Commotio Retinae
Clinical Features:
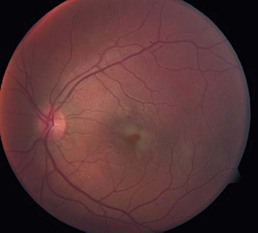
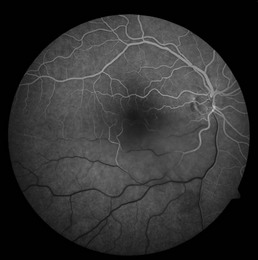
There is retinal whitening due to damage of the outer retinal layers. The whitening is generally patchy with ill-defined borders and does not follow a vascular distribution (Fig. 19.1.1).
OCT Features:
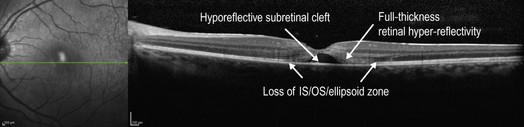
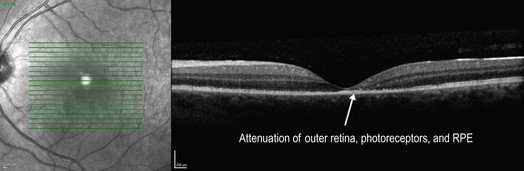
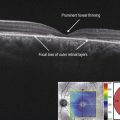
When involving the macula, acutely, there is obscuration of the retinal layers in the involved region with disruption of the IS–OS/ellipsoid zone and retinal pigment epithelium inter-digitation, sometimes leaving a cleft of empty hyporeflective space under the neurosensory retina (Fig. 19.1.2). There can be a hyper-reflective signal throughout the retinal layers, but this tends to be most pronounced in the outer layers. Later, the retina can return to normal in mild cases, or there may be permanent loss of outer retina including photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium in severe cases (Fig. 19.1.3).