82 Cerebellopontine angle tumour
Salient features
Advanced-level questions
Mention a few causes of cerebellopontine angle lesions
• Acoustic neuroma (now knowns as vestibular schwanommas) accounts for 70–80% of cerebellopontine angle tumours
• Meningioma, cholesteatoma, haemangioblastoma, aneurysm of the basilar artery
• Medullablastoma and astrocytoma of the cerebellum
What is the histology of acoustic neurofibroma?
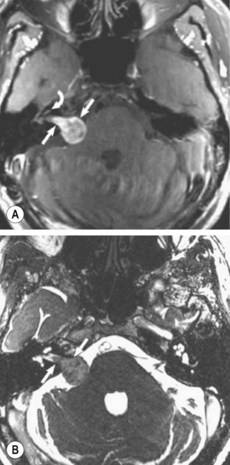
It consists of elongated cells similar to spindle fibroblasts with much collagen and reticulum. They are believed to arise from Schwann cells and are also known as schwannomas. These lesions most often arise from the inferior vestibular nerve within the internal auditory canal and present with hearing loss or tinnitus. Schwannomas can be entirely intracanalicular or have intracanalicular and cisternal components, resulting in the description of an ‘ice-cream cone’ tumour (Fig. 82.1).