Chapter 52 Child Abuse
1 What four elements should you consider in making a diagnosis of suspected child abuse?
3 Which form of abuse is reported most often? What form occurs most often?
Tenney-Soeiro R, Wilson C: An update on child abuse and neglect. Curr Opin Pediatr 16:233–237, 2004.
9 How many abuse victims are killed each year in the United States?
Approximately 1400 children annually. This rate has been fairly constant.
Sirotnak AP, Grigsby T, Krugman RD: Physical abuse of children. Pediatr Rev 25:264–277, 2004.
11 In a child with multiple bruises and normal neurologic examination, is computed tomography (CT) of the head indicated?
15 A 2-week-old infant, seen in the emergency department (ED) for crying, has several fractures at varying stages of healing. What may you conclude from these findings?
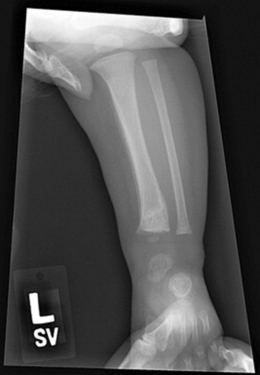
17 Which specific fractures have a high probability of being caused by child abuse?
Rib fractures, metaphyseal chip fractures (Fig. 52-1), spine and scapula fractures, and complex skull fractures.
20 A child appears to be tender when his upper humerus is palpated. Plain radiographs fail to show any injury. What other studies may be helpful?
22 What tests should be used to differentiate rickets from child abuse as the cause of skeletal abnormality?
The best radiograph to demonstrate rickets is that of the distal radius and ulna (wrist).
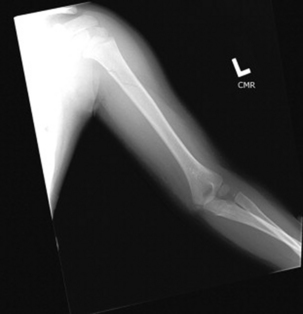
23 What history of injury matches a spiral fracture?
A spiral injury is caused by torque or twisting (Fig. 52-2). The extremity is twisted, or the child’s body is twisted while the extremity is held in a fixed position. If the mechanism of injury does not match the nature of the injury, suspect abuse.
24 What study has the highest sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing a suspected skull fracture?
25 A 6-month-old boy is brought to the ED for new onset of seizures. You note retinal hemorrhages. A CT scan of the brain is read as normal. What is your conclusion?
28 True or false: In comparison between inflicted head trauma and noninflicted head trauma, the neurologic findings are similar
34 A child is taken to a babysitter. Six hours later the child collapses, has seizures, and is brought to the ED, where a serious head injury is found. The babysitter claims that the injury occurred at home before the parent dropped off the child. What is the likely determination?
35 Do children with preexisting causes of hydrocephalus or abnormal brain anatomy have an increased risk for CNS bleeding?
40 What factors help to differentiate an inflicted bathtub scald burn from an accidental burn?
Andronicus M, Oates RK, Peat J, et al: Non-accidental burns in children. Burns 24:552–558, 1998.
41 If a child is immersed in hot water while wearing some articles of clothing, what should physical examination of the burn reveal?
44 A child with multiple bruises is brought to the ED. Other than documentation of normal coagulation, what laboratory studies should be obtained?
45 In checking a urinalysis, how many red blood cells should prompt the ordering of radiologic studies?
46 A 10-month-old baby is brought to the ED, essentially dead on arrival. No marks, bruises, or ecchymoses are found on the child’s body, and there is no history of illness. Is sudden infant death syndrome the most likely diagnosis?
KEY POINTS: SUSPECTED CHILD ABUSE
1 Child abuse occurs frequently and should be considered a possible mechanism in every traumatic injury.
2 Physicians and nurses are mandated to report the suspicion of abuse.
3 A level of suspicion is built by compiling elements of history, physical examination, laboratory, radiographic data, and observed interactions of the family.
4 Injuries that kill children are head injuries from both direct trauma and shaking, and abdominal injuries.
5 The more similar the family is to you in such characteristics as age, race, socioeconomic status, and education level, the more difficult it will be to suspect abuse.
47 What metabolic disease may present to the ED as an apparent case of SIDS?
Deficiency of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a defect in fatty acid metabolism.
49 A child is brought to the ED for spitting up blood. The mother brings in a bib with a large blood spot. She reports that it has happened before and the child underwent an extensive workup at a nearby medical center. What should you do?
51 A child comes alone to the ED with abdominal pain. She does not want her mother called for permission and states that she is afraid of her mother. Is this a case of child abuse?
55 Should vaginal, pharyngeal, and rectal cultures be performed on every child undergoing a sexual abuse evaluation?
56 Does a Gram stain showing gram-negative intracellular diplococci indicate gonorrheal infection and possible sexual abuse?
58 Which sexually transmitted diseases are less specific because they have other modes of transmission?
59 In examining a child for possible sexual abuse, how helpful is the width of the intralabial distance?
60 A child comes to the ED for bloodstains in her underpants. Physical examination reveals a red doughnut-shaped mass just inferior to the clitoris. What is the likely diagnosis?
61 True or false: The physical examination of a recently sexually abused child will be abnormal
False. The physical examination of most sexually abused children is expected to be normal.