W12 Chest Tube Placement, Care, and Removal
 Before Procedure
Before Procedure
Contraindications
Equipment

Figure W12-1 Standard chest tube (top) with trocar (middle) and angled chest tube (bottom) without trocar.
 Anatomy
Anatomy
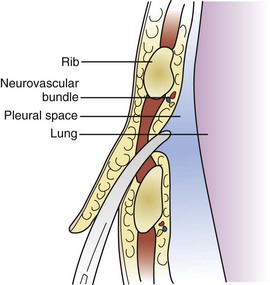
Entry into the pleural space should generally be gained via a location based on ease of access, safety, and avoidance of complications. The American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma recommends drain insertion between the anterior and posterior axillary lines at a level with or just above the fifth intercostal space (nipple level). In this location, the chest wall is thinnest, and the operator can avoid the pectoralis major muscle and breast parenchyma (anteriorly), the latissimus dorsi muscle (posteriorly), the axillary vessels/brachial plexus (superiorly), and the diaphragm/intraabdominal contents (inferiorly). Within the intercostal space, coursing along the inferior surface of each rib is the neurovascular bundle. Insertion of the tube over the superior aspect of the rib is recommended so that injury to these structures can be avoided (Figure W12-3). From superficial to deep, one will first encounter skin, followed by a variable amount of subcutaneous tissue, the superior surface of the rib, the intercostal space with its musculature, and finally the parietal pleura. The pulmonary parenchyma and mediastinal structures are deep to the parietal pleura, so it is important to avoid overzealous insertion of the chest tube. In some instances (e.g., a loculated collection), specialized placement may be required, and the assistance of a surgeon or insertion under image guidance is encouraged.
 Procedure
Procedure
 After Procedure
After Procedure
Postprocedure Care
 Sequentially clamp the accessory tubing with distal suction applied. The leak will cease when a clamp is placed proximal to the site, and the problem can then be addressed.
Sequentially clamp the accessory tubing with distal suction applied. The leak will cease when a clamp is placed proximal to the site, and the problem can then be addressed.Complications
 Outcomes and Evidence
Outcomes and Evidence
Laws D, Neville E, Duffy J, Pleural Diseases Group, Standards of Care Committee, British Thoracic Society. BTS guidelines for the insertion of a chest drain. Thorax. 2003 May;58(Suppl. 2):ii53-ii59.
Durai R, Hoque H, Davies TW. Managing a chest tube and drainage system. AORN J. 2010 Feb;91(2):275-280.
Miller KS, Sahn SA. Chest tubes: indications, techniques, management, and complications. Chest. 1987;91:258-264.
American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma. Thoracic trauma. In Student manual of advanced trauma life support course for physicians, 5th ed, Chicago: American College of Surgeons; 1993:111-139.
Peek GJ, Firmin RK, Arsiwala S. Chest tube insertion in the ventilated patient. Injury. 1995;26:425-426.
Baumann MH. What size chest tube? What drainage system is ideal? And other chest tube management questions. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2003 Jul;9(4):276-281.
Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS. The management of chest tubes after pulmonary resection. Thorac Surg Clin. 2010 Aug;20(3):399-405.
Schulman CI, Cohn SM, Blackbourne L, et al. How long should you wait for a chest radiograph after placing a chest tube on water seal? A prospective study. J Trauma. 2005 Jul;59(1):92-95.
Martino K, Merritt S, Boyakye K, et al. Prospective randomized trial of thoracostomy removal algorithms. J Trauma. 1999 March;46(3):369-371.
Younes RN, Gross JL, Aguiar S, et al. When to remove a chest tube? A randomized study with subsequent prospective consecutive validation. J Am Coll Surg. 2002 November;195(5):658-662.
Bell RL, Ovadia P, Abdullah F, et al. Chest tube removal: end-inspiration or end-expiration? J Trauma. 2001 April;50(4):674-677.
Pizano LR, Houghton DE, Cohn SM, et al. When should a chest radiograph be obtained after chest tube removal in mechanically ventilated patients? a prospective study. J Trauma. 2002 December;53(6):1073-1077.
Palesty JA, McKelvey AA, Dudrick SJ. The efficacy of x-rays after chest tube removal. Am J Surg. 2000 January;179(1):13-16.
Etoch SW, Bar-Natan MF, Miller FB, et al. Tube thoracostomy. Factors related to complications. Arch Surg. 1995;130:521-526.
Chan L, Reilly KM, Henderson C, et al. Complication rates of tube thoracostomy. Am J Emerg Med. 1997 July;15(4):368-370.
Aylwin CJ, Brohi K, Davies GD, et al. Pre-hospital and in-hospital thoracostomy: indications and complications. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008 Jan;90(1):54-57.
Remerand F, Luce V, Badachi Y, et al. Incidence of chest tube malposition in the critically ill: a prospective computed tomography study. Anesthesiology. 2007 Jun;106(6):1112-1119.
Sanabria A, Valdivieso E, Gomez G, et al. Prophylactic antibiotics in chest trauma: a meta-analysis of high-quality studies. World J Surg. 2006 Oct;30(10):1843-1847.