all benign ovarian tumors and occur mostly during the third to fifth decades. These mucinous tumors are comprised most often of the mucin-producing cell type similar to a cell type that lines the intestinal tract, although a minority of the tumors have endocervical-like mucin-producing cells. Some tumors may contain both cell types.
Borderline mucinous cystadenomas are of low malignant potential and carry a 5-year survival prognosis of 95%. The less common borderline the endocervical type has a worse prognosis and higher recurrence rate than the intestinal type. For the borderline and invasive neoplasms, see elsewhere in this book.
Ultrasound Findings
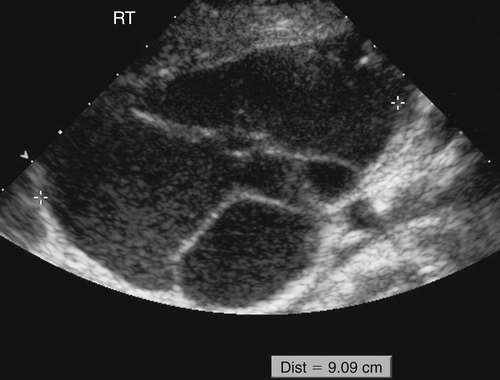
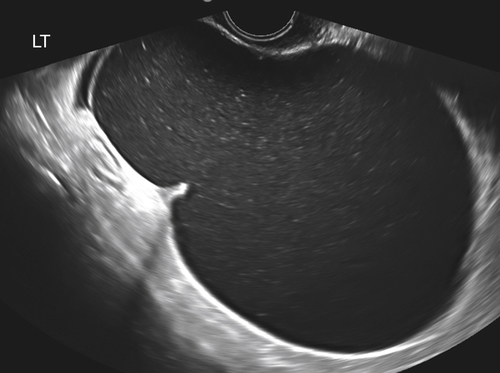
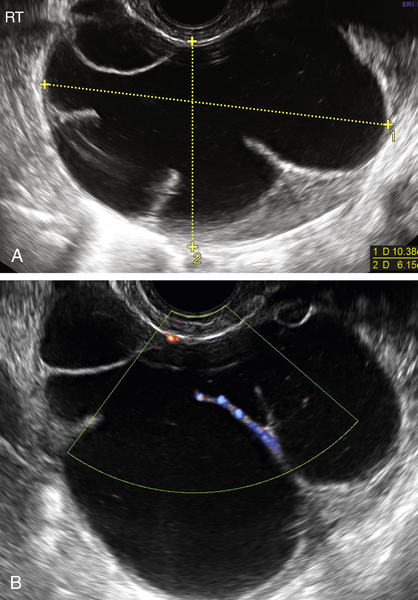
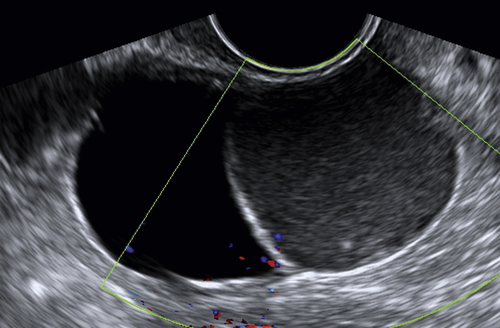
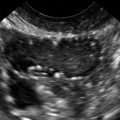
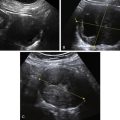
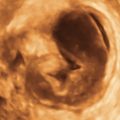
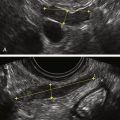
Mucinous cystadenomas are multilocular in 50% of cases, with solid components or papillary projections in 40% of borderline and malignant cases. The fluid inside the cystic area typically contains low-level echoes much like an endometrioma; however, when interrogated with Doppler, the echoes stream compared with those in endometriomas, which usually do not. The different compartments of the cystic mass may differ as to the texture of the echoes within, likely secondary to different cell types within a single tumor. When internal nodules with blood flow are present, the possibility of a borderline or invasive malignancy must be considered. Typically, borderline malignancies have fewer nodules and less blood flow within them compared with invasive tumors, although this is a very subjective finding.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis includes any complex cystic mass of the adnexa. These diagnoses are numerous and include serous cystadenoma, cystadenofibroma, endometrioma, peritoneal inclusion cyst, degenerating fibroid, complex hydrosalpinx, and so on. It may not be possible to arrive at a specific diagnosis sonographically when faced with a multiseptate cystic mass; however, the characteristic finding to consider in a mucinous cystadenoma is the presence of low-level echoes, much like an endometrioma but with multiple septations. Often a patient with endometriosis will be symptomatic and may have other sites of endometriotic implants that would differentiate it from a single asymptomatic mass such as a cystadenoma. If a separate ovary can be found, the differential might include non-ovarian diagnoses such as hydrosalpinx or peritoneal inclusion cyst.
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Like any adnexal mass, mucinous cystadenomas may present with pelvic pain, especially during activities such as intercourse, exercise, or defecation. However, most commonly they are asymptomatic and are appreciated on routine bimanual pelvic examination or incidentally found at the time of pelvic imaging for virtually any indication. Benign mucinous ovarian neoplasms can become extremely large and thus come to surgical exploration. When they are multilocular, they may raise suspicion for malignancy. Increasingly, however, a minimally invasive approach using laparoscopic surgery is favored over laparotomy, especially to preserve ovarian function when the mass is considered benign. Although less common, when unilocular and small, these masses can be treated expectantly. Tumor markers such as CA125 are elevated in less than 50% of malignant neoplasms, and thus would not be expected to be extremely helpful in such cases. If conservative management is undertaken, follow-up sonographic surveillance at periodic intervals is appropriate.
Figures
Suggested Reading
Caspi B., Hagay Z., Appelman Z. Variable echogenicity as a sonographic sign in the preoperative diagnosis of ovarian mucinous tumors. J Ultrasound Med. 2006;25:1583–1585.
Fruscella E., Testa A.C., Ferrandina G., De Smet F., Van Holsbeke C., Scambia G., Zannoni G.F., Ludovisi M., Achten R., Amant F., Vergote I., Timmerman D. Ultrasound features of different histopathological subtypes of borderline ovarian tumors. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005;26:644–650.
Hart W.R. Mucinous tumors of the ovary: a review. In J Gynecol Pathol. 2005;24:4–25.