Epidermoid Cyst
Synonyms/Description
Epidermal cyst or sebaceous cyst of the ovary
Mature monophyletic teratoma
Etiology
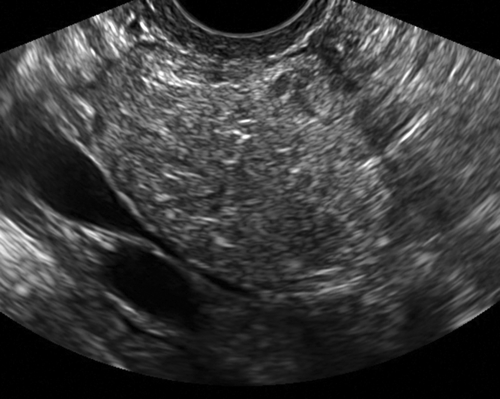
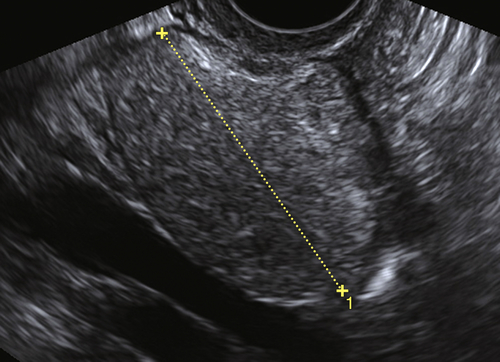
Epidermoid cysts are benign cysts, lined by mature keratinizing squamous epithelium but without hair (unlike dermoids). These lesions represent less than 0.25% of all ovarian neoplasms. Two main theories exist regarding the etiology: This may be a monophyletic variant of a dermoid or teratoma with only the epithelial component present, resulting in a highly differentiated lesion. Alternatively, epidermoid cysts may arise from epithelial cell nests in the ovary similar to those seen in Brenner tumors. The cysts can contain keratin and other sebaceous material. There is a similar counterpart tumor that occurs in the testes.
Ultrasound Findings
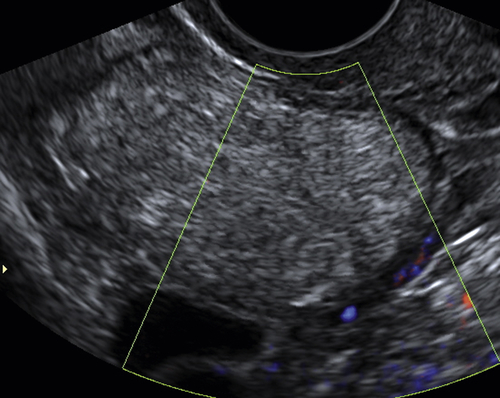
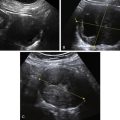
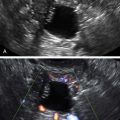
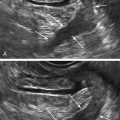
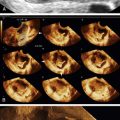
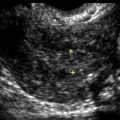
Epidermoid cysts are solid-appearing lesions with heterogeneous and echogenic texture but no internal color flow on Doppler evaluation. The detectable blood flow is peripheral, suggesting a cyst wall. Epidermoid cysts are not as echogenic as dermoids, making the appearance nonspecific. The lack of flow inside is helpful in this otherwise solid-appearing lesion.
Differential Diagnosis
The presence of a solid ovarian mass brings to mind many diagnoses. The lack of internal blood flow typical of the epidermoid cyst helps to narrow the differential diagnoses to dermoid, endometrioma, fibroma, or other benign solid ovarian tumor.
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Epidermoid cyst is usually detected as an incidental finding on a pathology specimen, benign, and rarely symptomatic.