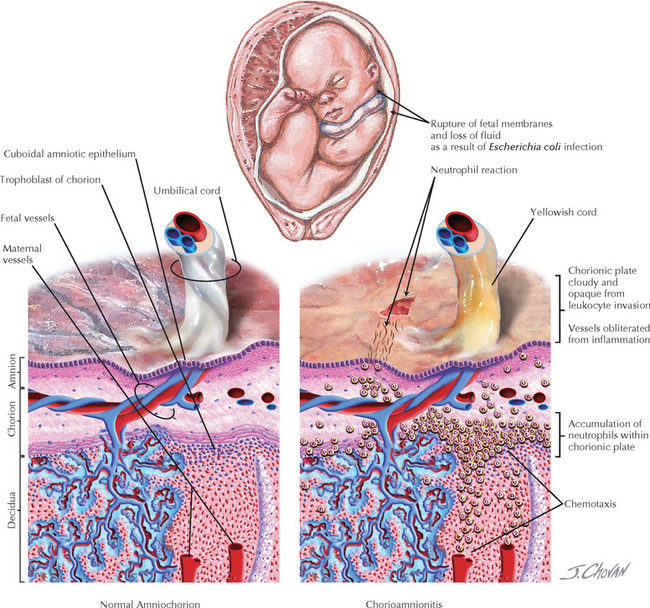
Chapter 204 Chorioamnionitis
INTRODUCTION
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
Workup and Evaluation
FOLLOW-UP
MISCELLANEOUS
Chapman SJ, Owen J. Randomized trial of single-dose versus multiple-dose cefotetan for the postpartum treatment of intrapartum chorioamnionitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177:831.
Grable IA, Garcia PM, Perry D, Socol ML. Group B Streptococcus and preterm premature rupture of membranes: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial of antepartum ampicillin. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996;175:1036.
Locksmith GJ, Chin A, Vu T, et al. High compared with standard gentamicin dosing for chorioamnionitis: a comparison of maternal and fetal serum drug levels. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105:473.
Mitra AG, Whitten MK, Laurent SL, Anderson WE. A randomized, prospective study comparing once-daily gentamicin versus thrice-daily gentamicin in the treatment of puerperal infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177:786.
Owen J, Groome LJ, Hauth JC. Randomized trial of prophylactic antibiotic therapy after preterm amnion rupture. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:976.
Turnquest MA, How HY, Cook CR, et al. Chorioamnionitis: is continuation of antibiotic therapy necessary after cesarean section? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:1261.
Chi BH, Mudenda V, Levy J, et al. Acute and chronic chorioamnionitis and the risk of perinatal human immunodeficiency virus-1 transmission. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:174.
Edwards RK, Duff P. Single additional dose postpartum therapy for women with chorioamnionitis. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102:957.
Kenyon S, Boulvain M, Neilson J. Antibiotics for preterm rupture of the membranes: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104:1051.
Livingston JC, Llata E, Rinehart E, et al. Gentamicin and clindamycin therapy in postpartum endometritis: the efficacy of daily dosing versus dosing every 8 hours. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:149.
Mozurkewich EL, Wolf FM. Premature rupture of membranes at term: a meta-analysis of three management schemes. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;89:1035.
Rouse DJ, Landon M, Leveno KJ, et alNational Institute of Child Health And Human Development, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network. The Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units cesarean registry: Chorioamnionitis at term and its duration-relationship to outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191:211.
Segel SY, Miles AM, Clothier B, et al. Duration of antibiotic therapy after preterm premature rupture of fetal membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:799.
Trochez-Martinez RD, Smith P, Lamont RF. Use of C-reactive protein as a predictor of chorioamnionitis in preterm prelabour rupture of membranes: a systematic review. BJOG. 2007;114:796.
Ugwumadu A, Reid F, Hay P, et al. Oral clindamycin and histologic chorioamnionitis in women with abnormal vaginal flora. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107:863.
Wu YW, Colford JMJr. Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2000;284:1417.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal disease in newborns. ACOG Committee Opinion 279. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100:1405.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Prophylactic antibiotics in labor and delivery. ACOG Practice Bulletin 47. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102:875.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Premature rupture of membranes. ACOG Practice Bulletin 80. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;109:1007.
Gibbs RS. Chorioamnionitis and bacterial vaginosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:460.
Gibbs RS, Romero R, Hillier SL, et al. A review of premature birth and subclinical infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:1515.
Gibbs RS, Schrag S, Schuchat A. Perinatal infections due to group B streptococci. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104:1062.
Mercer BM, Arheart KL. Antimicrobial therapy in expectant management of preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Lancet. 1995;346:1271.
Simhan HN, Canavan TP. Preterm premature rupture of membranes: diagnosis, evaluation and management strategies. BJOG. 2005;112:32.