Cranial Nerve VIII
Auditory Nerve
There are two components: auditory and vestibular.
AUDITORY
WHAT TO DO
Test the hearing
Test one ear at a time. Block the opposite ear; either cover it with your hand or produce a blocking white noise, e.g. crumpling paper.
Hold your watch by the patient’s ear. Discover how far away from the ear it is still heard. Alternative sounds are whispering or rubbing your fingers together. Increase in volume to normal speech or loud speech until your patient hears.
If the hearing in one ear is reduced, perform Rinne’s and Weber’s tests.
Rinne’s test
WHAT YOU FIND
| Rinne test in deaf ear | Weber test | |
| Conductive deafness | BC > AC | Deaf ear |
| Sensorineural deafness | AC > BC | Good ear |
N.B. With complete sensorineural deafness in one ear, bone conduction from the other ear will be better than air conduction.
VESTIBULAR
BACKGROUND
The vestibular system is not easy to examine at the bedside because it is difficult to test one part of the system, or even one side, in isolation. In some respects this is fortunate, as it is this ability of the vestibular system that allows patients to make good recoveries even after severe unilateral vestibular lesions by learning to operate on only one functioning vestibular system.
The vestibular system can be examined indirectly by checking gait, looking for nystagmus and carrying out more specific tests (see below).
Gait
See Chapter 4. Always test heel–toe walking. Gait is unsteady, veering to the side of the lesion.
Nystagmus
See Chapter 10. Vestibular nystagmus is associated with vertigo, horizontal and unidirectional. It may be positional.
Head impulse test
See Chapter 25. This is a dynamic test of vestibular function.
Caloric test
This is normally performed in a test laboratory.
The patient lies down with his head on a pillow at 30 degrees so the lateral semicircular canal is vertical.
Cool water (usually about 250 ml at 30°C) is instilled into one ear over 40 seconds. The patient is asked to look straight ahead and the eyes are watched. This is repeated in the other ear, and then in each ear with warm water (44°C).
CALORIC TESTING: WHAT YOU FIND
– cold water: nystagmus fast-phase away from stimulated ear
– warm water: nystagmus fast-phase towards stimulated ear.
• Reduced response to cold and warm stimuli in one ear: canal paresis.
N.B. In the unconscious patient, the normal responses are as follows:
• cold water: tonic movement of the eyes towards the stimulus
• warm water: tonic movement of the eyes away from the stimulus.
(The fast phase of nystagmus is produced by the correction of this response, which is absent in the unconscious patient.)
CALORIC TESTING: WHAT IT MEANS
FURTHER TESTS OF VESTIBULAR FUNCTION
Hallpike’s test
This is used in patients with positional vertigo.
• Sit the patient on a flat bed so that when he lies down his head will not be supported.
• Turn the head to one side and ask the patient to look to that side.
• The patient then lies back quickly until he is flat, with his neck extended and his head supported by the examiner (Fig. 12.1).
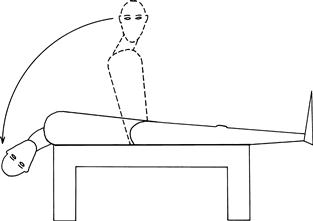
Figure 12.1 Hallpike’s manœuvre
Turning test
• Ask the patient to stand facing you.
• Ask him to point both arms straight out in front of him towards you.
• Ask him to walk on the spot; when he is doing this, he should then close his eyes.
What you find and what it means
The patient gradually turns to one side, and may turn through 180 degrees. This indicates a lesion on the side he turns towards.