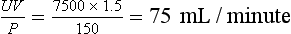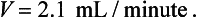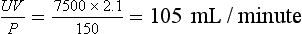Case history comments
Case history 9
U = 7.5 mmol/L = 7500 µmol/L. His serum creatinine: P = 150 µmol/L. Thus,
This is low for a young male.
Recalculating his creatinine clearance:
Case history 44
In a patient such as this in ITU the biochemical measurements that are most frequently helpful are:
 Serum urea and electrolytes to monitor renal function and serum potassium as he may become hyperkalaemic as a result of tissue damage.
Serum urea and electrolytes to monitor renal function and serum potassium as he may become hyperkalaemic as a result of tissue damage.
 Pulse oximetry to assess tissue oxygenation.
Pulse oximetry to assess tissue oxygenation.
 Blood gas analysis and plasma lactate, to detect and quantify acid–base disorders that may arise.
Blood gas analysis and plasma lactate, to detect and quantify acid–base disorders that may arise.
 Serum muscle enzymes, such as CK may help detect a compartment syndrome or monitor rhabdomyolysis.
Serum muscle enzymes, such as CK may help detect a compartment syndrome or monitor rhabdomyolysis.