Chemotherapy and related treatments
General principles
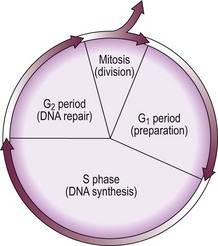
The life cycle of the normal cell is shown schematically in Figure 27.1. Conventional anti-leukaemic and lymphoma cytotoxic drugs can be broadly divided into those agents active during only one phase of the cell cycle (‘phase-specific’) and those acting at all stages (‘phase non-specific’). In practice, most anti-leukaemic drugs act predominantly against proliferating cells and therefore affect a fraction of the malignant cell population. Thus, if in advanced acute leukaemia the total number of malignant cells is 1010, a single course of chemotherapy could be expected to kill between 2 and 5 log of cells, leaving between 105 and 108 residual leukaemic cells. It can be seen that the chance of eradication of the disease by chemotherapy is favoured by early treatment when the leukaemic mass is small and by repeated courses of cytotoxic drugs. It is also logical to combine different agents to maximise the anti-leukaemic activity and exploit different toxicities (‘combination chemotherapy’).
Major classes of conventional cytotoxic drugs
Side-effects of conventional cytotoxic drugs
Some toxic effects are common to many cytotoxic drugs and must be discussed with all patients receiving a relevant single agent or combination chemotherapy (Table 27.1). Myelosuppression and alopecia are often unavoidable. However, nausea and vomiting can usually be minimised or even completely avoided by modern antiemetic protocols. The probability of infertility is influenced by the agents used, the total dosage, the duration of administration and the age and sex of the patient. Strategies to minimise infertility include prechemotherapy storage of germ cells (unfortunately, fertility is often abnormal at presentation) or choice of regimens which are relatively non-sterilising. Gonadal failure occurs more commonly in women and may be managed by hormone replacement therapy; androgens are used in men. Chemotherapy is associated with an increased risk of secondary malignancy including leukaemia and solid tumours. Alkylating agents are particularly leukaemogenic.
Table 27.1
Common adverse effects of cytotoxic drugs
| Short-term effects | Long-term effects |
| Myelosuppression | Infertility |
| Nausea and vomiting | Secondary malignancy |
| Alopecia | |
| Mucositis |
Note: If extravasated from the vein some drugs can cause severe tissue injury.