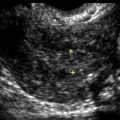
Granulosa Cell Tumor
Synonyms/Description
Granulosa-theca cell tumor
Sex cord–gonadal stromal tumor
Etiology
Granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) are relatively rare malignant neoplasms representing 3% of all ovarian cancers and 70% of tumors in the category of ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors. Granulosa cell tumors arise from a hormonally active component of the ovarian stroma that is responsible for estradiol production and hence represents 80% of hormone-producing ovarian tumors.
Granulosa cell tumor neoplasms are divided into the rare juvenile form (5%) and the more common adult type, which typically occurs in perimenopausal or postmenopausal women. The GCT is a slow-growing malignant tumor that typically spreads locally in the peritoneum and in 25% of patients recurs 5 to 10 years later, although sometimes decades after initial presentation.
Ultrasound Findings
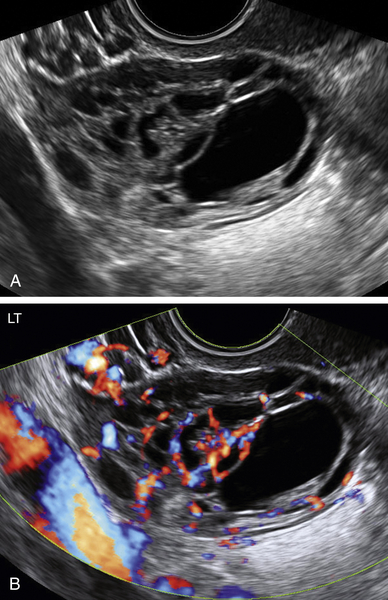
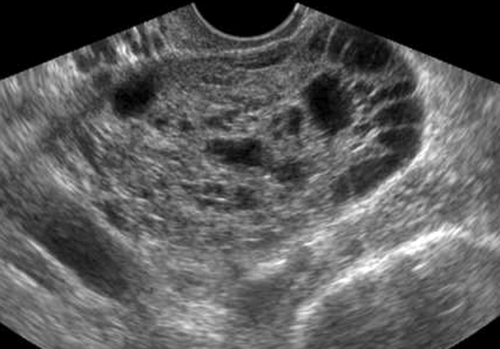
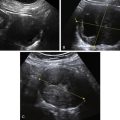
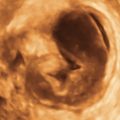
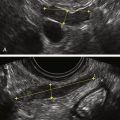
Granulosa cell tumors can present as cystic/septated or solid masses arising from the ovary.
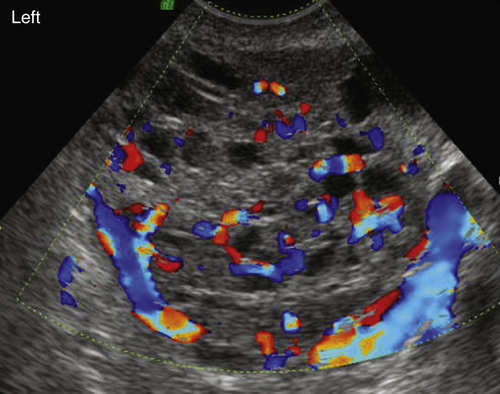
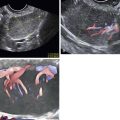
In the study by Van Holsbeke and colleagues, almost all tumors had solid components; 52% were multilocular with solid areas, 39% were purely solid, 4% were unilocular with a solid component, and 4% were multilocular. Granulosa cell tumors are typically large, with a median diameter of 10.2 cm (range, 3.7 to 24.2cm) in this study. Only one mass was smaller than 5 cm, and more than 50% were larger than 10 cm. Ascites was present in 22% of patients. Most of the tumors had a high vascular content shown by color Doppler, indicating a high likelihood of malignancy.
These tumors typically produce hyperestrogenemia, so patients are at increased risk for development of endometrial hyperplasia or concomitant endometrial adenocarcinoma. Sonographically, there may be evidence of a thickened endometrial lining.
Differential Diagnosis
Granulosa cell tumors are large tumors that can be solid, solid/cystic, and cystic with multiple septations. They tend to be large and associated with evidence of hyperestrogenemia such as abnormal bleeding. The differential diagnosis is vast and includes practically all large adnexal masses that contain septations, solid components, and vascularity. Other tumors such as epithelial malignancies can have a similar appearance. Fibromas tend to be predominantly solid with less blood flow than GCTs. Fibrothecomas are also solid in appearance and can produce estrogen, similar to the GCT.
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Postmenopausal or irregular bleeding is a common presenting sign in the adult form of GCT, likely because of exposure to estradiol, ultimately leading to endometrial hyperplasia or adenocarcinoma.
The juvenile type of GCT may present with precocious puberty or abdominal/pelvic pain as these can grow to large sizes.
The survival for GCT patients depends on staging. The 10-year survival rates for stages 1, 2, and 3/4 are 84% to 95%, 50% to 65%, and 17% to 33%, respectively. The management is surgical and depends on stage of disease.
Suggested Reading
Jung S.E., Lee J.M., Rha S.E., Byun J.Y., Jung J.I., Hahn S.T. CT and MR imaging of ovarian tumors with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Radiographics. 2002;22:1305–1325.
Pectasides D., Pectasides E., Psyrri A. Granulosa cell tumor of the ovary. Cancer Treat Rev.. 2008;34:1–12.
Schumer S.T., Cannistra S.A. Granulosa cell tumor of the ovary. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1180–1189.