Chest
Chest—Positioning Considerations and Radiation Protection*
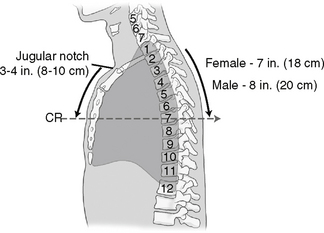
Correct CR Location
The CR for the AP chest is 3-4 inches (8-11cm) below the jugular notch and angled 3°–5° caudad.
Digital Imaging Considerations*
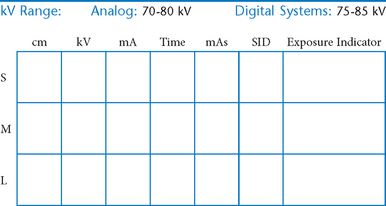
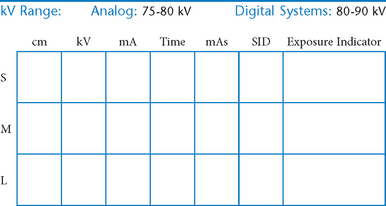
The following technical factors will reduce dose to the patient and improve image quality:
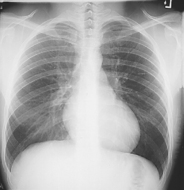
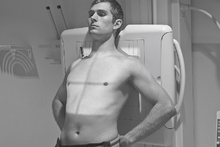
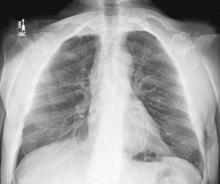
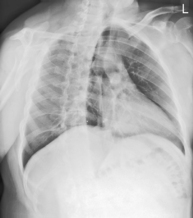
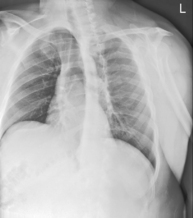
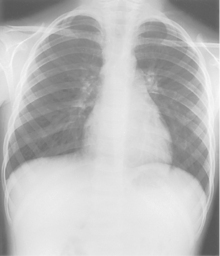
PA Chest*
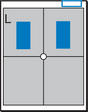
Position
• Erect, chin raised, hands on hips with palms out, roll shoulders forward
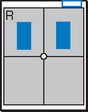
• Center CR to T7 region. Top of IR will be approximately 2″ (5 cm) above shoulders on average patient.
• Center thorax bilaterally to IR borders with equal margins on both sides; ensure there is no rotation of thorax.
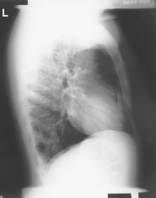
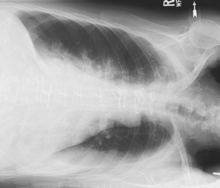
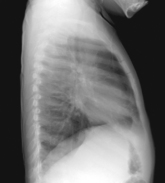
Lateral Chest*
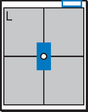
Position
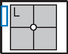
• Erect, left side against IR (unless right lateral is indicated)
• Arms raised, crossed above head, chin up
• True lateral, no rotation or tilt. Midsagittal plane parallel to IR (Don’t push hips in against the IR holder.)
• Thorax centered to CR, and to IR anteriorly and posteriorly
Lateral, Wheelchair or Stretcher*
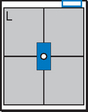
Position
• Erect, on stretcher or in wheelchair
• Arms raised, crossed above head, or hold on to support bar
• Center thorax to CR, and to IR anteriorly and posteriorly
• No rotation or tilt, midsagittal plane parallel to IR, keep chin up
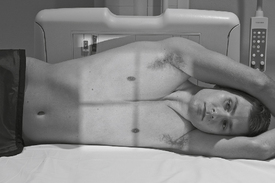
Lateral Decubitus*
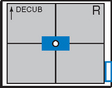
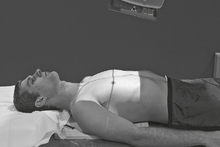
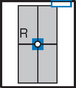
AP Lordotic*
AP Lordotic Chest
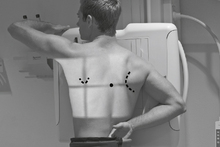
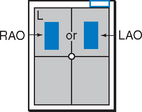
Anterior Oblique Chest (RAO and LAO)*
Position
• Erect, rotated 45°, right shoulder against IR holder (RAO) (Certain heart studies require LAO, 60° rotation from PA.)
• Arm away from IR up resting on head or on IR holder
• Arm nearest IR down on hip, keep chin up
• Center thorax laterally to IR margins; vertically to CR at T7
Anterior Oblique Chest—RAO and LAO
AP and Lateral Upper Airway (Trachea and Larynx)*
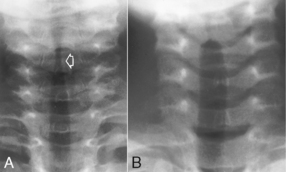
AP Pediatric Chest*
• 18 × 24 cm or 24 × 30 cm C.W. (8 × 10″ or 10 × 12″)
• TT (tabletop; nongrid). Grid with systems when it can’t be removed.
Erect PA Pediatric Chest (with Pigg-O-Stat)*
• 18 × 24 cm or 24 × 30 cm C.W. (8 × 10″ or 10 × 12″)
• IR (nongrid) or grid with systems when it can’t be removed
Position
• Patient on seat, legs through openings
• Adjust height of seat to place shoulders ≈1″ (2.5 cm) below upper margin of IR.
• Raise arms, and gently but firmly place side body clamps to hold raised arms and head in place.
• Set upper border of lead shield with R and L markers 1-2″ (2.5-5 cm) above level of iliac crest.
Lateral Pediatric Chest*
• 18 × 24 cm or 24 × 30 cm L.W. (8 × 10″ or 10 × 12″)
• TT (tabletop, nongrid) or grid with systems when it can’t be removed
Erect Lateral Pediatric Chest (with Pigg-O-Stat)*
• 18 × 24 cm or 24 × 30 cm L.W. (8 × 10″ or 10 × 12″)
• IR (nongrid) or grid with systems when it can’t be removed
PA (AP) Pediatric Chest
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 83 and 84.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 79 and 85.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 90.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 92.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 93.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 95.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 96.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 97.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 100 and 101.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 631.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 632.

 PA (R)
PA (R) Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) Lateral, wheelchair or stretcher (R)
Lateral, wheelchair or stretcher (R) AP chest (R)
AP chest (R) PA and lateral chest critique
PA and lateral chest critique Lateral decubitus (S)
Lateral decubitus (S) AP lordotic (S)
AP lordotic (S) Lateral decubitus and AP lordotic chest critique
Lateral decubitus and AP lordotic chest critique Anterior oblique chest (RAO and LAO) (S)
Anterior oblique chest (RAO and LAO) (S) Anterior oblique chest critique
Anterior oblique chest critique AP and lateral upper airway (S)
AP and lateral upper airway (S) AP and lateral upper airway critique
AP and lateral upper airway critique AP (tabletop) (R)
AP (tabletop) (R) PA (with Pigg-O-Stat) (R)
PA (with Pigg-O-Stat) (R) Lateral (tabletop) (R)
Lateral (tabletop) (R) Lateral (with Pigg-O-Stat) (R)
Lateral (with Pigg-O-Stat) (R) AP and lateral pediatric chest critique
AP and lateral pediatric chest critique