1.8 Common ABG values
H+ (35–45 nmol/L) < 35 = alkalaemia, >45 = acidaemia
Concentration of free hydrogen ions: this is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is.
pH (7.35–7.45) < 7.35 = acidaemia, >7.45 = alkalaemia
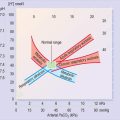
PO2 (>10.6 kPa or >80 mmHg in arterial blood on room air)
PCO2 (4.7–6.0 kPa or 35–45 mmHg in arterial blood)
O2 saturation of haemoglobin: the percentage of O2-binding sites on Hb proteins occupied by O2 molecules. This is a measure of how much of the blood’s O2-carrying capacity is being used. SaO2 refers specifically to the O2 saturation of arterial blood.
An indirect measure of lactic acid: high levels of lactic acid are a sign of tissue hypoxia.
Hb (13–18 g/dL men, 11.5–16 g/dL women)
Plasma haemoglobin concentration: this effectively determines blood’s capacity to carry O2.
Na (135–145 mmol/L) Plasma sodium concentration.
K (3.5–5 mmol/L) Plasma potassium concentration.
Cl (95–105 mmol/L) Plasma chloride concentration.
iCa (1.0–1.25 mmol/L) Plasma ionised calcium concentration.
Glucose (3.5–5.5 mmol/L if fasting) Plasma glucose concentration.