Chapter questions
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
3 During moderate exercise, cardiac output rises due to increases in both heart rate and stroke volume, but stroke volume peaks at a workload that is significantly below maximum work capacity and further increase of cardiac output is due solely to heart rate elevation. Factors that limit the rise in stroke volume include all of the following EXCEPT:
Chapter 4
1 The elevation of systolic blood pressure caused by sympathetic nervous system activation involves:
2 A subject has a resting heart rate of 66 beats/min and a blood pressure of 114/60 mmHg. Her mean arterial blood pressure is, therefore:
3 Routine measurement of blood pressure by auscultation involves detection of Korotkow sounds during inflation of an occlusive cuff around the arm. These sounds are caused by:
Chapter 5
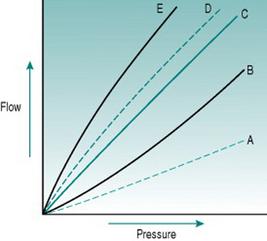 In the above set of curves describing the relationship between pressure gradient and blood flow, which curve represents:
In the above set of curves describing the relationship between pressure gradient and blood flow, which curve represents:Chapter 7
1 The baroreflex response to reduced venous return:
2 During exercise there is a generalized increase in sympathetic vasoconstrictor discharge. However, glomerular filtration is maintained because:
Chapter 8
2 The pulmonary pressure gradient is only around one-seventh of that in the systemic circulation. As a result:
4 Full O2 saturation of blood can be achieved during moderate exercise without any alterations in ventilation:perfusion matching BECAUSE:
B At rest, the O2 content of the pulmonary capillary plasma is higher than is needed for haemoglobin saturation
Chapter 9
1 Fluid loss due to sweating during exercise:
Chapter 10
1 The Valsalva manoeuvre can result in fainting in athletes undertaking heavy resistive exercise. Factors involved in this loss of consciousness include:
Chapter 11
A Heart rate reserve 150 beats/min, cardiac reserve 18 l/min, maximum sweat rate 1.2 l/h, sweat sodium content 45 mmol
B Heart rate reserve 120 beats/min, cardiac reserve 18 l/min, maximum sweat rate 1.2 l/h, sweat sodium content 45 mmol
C Heart rate reserve 130 beats/min, cardiac reserve 19 l/min, maximum sweat rate 1.5 l/h, sweat sodium content 10 mmol
D Heart rate reserve 150 beats/min, cardiac reserve 24 l/min, maximum sweat rate 1.5 l/h, sweat sodium content 10 mmol
E Heart rate reserve 120 beats/min, cardiac reserve 24 l/min, maximum sweat rate 1.5 l/h, sweat sodium content 10 mmol
In a healthy, 30-year-old subject (resting HR 72 beats/min, resting cardiac output 5.4 l/min), which of the above sets of values best represent the situation:

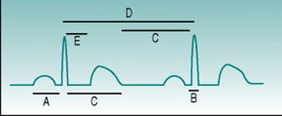 Which of the labelled time intervals on the ECG record shown above:
Which of the labelled time intervals on the ECG record shown above: