4 Computers in hospitals
The Advantages of Computerisation
| Eliminates Repetitive Tasks | |
| Eliminates Paper Handling and Filing | Elimination of hardcopies of: |
| Improves Interdepartmental Communications | Virtually instant access to: |
| Improves efficiency | Elimination of: |
| Improves Confidentiality and Security | |
| Automated Data Collection | Improves information handling on, e.g.: |
| Overview | |
| Integrating Health Enterprise (IHE) | An initiative introduced in 1999 Aim: |
| Individual Computer Systems | Overview |
| Web-based Integration | Works in a similar way to the World Wide Web and has: |
| Advantages | |
| Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) | An initiative sponsored by the Radiological Society of North America and the Health and Management Systems Society |
| Aim | |
| Health Level 7 (HL7) | |
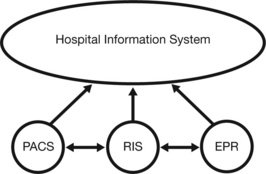
| Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) | |
| Electronic Patient Record (EPR) | Aims to contain |
| Hospital Information System (HIS) | |
| Aims to contain all patient information, e.g. | |
| Electronic Remote Requesting System (RRS)) | |
| Order Communications (OCM) | |
| Structure | |
| Advantages | |
| Disadvantages | |
| Radiological Information System (RIS) | |
| Using the system
• If not on the system (if they have not attended the hospital before as an in-patient or out-patient) an RIS number is allocated
• If the patient details are not known, a local protocol needs to be in place to allocate an RIS number, e.g.
|
|
| Imaging the patient | |
| Reporting | |
| Auditing The system can be used for auditing and creating management reports, e.g. |
|
| Links to conventional film filing system |