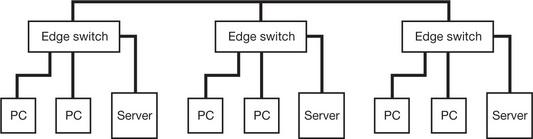
| Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) |
A fast and expensive method of setting up a computer network; tends to be used to provide the backbone to a system |
| Backbone |
A physical connection between hubs that carries all data back to the server |
| Bandwidth |
The amount of information in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (kbps), or megabits per second (Mbps) that can be sent via a communication channel or a network connection in a set period of time, i.e. the speed of the system |
| Bus |
|
| Collision |
When two or more computers try to send data at the same time down the same network |
| Deterministic |
The method of calculating how long it will take data to travel round a network and how quickly the system can be accessed |
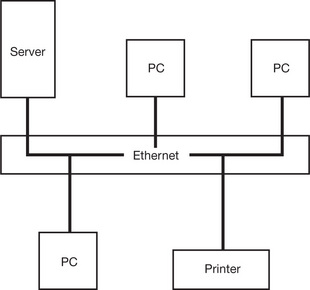
| Ethernet |
A method of setting up a computer network developed by Xerox, using cabling to connect the parts of the system together |
| Global Area Network (GAN) |
Worldwide connecting systems, e.g.
|
| Hub |
|
| IP Address |
|
| ISDN Connection |
A digital telephone line allowing computer connections |
| Local Area Network (LAN) |
A method of linking computers, printers, etc. within a building to enable the sharing of data between computers |
| Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) |
Linking of local area networks over a local district |
| Modem |
Device connecting computers to the telephone system Consists of:
|
| Network |
A method of linking computers, printers, etc. to enable the sharing of data between them |
| Network Interface Cards (NICs) |
|
| Node |
Equipment that communicates in a network, e.g.
|
| Router |
|
| Segment |
Section of a network where several nodes are linked together |
| Server |
A method of enabling computers to communicate with each other either by using another computer or software on a computer |
| Switches |
Send information directly to any linked computer in a segment without using the hub |
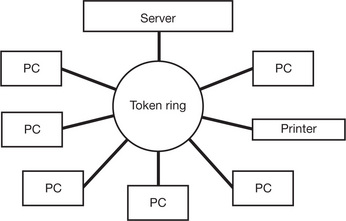
| Token Ring |
A method developed by IBM, of setting up a computer network using cabling that is joined in a ring |
| Wide Area Network (WAN) |
A method of linking computers to external users via a modem |
| Wireless System |
Used in place of a modem where direct connections are expensive or difficult Uses:
|