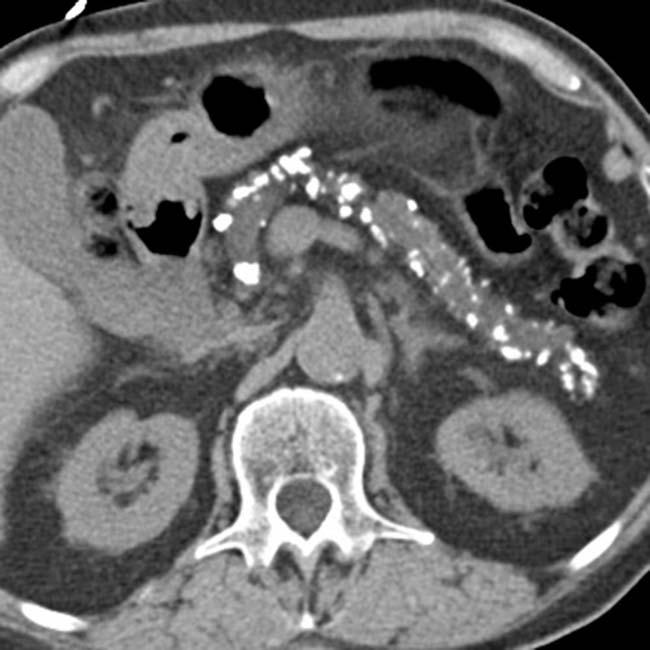
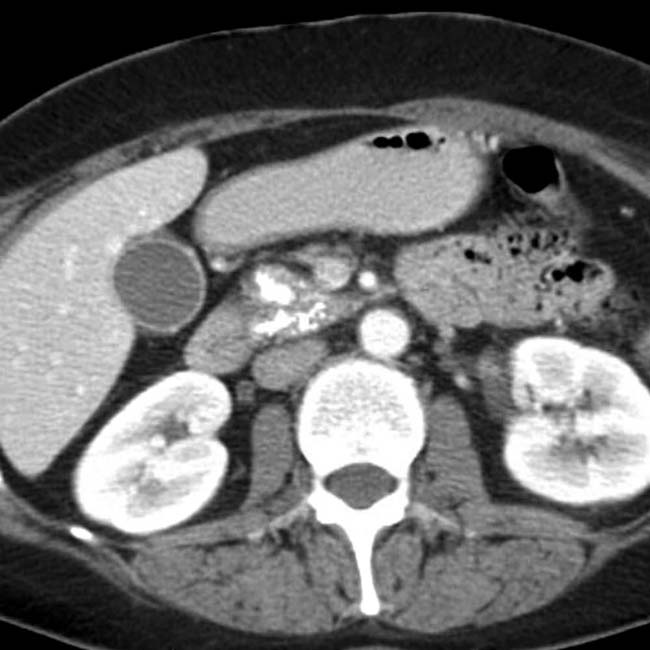
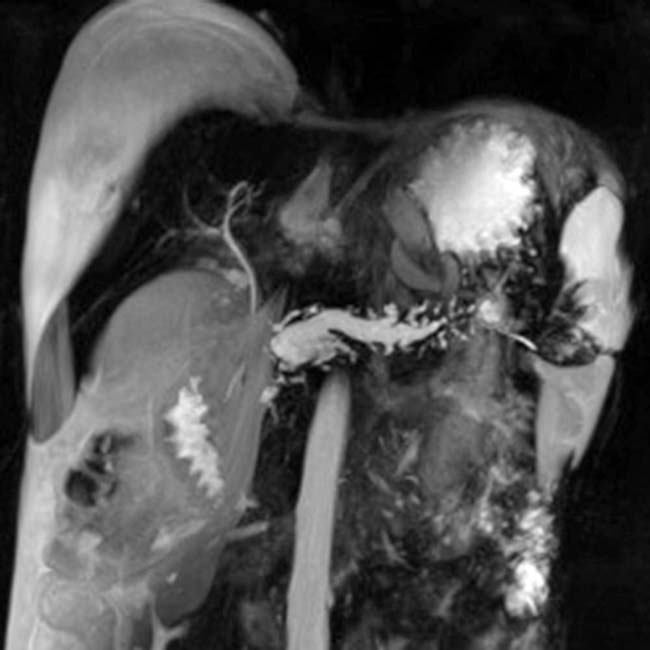
Pancreatic parenchymal and intraductal calcification virtually diagnostic of chronic pancreatitis
 Fibroinflammatory “mass” related to chronic pancreatitis may be very difficult to differentiate from malignancy
Fibroinflammatory “mass” related to chronic pancreatitis may be very difficult to differentiate from malignancy
• MR: More sensitive for early changes compared to CT
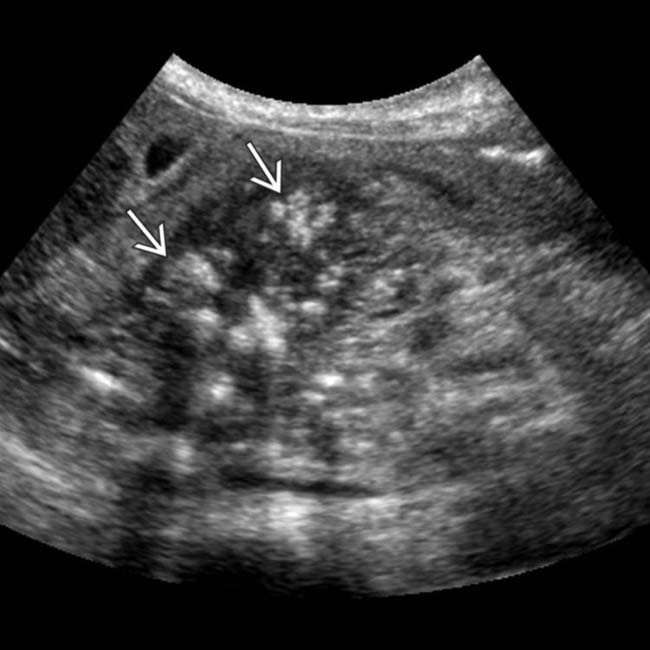
 in the pancreatic head, some of which demonstrate posterior acoustic shadowing, compatible with chronic pancreatitis.
in the pancreatic head, some of which demonstrate posterior acoustic shadowing, compatible with chronic pancreatitis.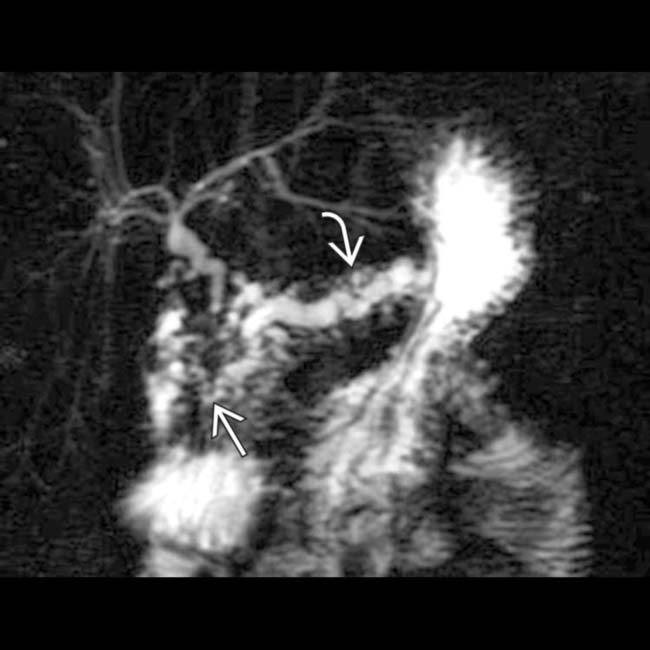
 , as well as a distal pancreatic duct stricture
, as well as a distal pancreatic duct stricture  . Chronic pancreatitis is a scirrhous process that commonly causes stricture or occlusion of the ducts.
. Chronic pancreatitis is a scirrhous process that commonly causes stricture or occlusion of the ducts.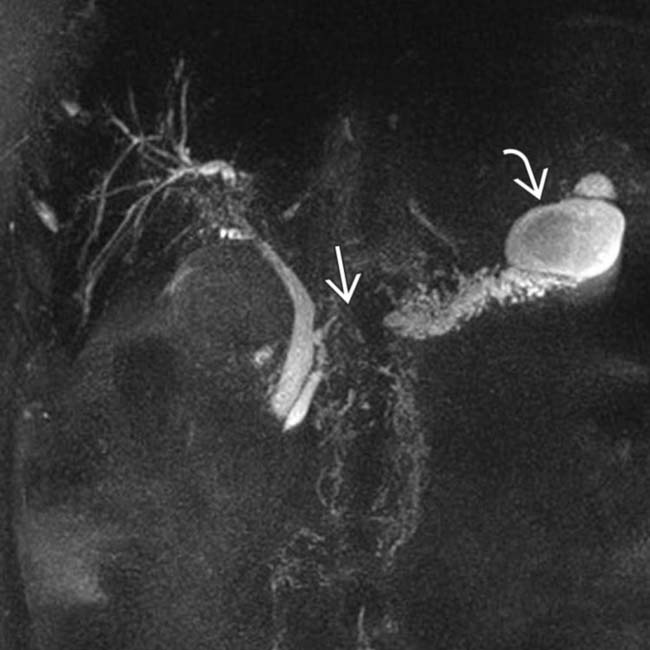
 in the downstream duct, and a large pseudocyst
in the downstream duct, and a large pseudocyst  near the pancreatic tail.
near the pancreatic tail.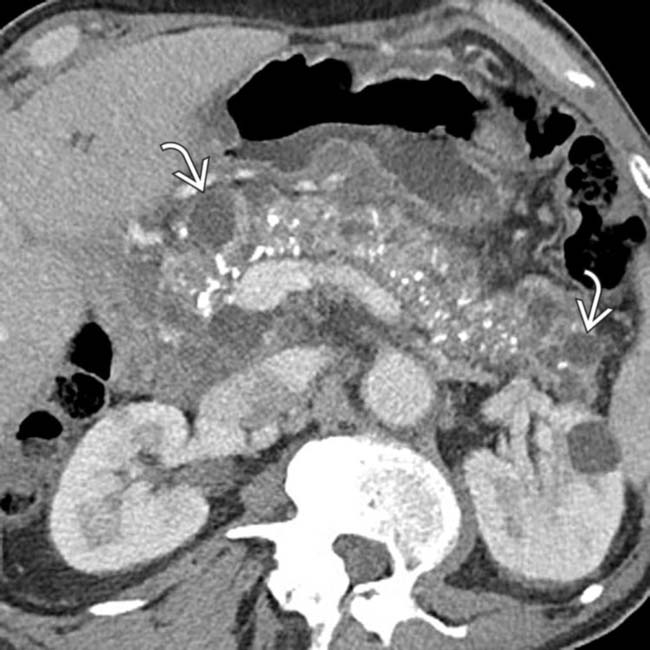
 scattered throughout the pancreas in this case represent small pseudocysts.
scattered throughout the pancreas in this case represent small pseudocysts.IMAGING
General Features
MR Findings
• Normal MR appearance of pancreas
• More sensitive for early changes of chronic pancreatitis compared to CT (although less sensitive for calcifications)
 Loss of normal high T1WI signal of parenchyma (due to fibrosis replacing parenchymal proteinaceous fluid)
Loss of normal high T1WI signal of parenchyma (due to fibrosis replacing parenchymal proteinaceous fluid)
 Loss of normal high T1WI signal of parenchyma (due to fibrosis replacing parenchymal proteinaceous fluid)
Loss of normal high T1WI signal of parenchyma (due to fibrosis replacing parenchymal proteinaceous fluid)• Changes in pancreatic duct (usually later finding) nicely demonstrated on T2WI or MRCP
Radiographic Findings
• Radiography
Ultrasonographic Findings
• Grayscale ultrasound
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma
PATHOLOGY
General Features
• Etiology
 Chronic pancreatitis most commonly caused by alcohol abuse (∼ 75% of cases in USA)
Chronic pancreatitis most commonly caused by alcohol abuse (∼ 75% of cases in USA)
 Chronic pancreatitis most commonly caused by alcohol abuse (∼ 75% of cases in USA)
Chronic pancreatitis most commonly caused by alcohol abuse (∼ 75% of cases in USA)
– Persistent, heavy alcohol consumption for > 10 years usually required to develop chronic pancreatitis
– Other causes include idiopathic (10-30% of cases), hereditary pancreatitis, tropical pancreatitis, autoimmune pancreatitis, and systemic diseases (most notably cystic fibrosis)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
• Most common signs/symptoms
Treatment
• Most patients treated with pain management, lifestyle modification (cessation of alcohol and smoking, frequent small meals), and pancreatic enzyme replacement
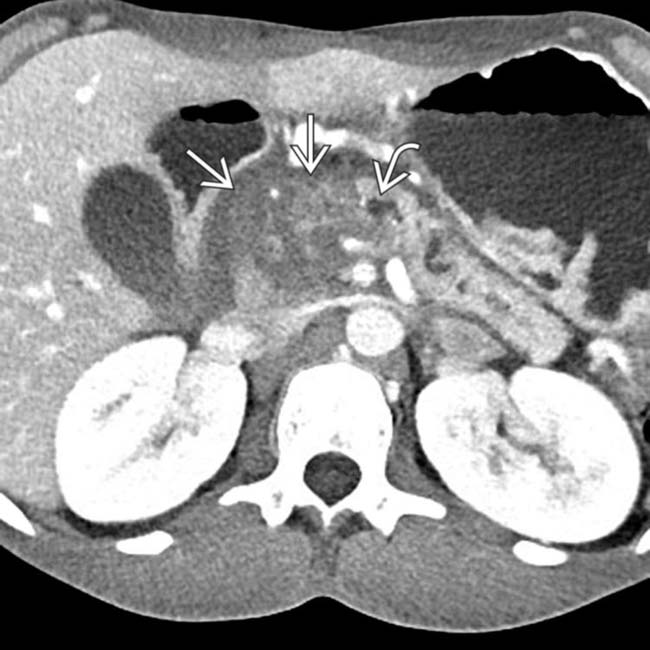
 , with a dilated upstream pancreatic duct
, with a dilated upstream pancreatic duct  . A few calcifications were present in the parenchyma (not shown). The patient underwent Whipple procedure due to concern for malignancy, where this was found to be a fibroinflammatory mass related to chronic pancreatitis.
. A few calcifications were present in the parenchyma (not shown). The patient underwent Whipple procedure due to concern for malignancy, where this was found to be a fibroinflammatory mass related to chronic pancreatitis.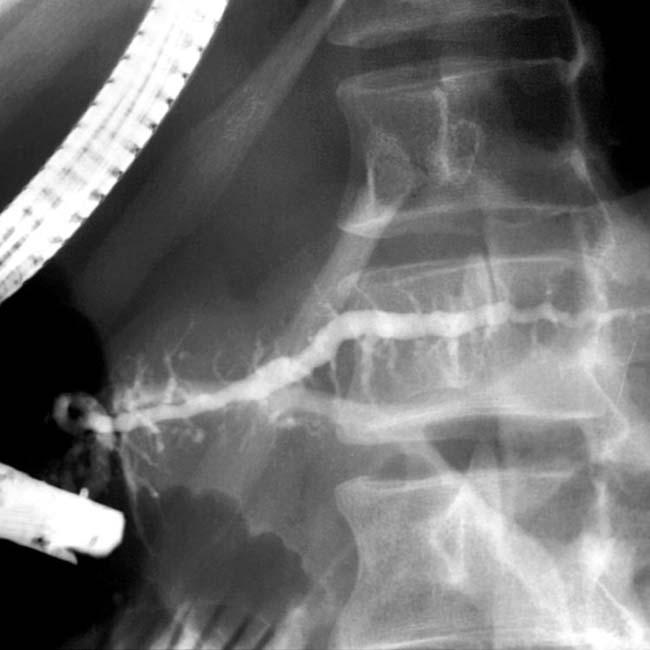
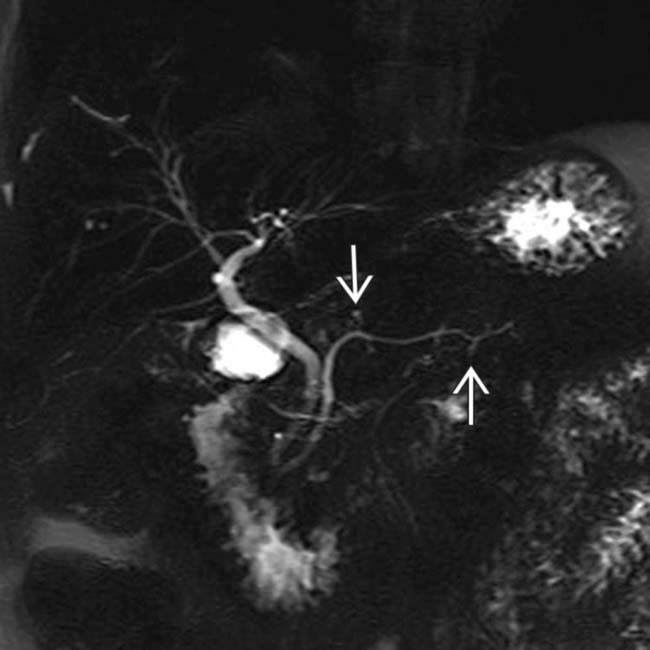
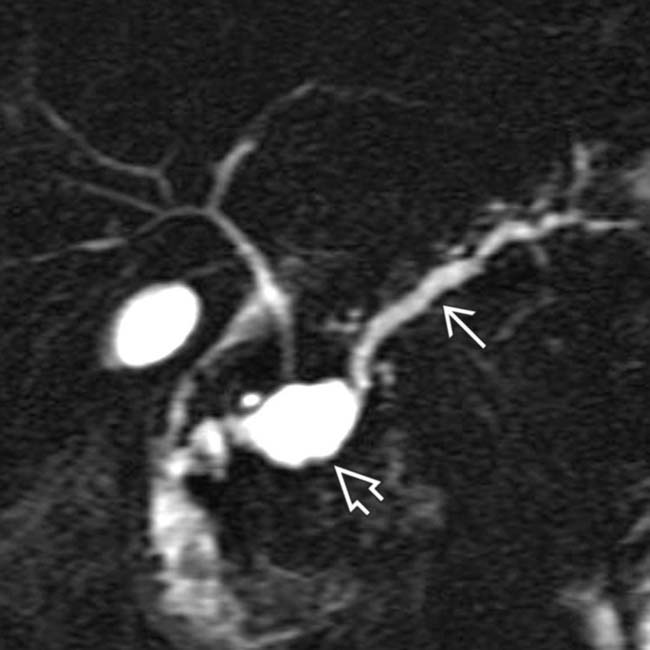
 . Side branch dilatation can be an early sign of chronic pancreatitis, subsequently confirmed in this patient using endoscopic ultrasound.
. Side branch dilatation can be an early sign of chronic pancreatitis, subsequently confirmed in this patient using endoscopic ultrasound.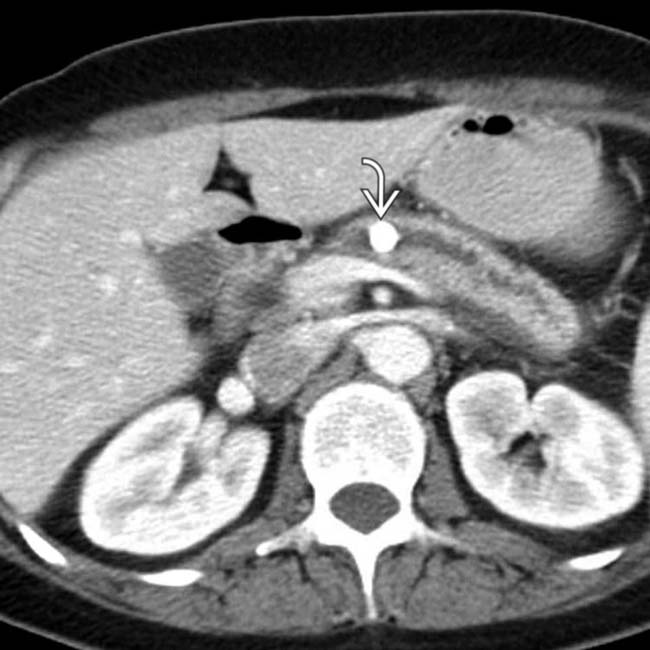
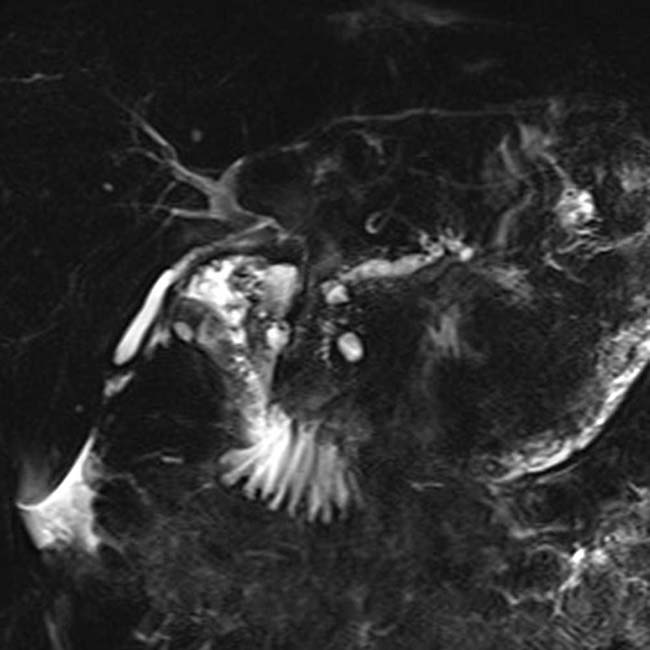
 within a dilated main pancreatic duct in a patient with known alcohol-related chronic pancreatitis. The duct itself appears subtly irregular and beaded.
within a dilated main pancreatic duct in a patient with known alcohol-related chronic pancreatitis. The duct itself appears subtly irregular and beaded.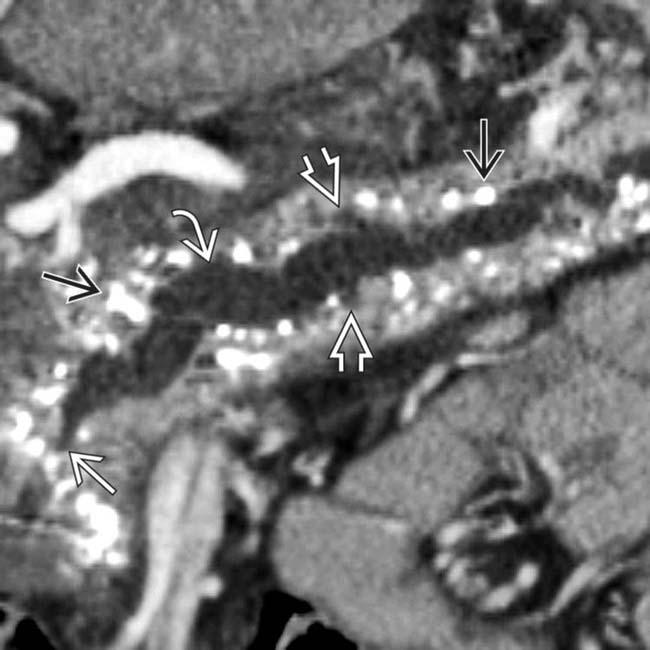
 upstream from a stricture
upstream from a stricture  in the head of the pancreas. Note the dilated side branches of the pancreatic duct
in the head of the pancreas. Note the dilated side branches of the pancreatic duct  and extensive parenchymal calcifications
and extensive parenchymal calcifications  , diagnostic of chronic pancreatitis.
, diagnostic of chronic pancreatitis.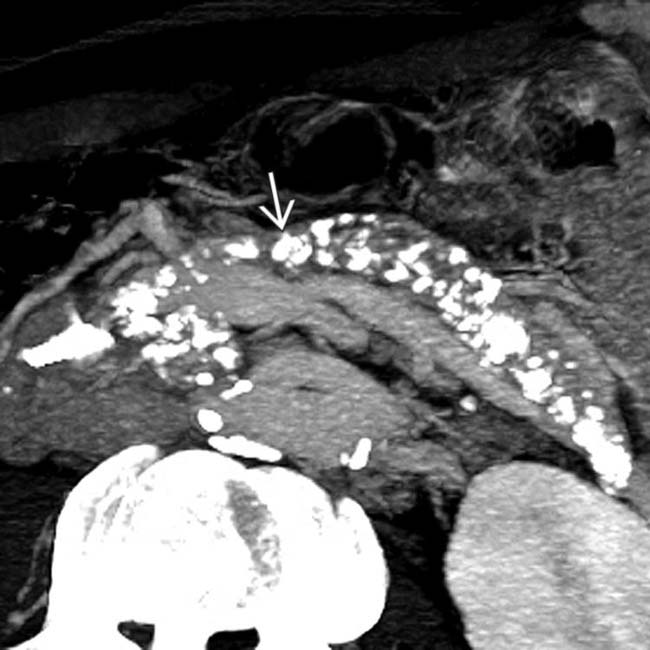
 . This patient required enzyme replacement therapy due to exocrine insufficiency.
. This patient required enzyme replacement therapy due to exocrine insufficiency.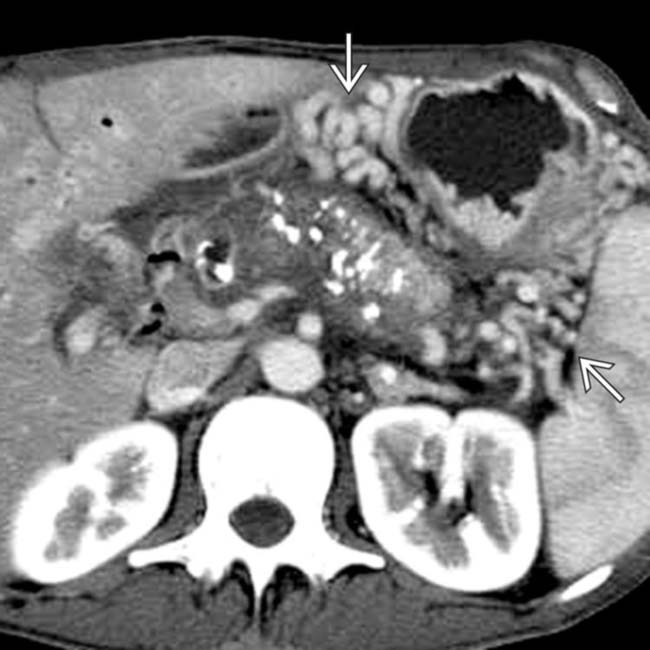
 due to obstruction of the splenic vein.
due to obstruction of the splenic vein.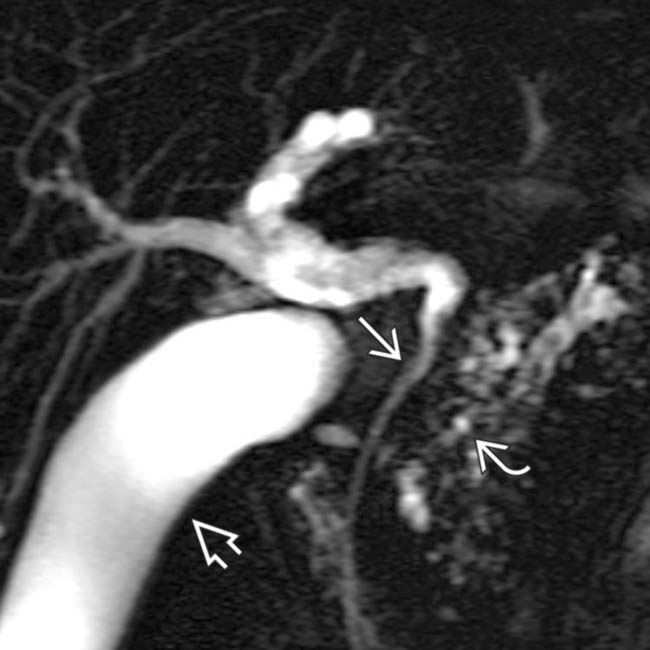
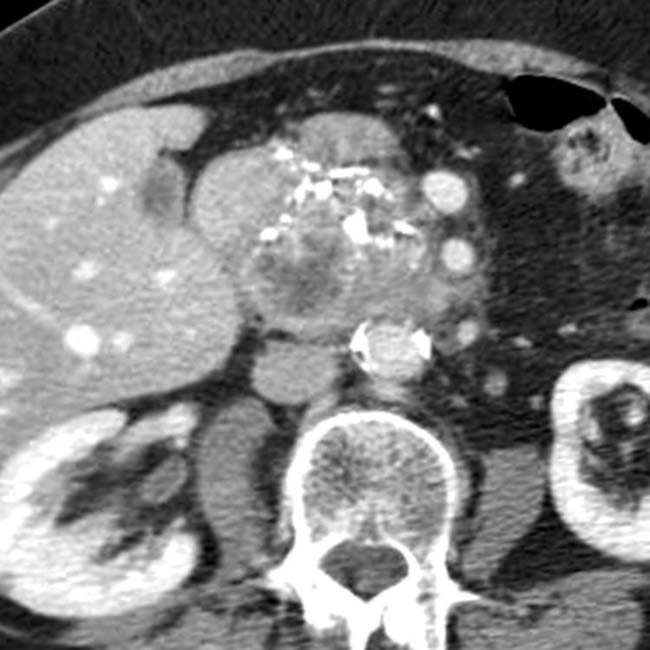
 as it passes through the head of the pancreas. Note the irregular strictures and dilatation of the pancreatic duct
as it passes through the head of the pancreas. Note the irregular strictures and dilatation of the pancreatic duct  . The gallbladder is also seen
. The gallbladder is also seen  .
.
 .
.
 with some fold thickening of the 3rd duodenum. The stomach was slow to empty.
with some fold thickening of the 3rd duodenum. The stomach was slow to empty.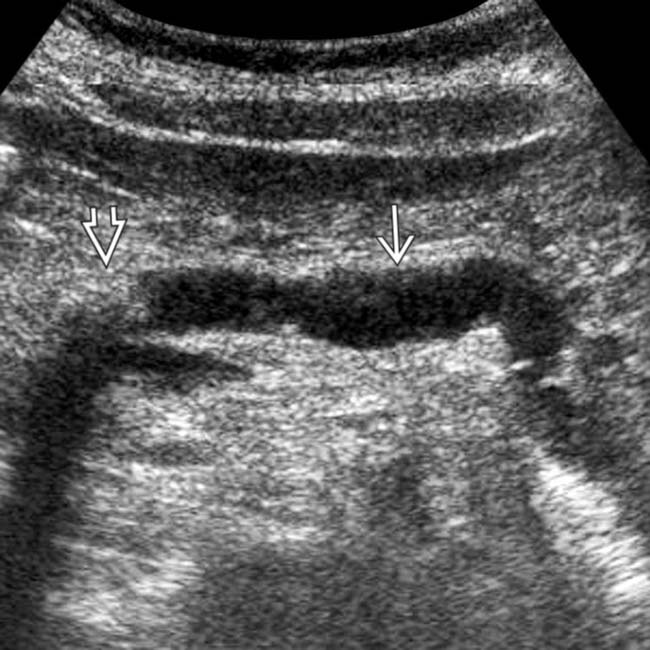
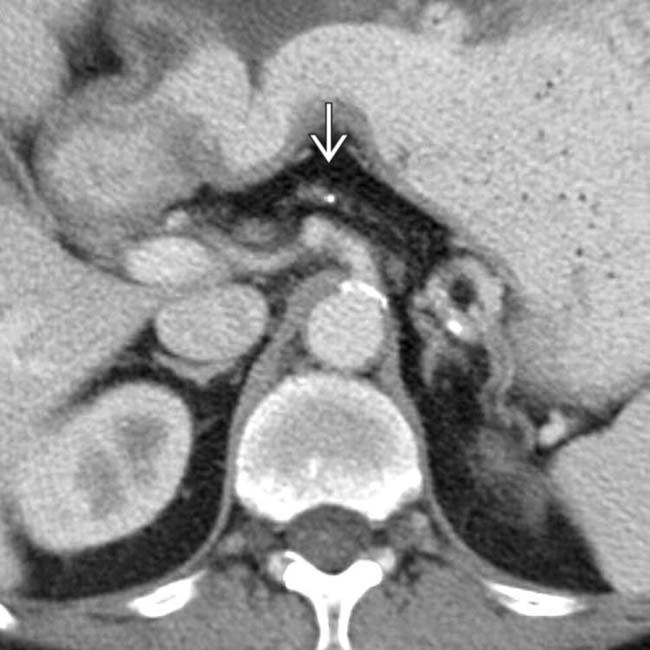
 upstream from an obstructing intraductal stone
upstream from an obstructing intraductal stone  .
.
 . Note the large intraductal stone
. Note the large intraductal stone  in the neck of the pancreas as well as a dilated common bile duct
in the neck of the pancreas as well as a dilated common bile duct  . There is fluid in the lesser sac
. There is fluid in the lesser sac  from acute pancreatitis. This is an example of acute and chronic pancreatitis.
from acute pancreatitis. This is an example of acute and chronic pancreatitis.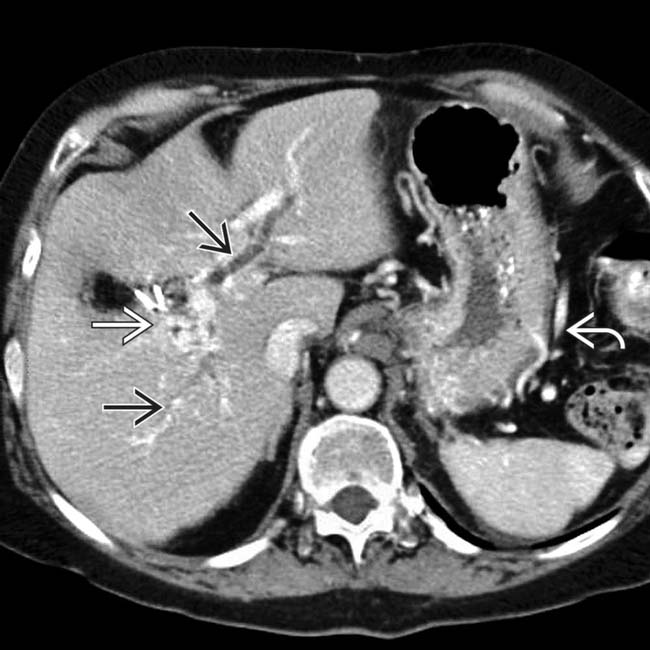
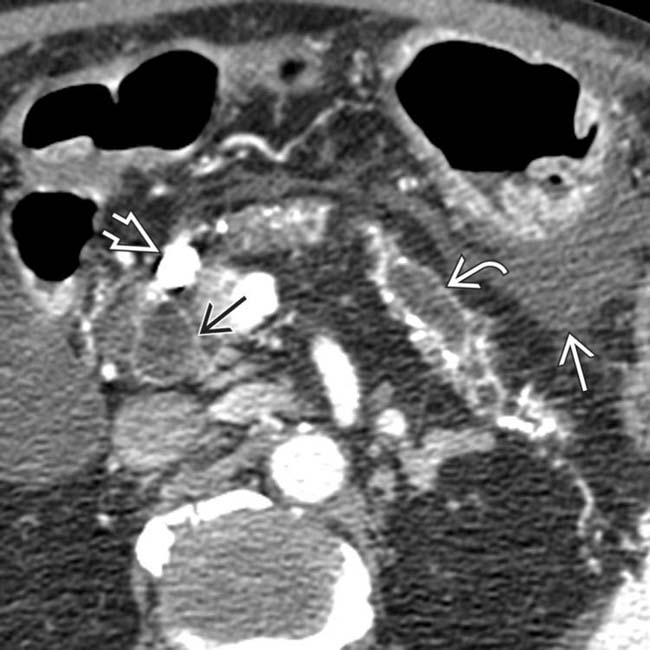
 of an occluded portal vein with collateral veins in the porta hepatis and around the stomach
of an occluded portal vein with collateral veins in the porta hepatis and around the stomach  . The intrahepatic bile ducts are dilated
. The intrahepatic bile ducts are dilated  due to a stricture of the common bile duct as it traverses the pancreas.
due to a stricture of the common bile duct as it traverses the pancreas.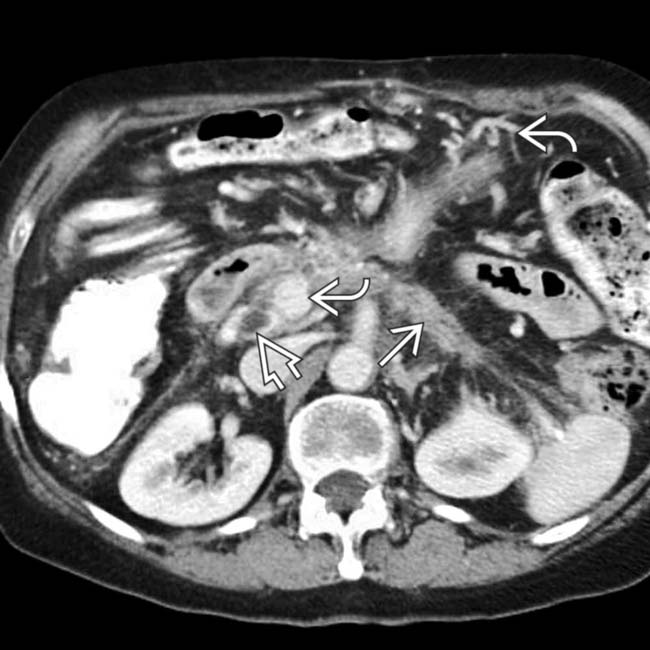
 , dilation of the distal pancreatic duct
, dilation of the distal pancreatic duct  , and varices
, and varices  within the pancreas and mesentery due to splenic and portal vein thrombosis.
within the pancreas and mesentery due to splenic and portal vein thrombosis.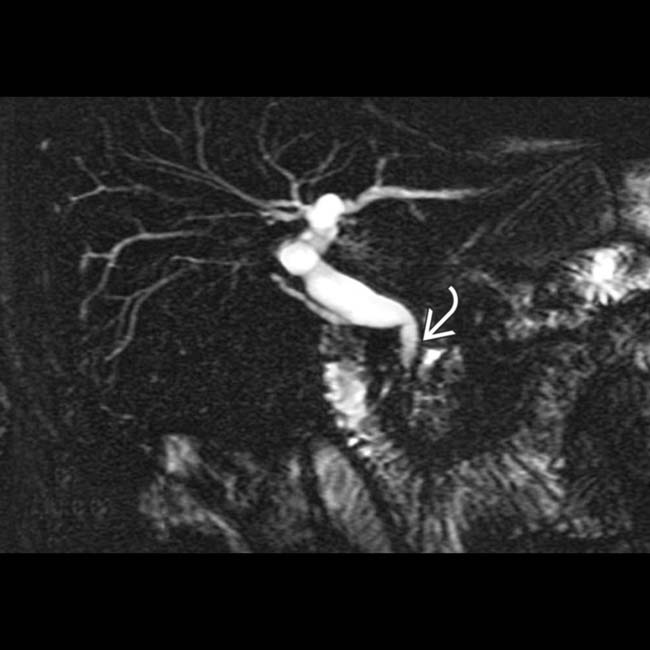
 with dilation of the intrahepatic ducts.
with dilation of the intrahepatic ducts.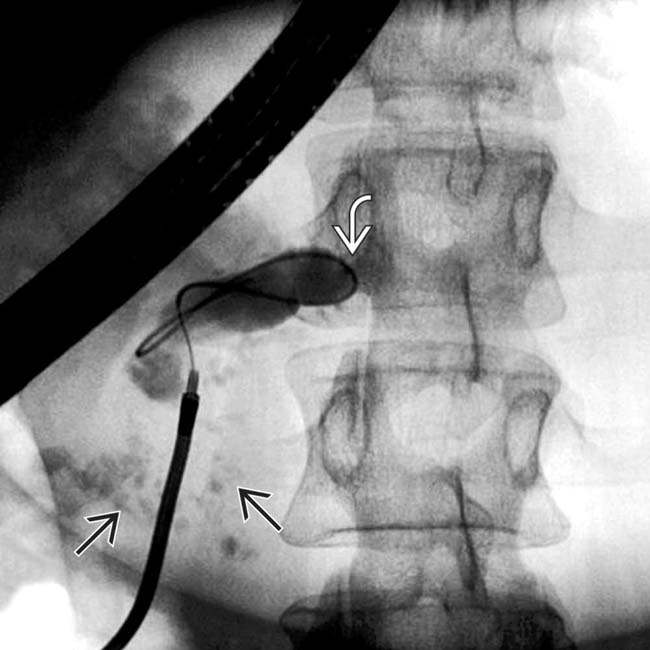
 in the head of the pancreas. Note the dilated duct with abrupt obstruction to retrograde filling, due to a stone or stricture in the main pancreatic duct
in the head of the pancreas. Note the dilated duct with abrupt obstruction to retrograde filling, due to a stone or stricture in the main pancreatic duct  .
.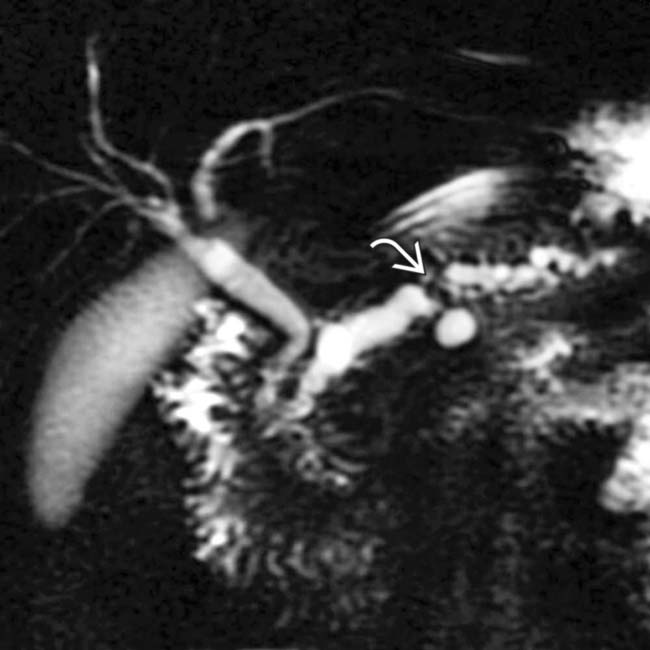
 and a dilated, irregular duct upstream that could not be shown by the ERCP.
and a dilated, irregular duct upstream that could not be shown by the ERCP.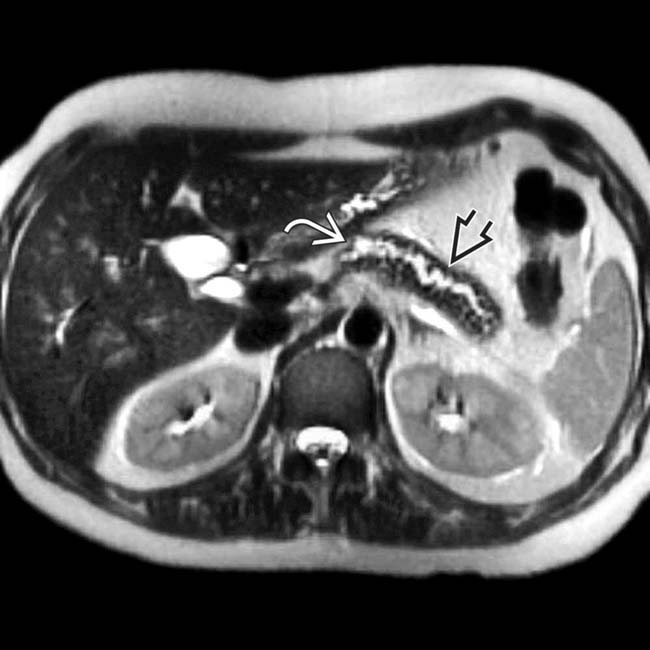
 associated with glandular atrophy in the body-tail segments of the pancreas
associated with glandular atrophy in the body-tail segments of the pancreas  .
.
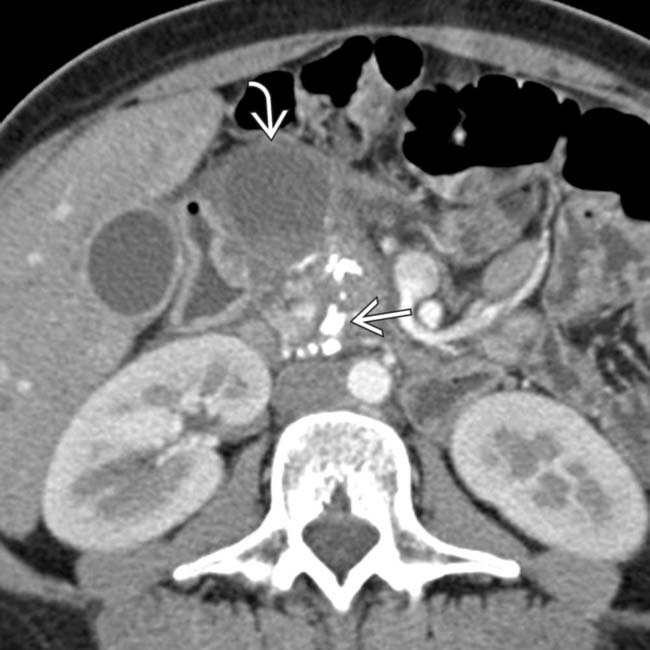
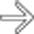
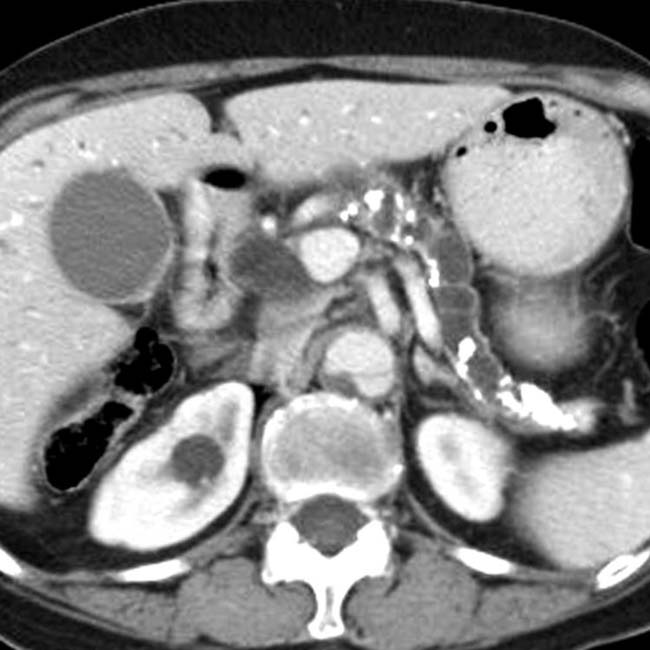
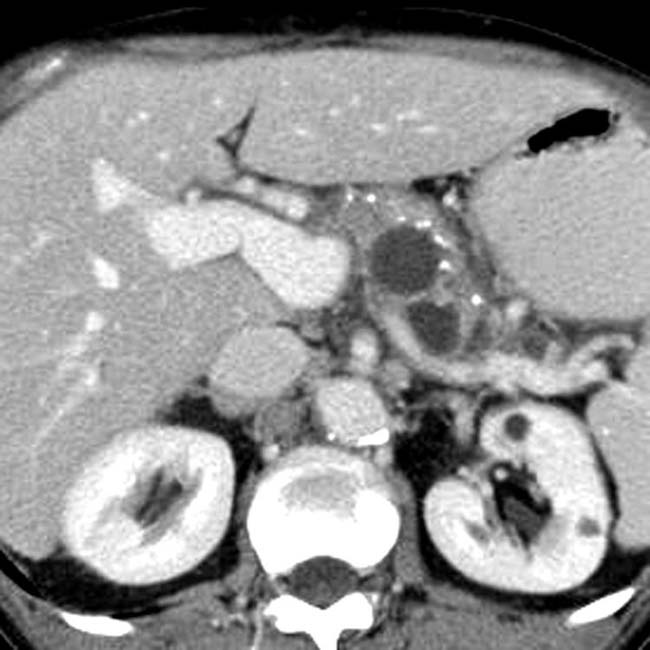
 in the pancreatic head, virtually diagnostic of chronic pancreatitis, as well as a focal cyst
in the pancreatic head, virtually diagnostic of chronic pancreatitis, as well as a focal cyst  adjacent to the pancreas representing a pseudocyst.
adjacent to the pancreas representing a pseudocyst.



































































 and adjacent pseudocyst
and adjacent pseudocyst  .
.