Throat Conditions
A sore throat is an extremely common symptom, especially in children and young adults. Prolonged sore throat in an elderly patient is a cause for concern, as it may indicate the presence of neoplasia.
History
Infective
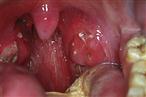
Sore throat, dysphagia, referred pain to ear, headache, malaise. A history of oral sex may suggest oropharyngeal gonorrhoea. Quinsy is a peritonsillar abscess. There is usually a history of acute tonsillitis but the patient becomes more ill with a high temperature, dysphagia and referred pain to the ear. In glandular fever, the patient can present with a severe membranous tonsillitis but usually has malaise and lymphadenopathy elsewhere.
Inflammatory
Subacute thyroiditis presents with a swelling of the thyroid, with neck pain, fever, weakness and malaise. It is a rare condition.
Neoplastic
Carcinoma of a tonsil presents with painful ulceration with induration. There is often referred pain to the ear and the patient may spit blood. Occasionally, the presenting symptom is a lump in the neck representing metastatic cervical lymphadenopathy. Carcinoma of the posterior third of the tongue may present with a feeling of soreness in the throat with difficulty in swallowing. The patient may spit blood and pain may be referred to the ear. Supraglottic carcinoma may present with a feeling of a lump in the throat but there is usually a change in voice and early cervical lymphadenopathy. Lymphoma of the tonsil rarely causes pain, the patient presenting with enlargement of one tonsil. Patients with a blood dyscrasia may present with a sore throat resulting from infection consequent upon neutropenia.
Neurological
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia presents as a sharp stabbing pain at the root of the tongue, radiating into the throat and ear, triggered by swallowing or touching the pharynx.
Referred pain
Angina may cause pain in the throat. It is usually associated with exercise. There may also be pain in the chest, radiating into the jaw and down the left arm. Occasionally, diffuse oesophageal spasm gives rise to chest pain radiating into the throat and jaw.
Other
Sore throat may occur with AIDS. It may be due to a variety of infective organisms, e.g. viral or fungal. Reflux oesophagitis may cause a burning pain in the throat or a sensation of a lump in the throat.
Examination
Infective
With tonsillitis, there is usually pyrexia, foetor and pus exuding from the tonsillar crypts. The pharyngeal mucosa is often inflamed. Cervical lymphadenopathy. Check for lymphadenopathy elsewhere, and splenomegaly, which may be associated with glandular fever. Quinsy is associated with trismus and the tonsil is pushed downwards and medially by the quinsy. The uvula is usually oedematous.
Inflammatory
Thyroiditis presents with a tender, diffuse swelling in the thyroid gland, which moves on swallowing. It is rare.
Neoplastic
Carcinoma of the tonsil presents as a hard, ulcerated swelling on the tonsil. Cervical lymphadenopathy may be present. In carcinoma of the posterior third of the tongue and supraglottic larynx, there is usually an indurated ulcer. Laryngoscopy is required as part of the examination. Check for cervical nodes and other sites for metastases, e.g. lung, liver. Lymphoma usually presents as a painless enlargement of the tonsil. Blood dyscrasias may present with lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Agranulocytosis results in ulceration and membrane formation on the tonsils and oral mucosa.
Neurological
The diagnosis of glossopharyngeal neuralgia is usually made from the history. Touching the palate may trigger the symptoms.
Referred pain
Angina and oesophageal spasms are usually diagnosed from the history.