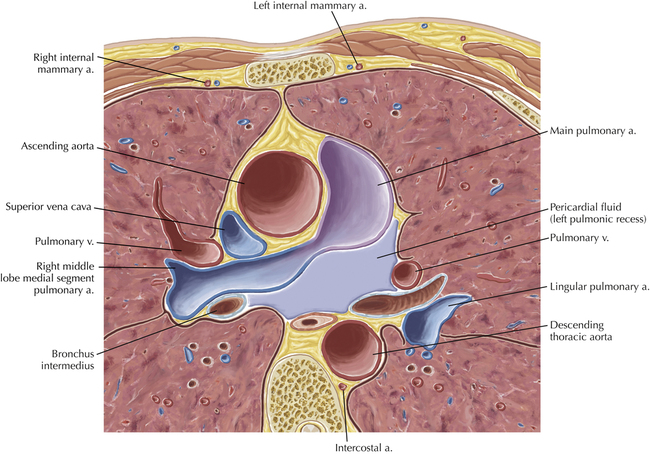
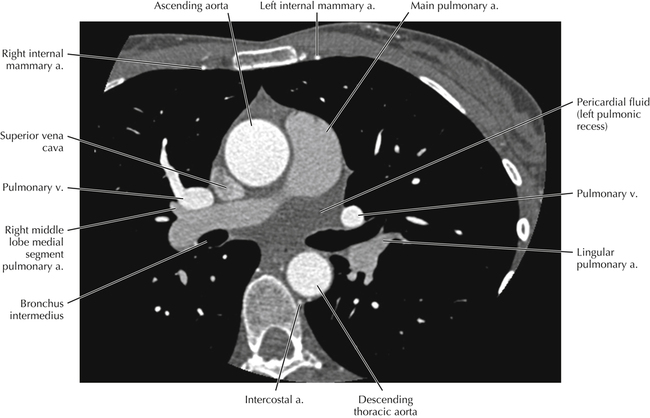
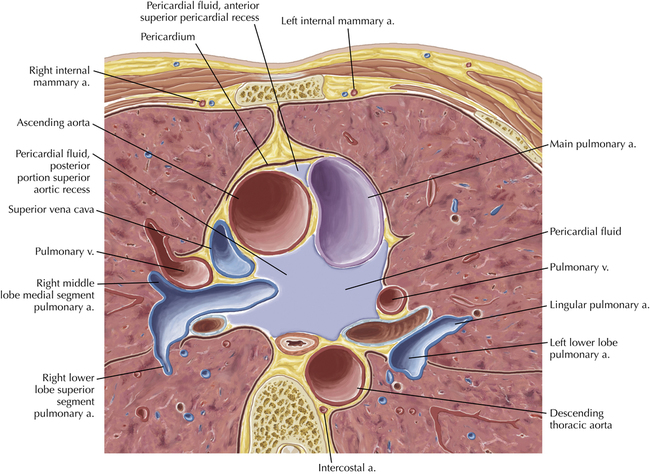
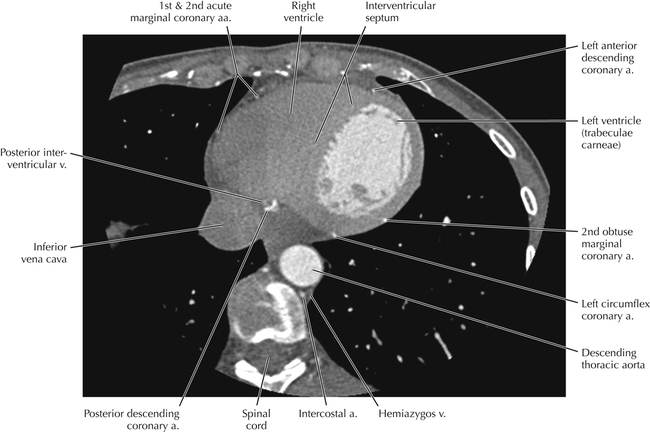
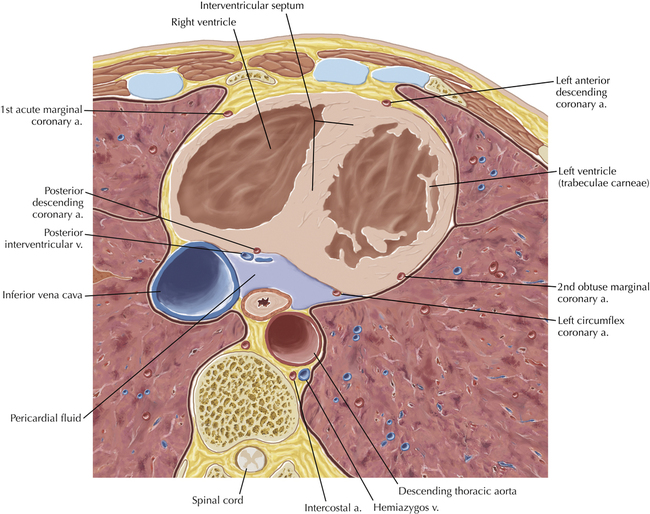
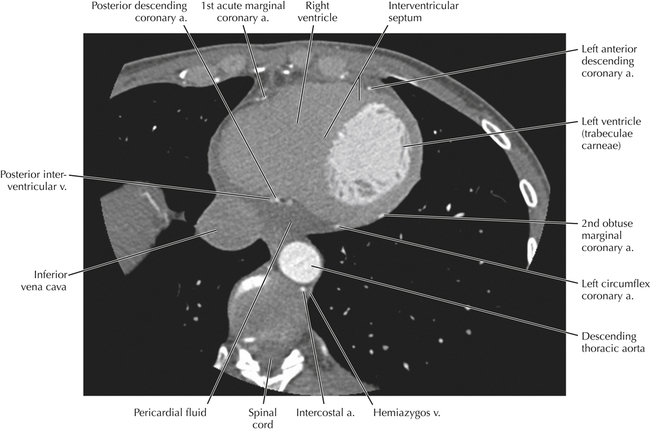
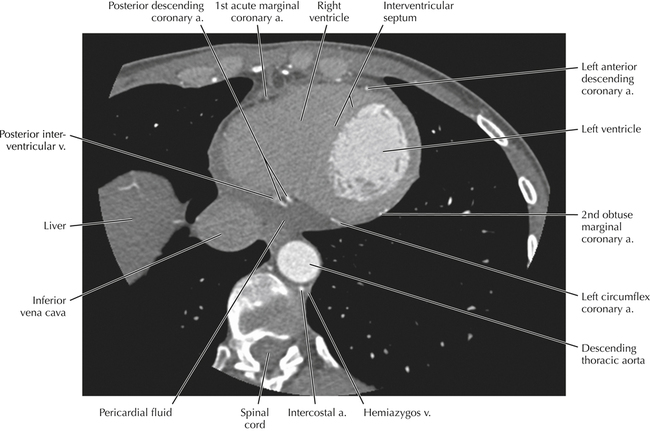
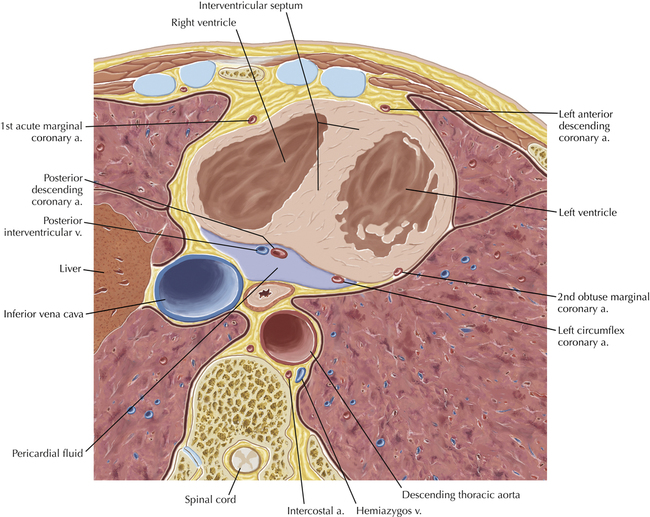
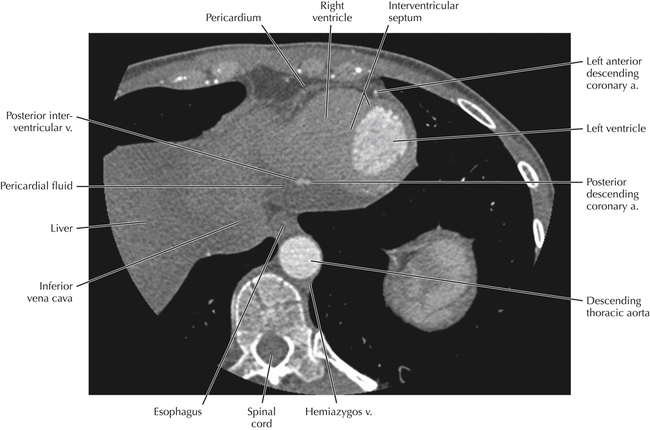
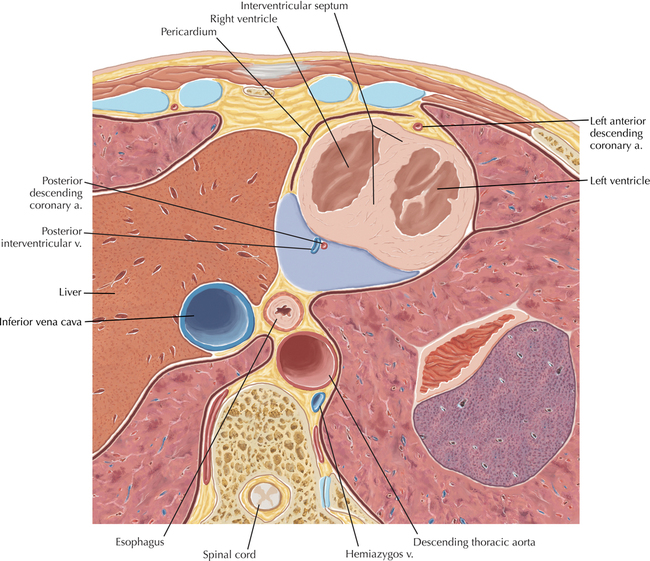
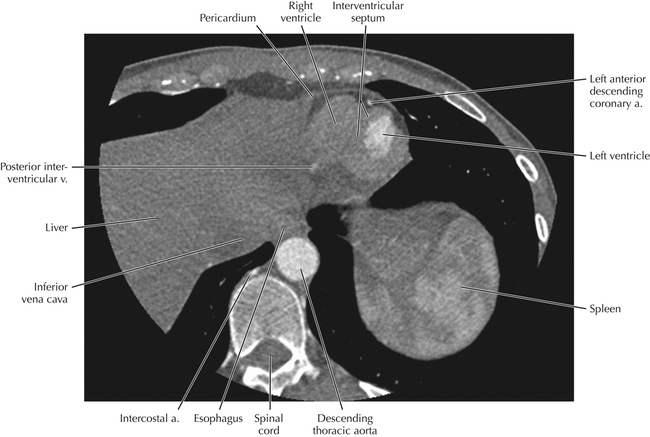
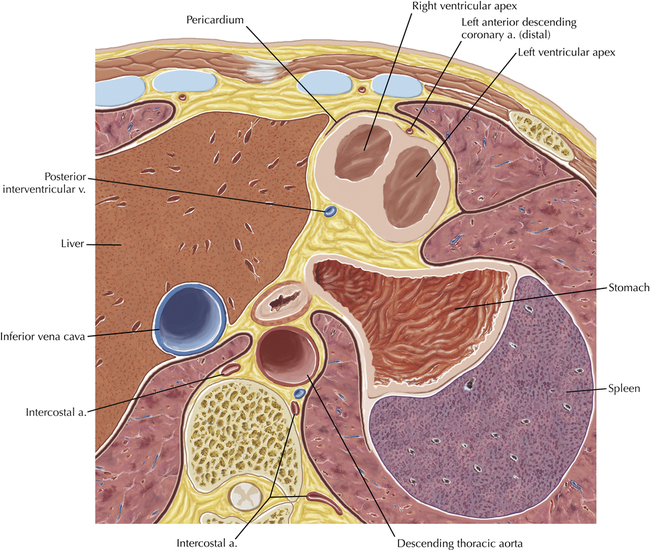
Cardiac Anatomy Using CT
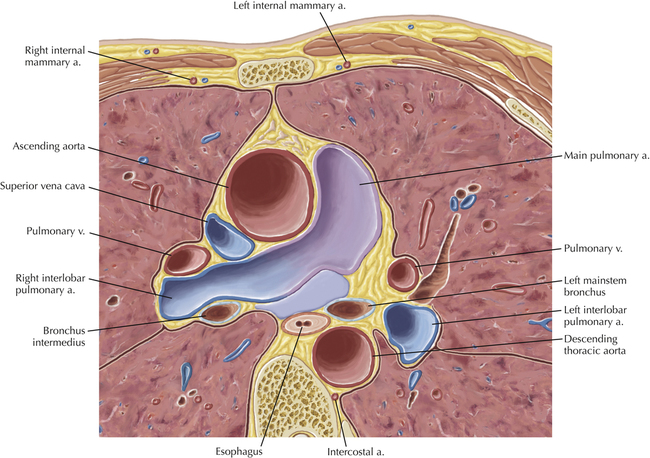
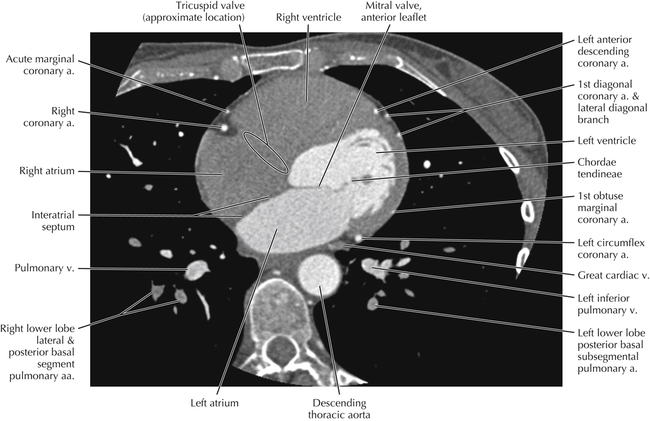
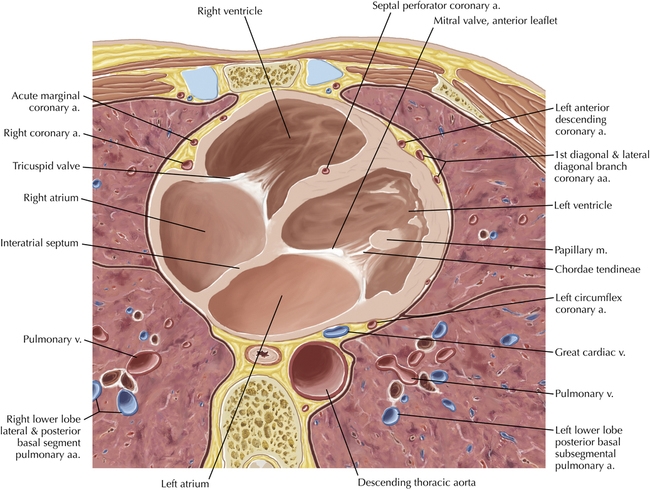
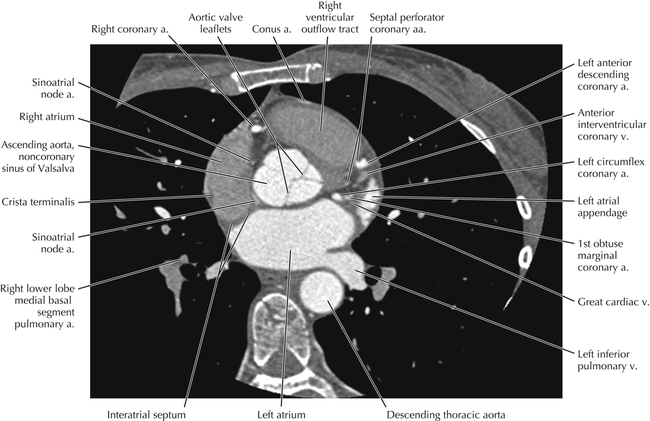
Cardiac CT Axial 19
Normal Anatomy
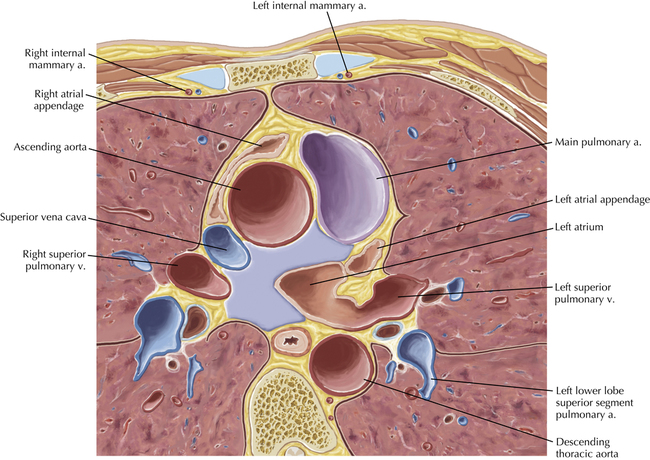
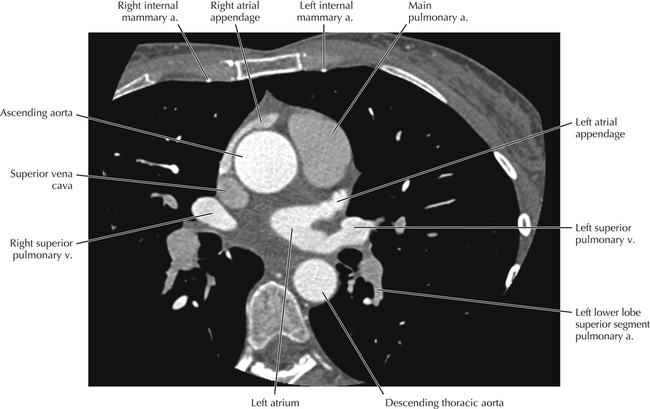
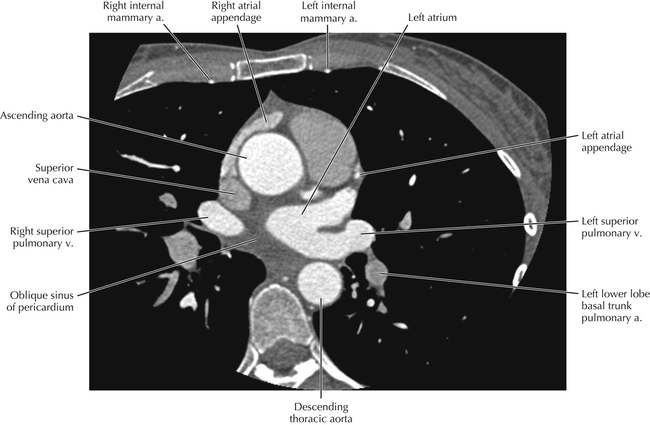
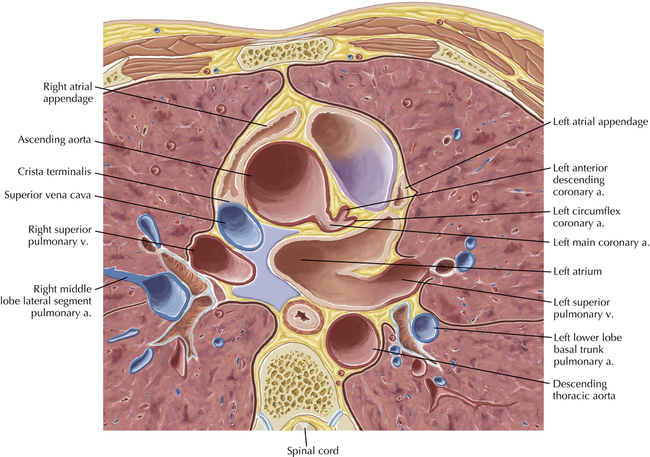
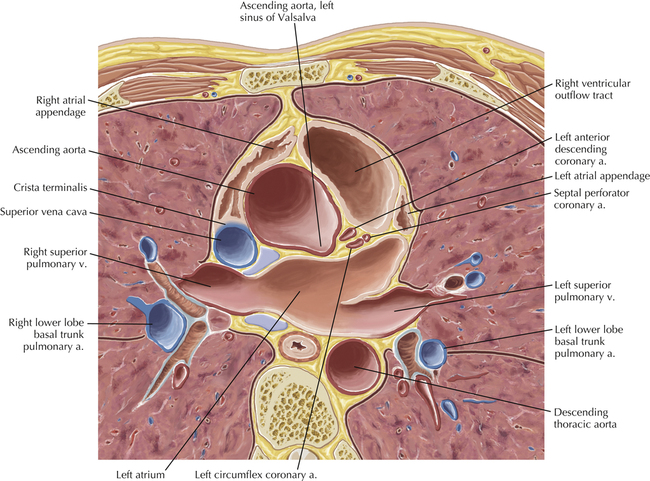
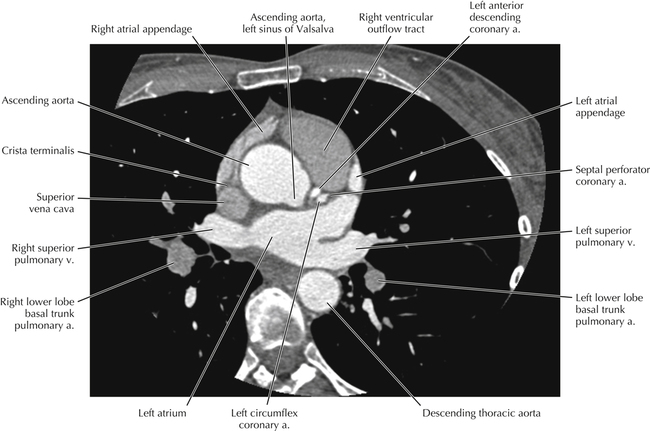
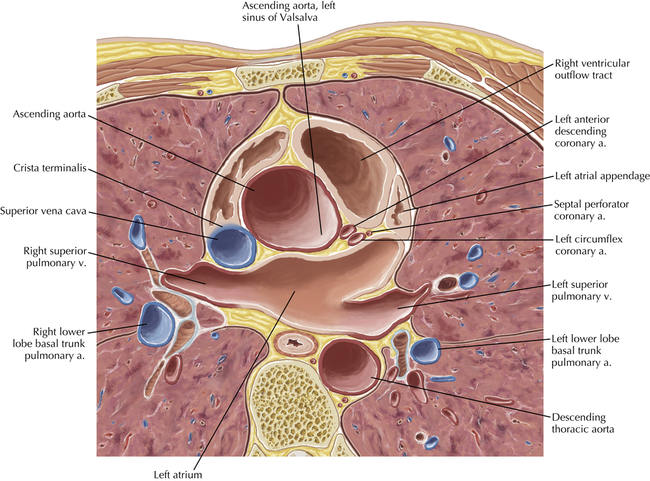
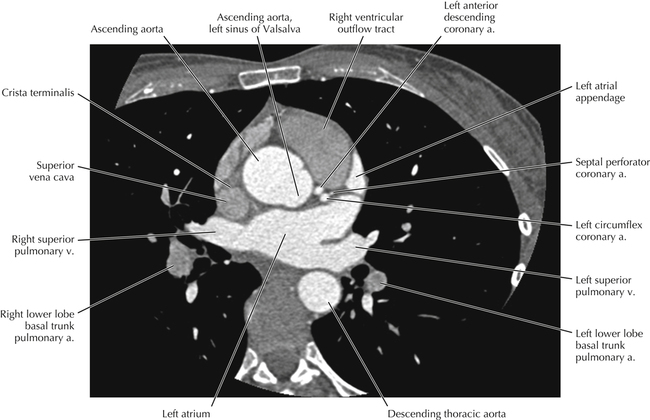
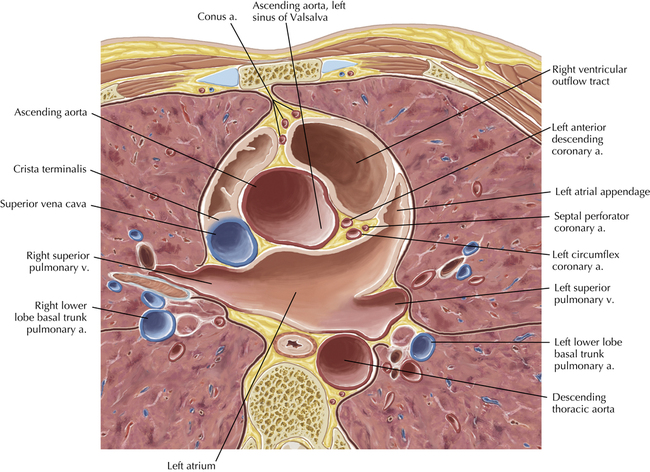
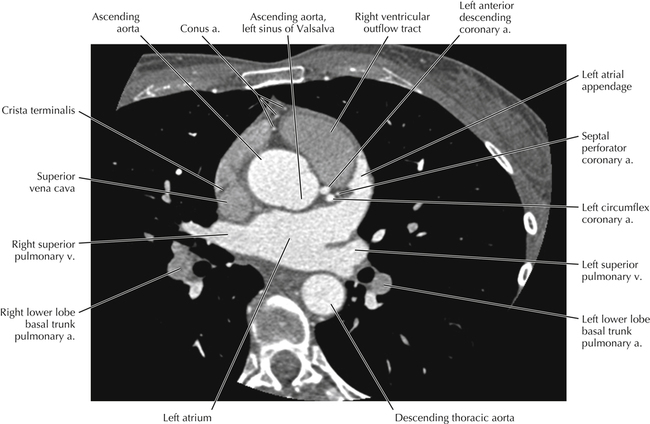
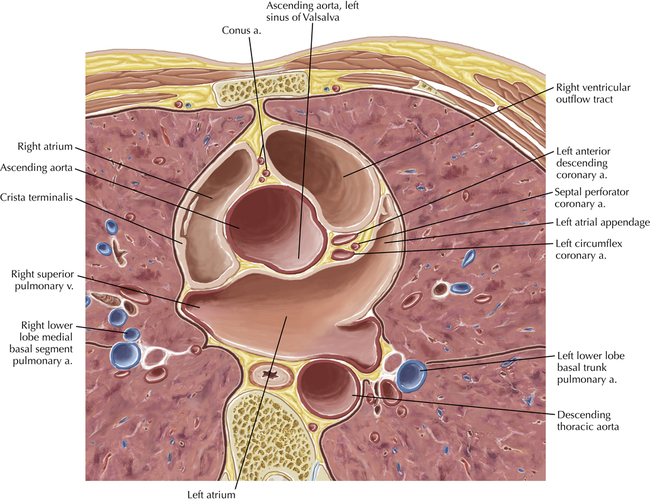
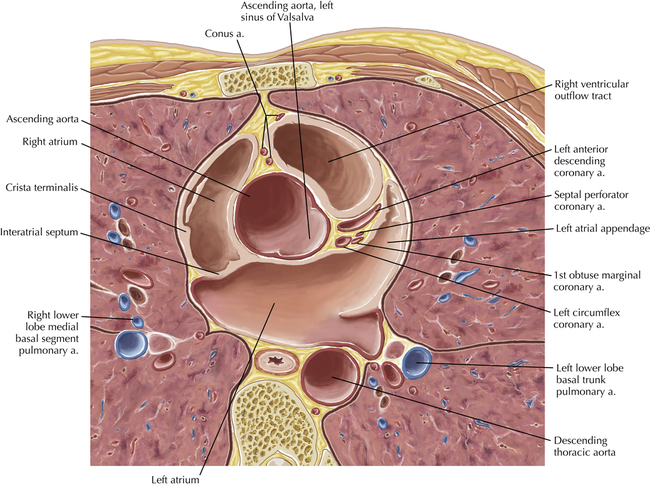
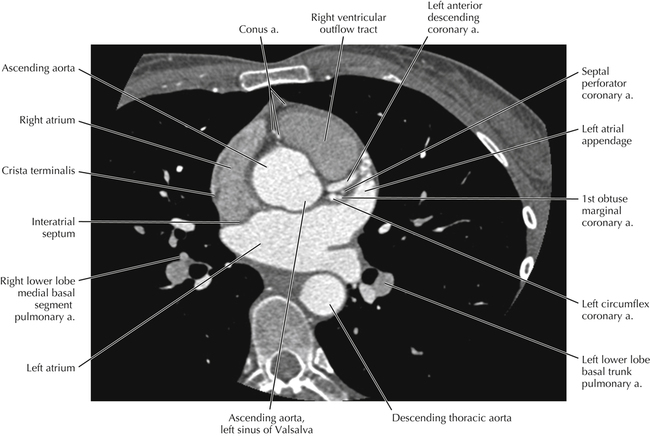
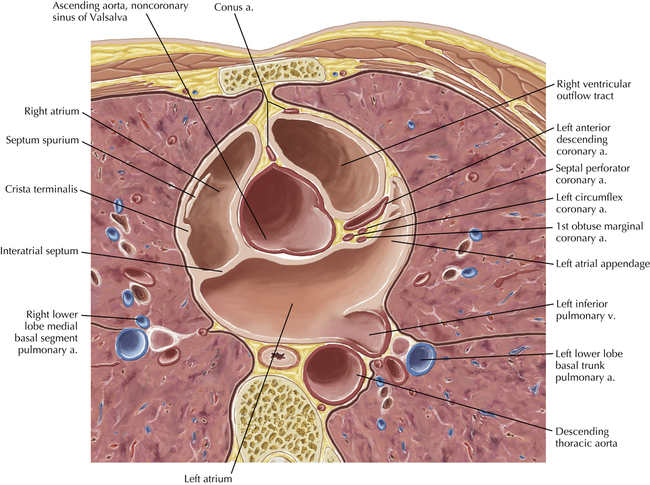
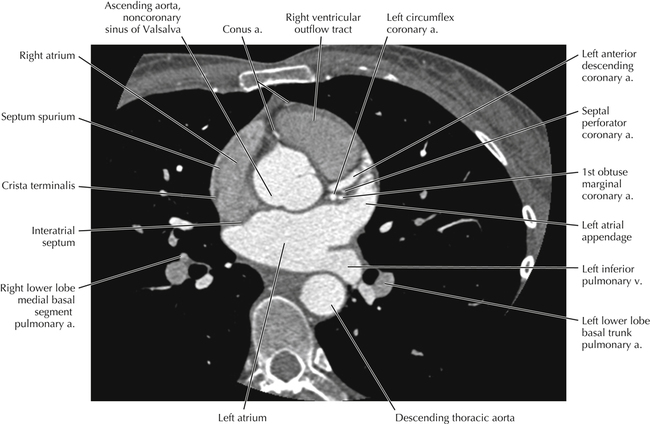
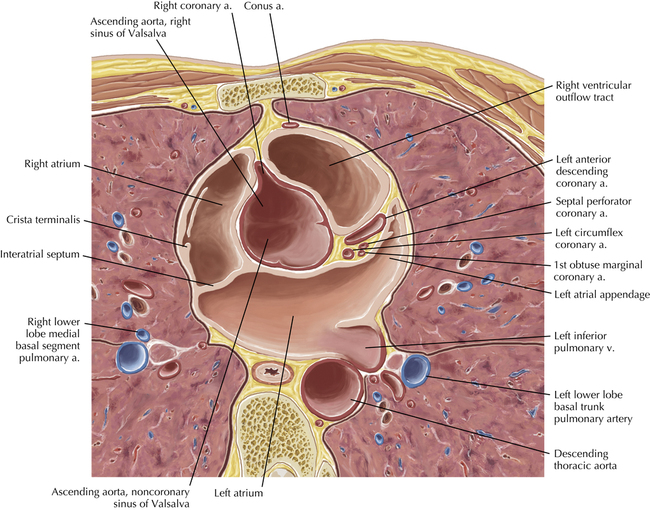
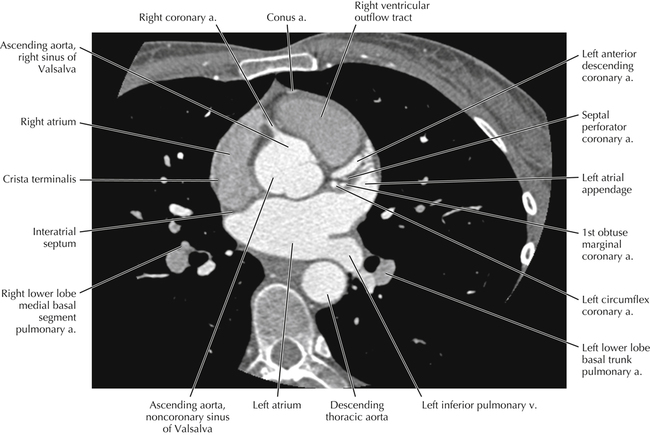
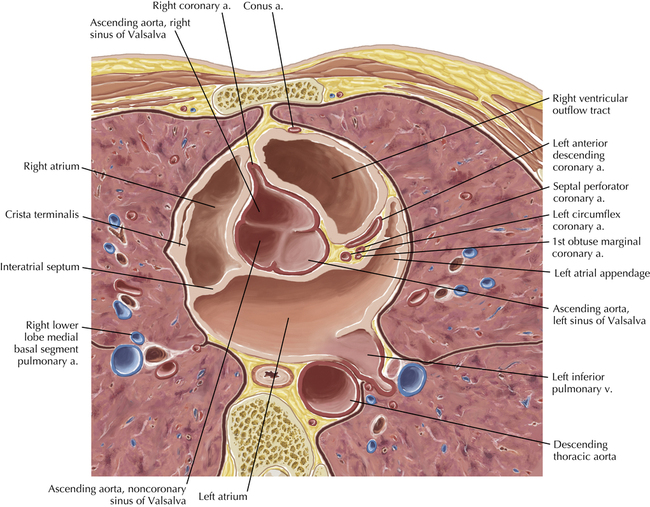
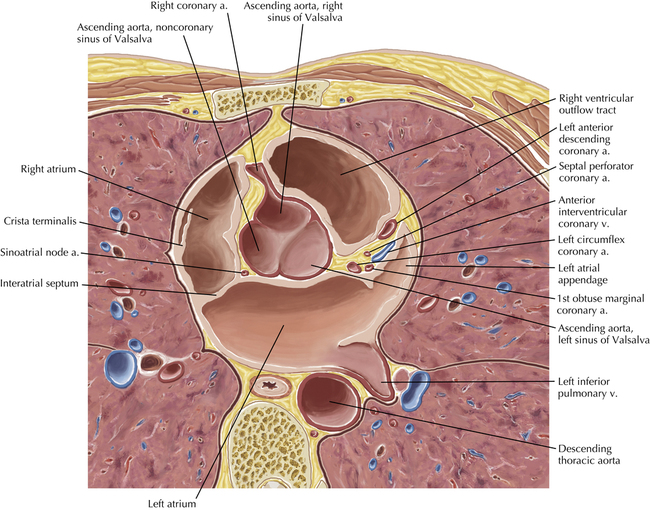
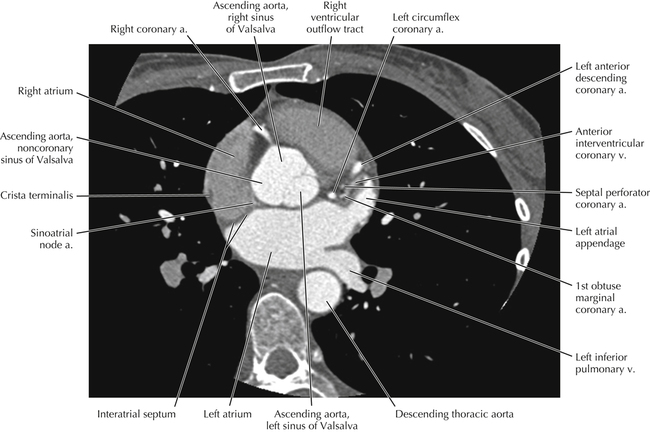
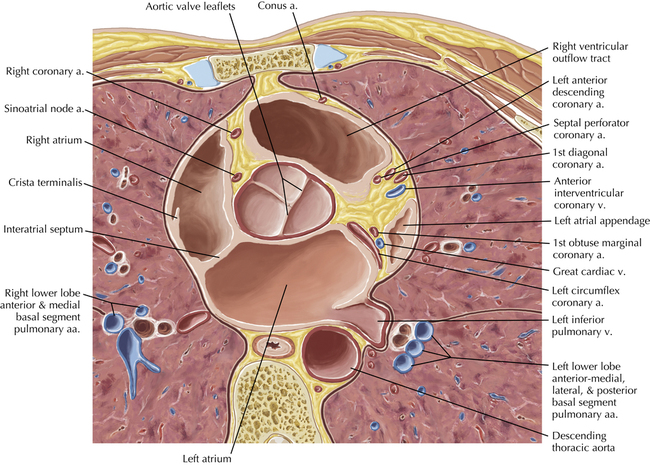
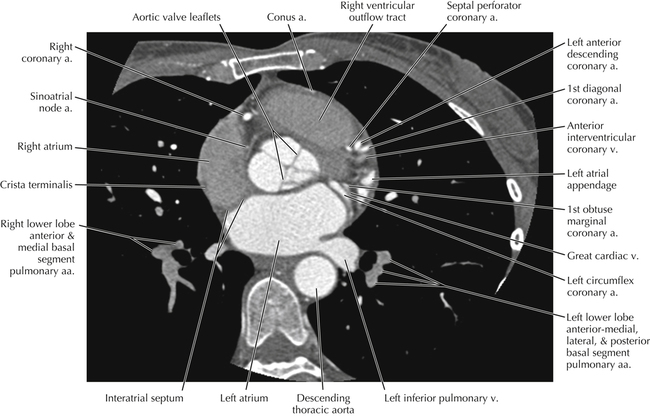
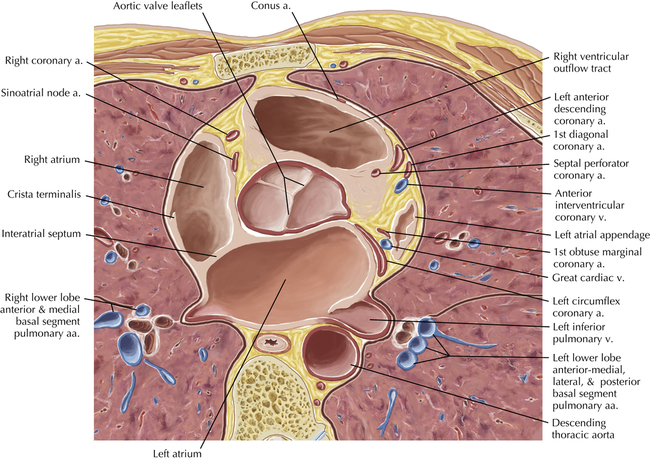
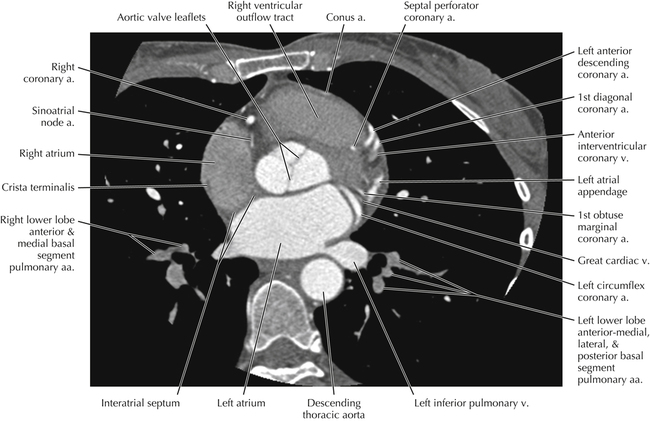
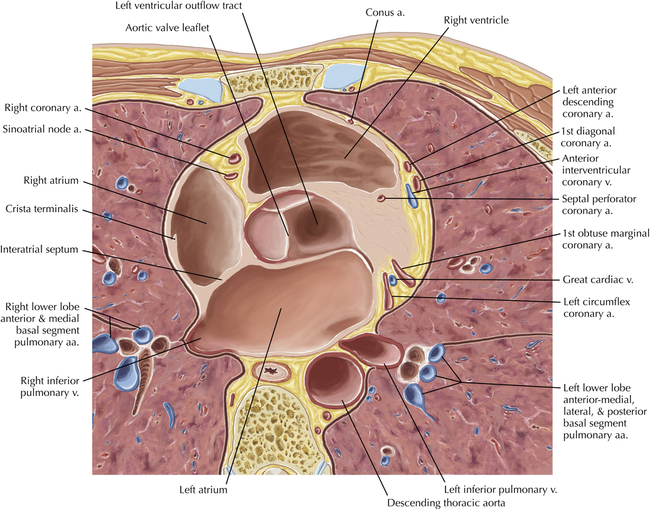
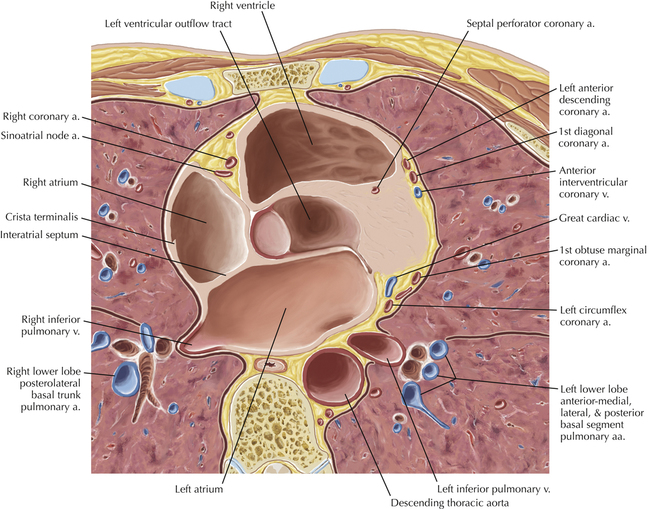
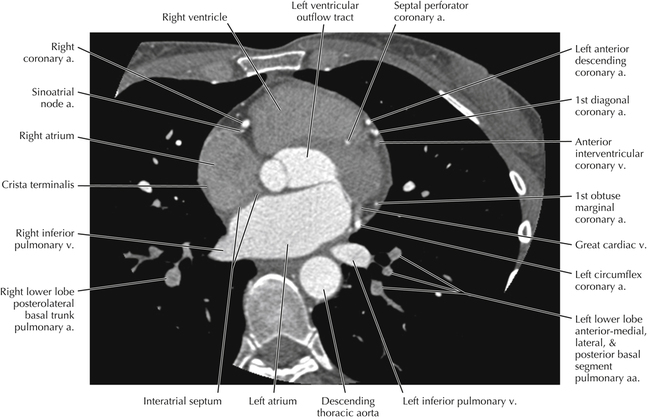
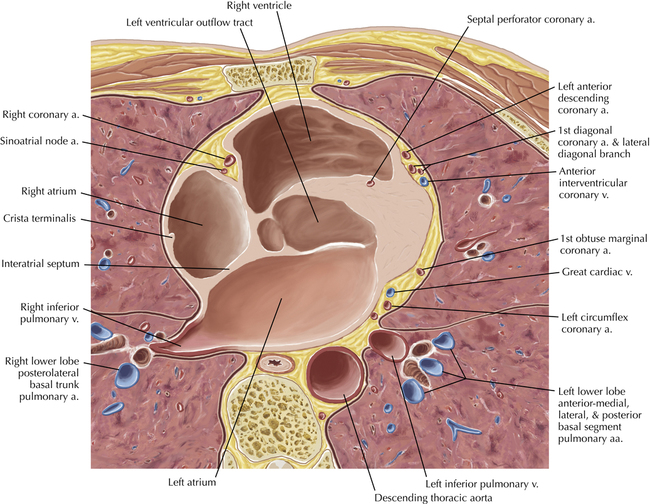
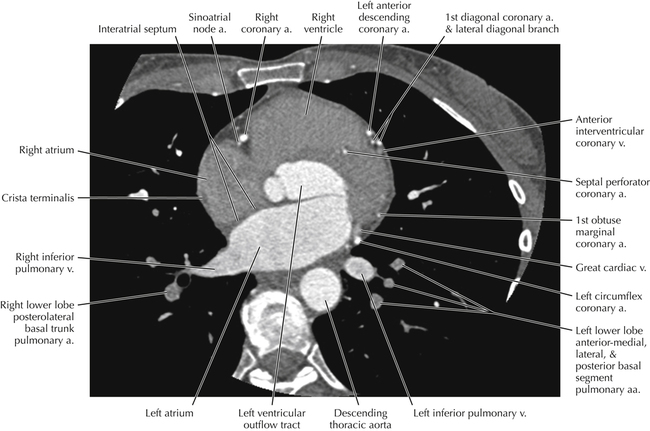
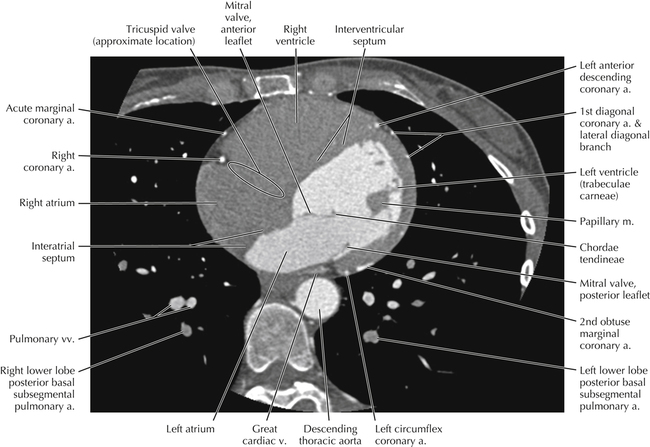
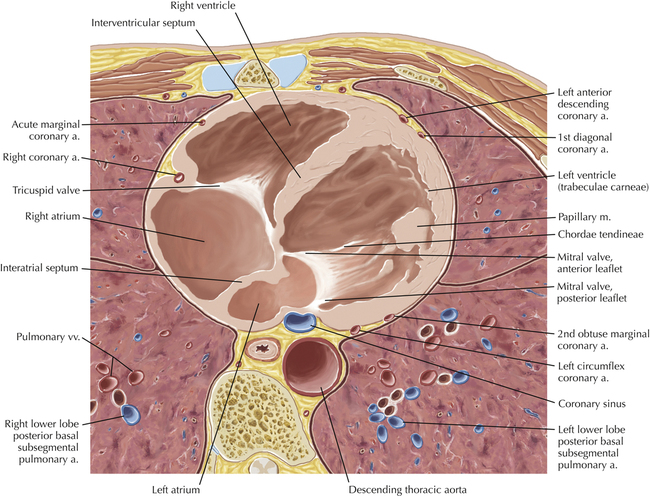
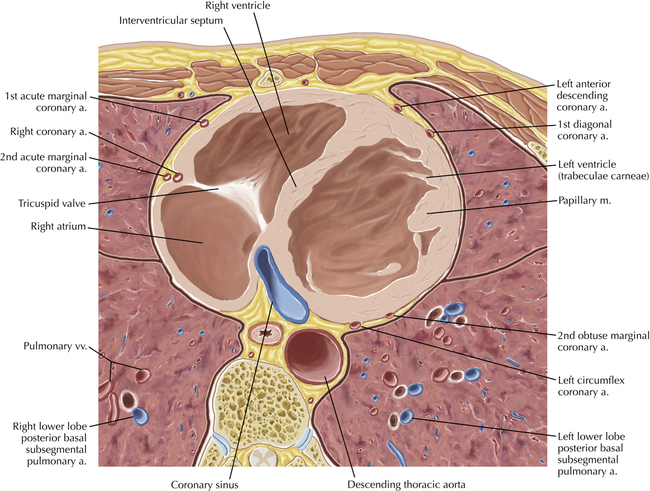
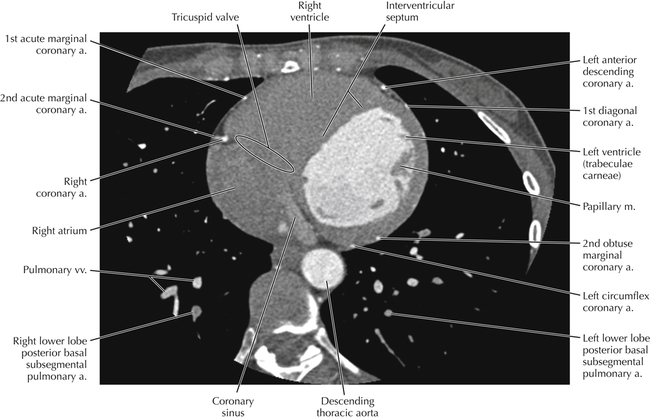
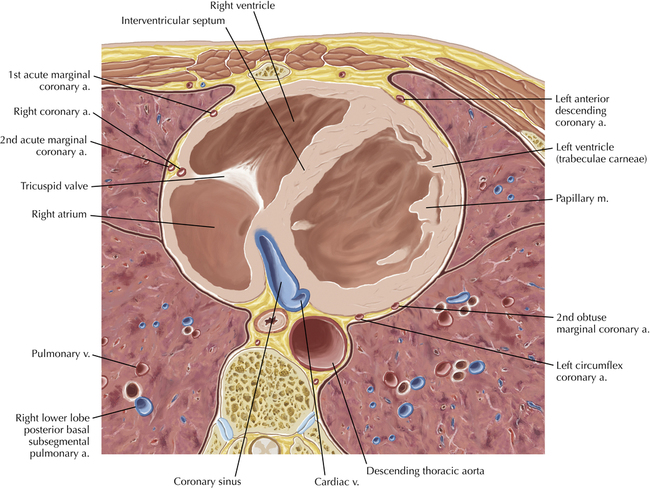
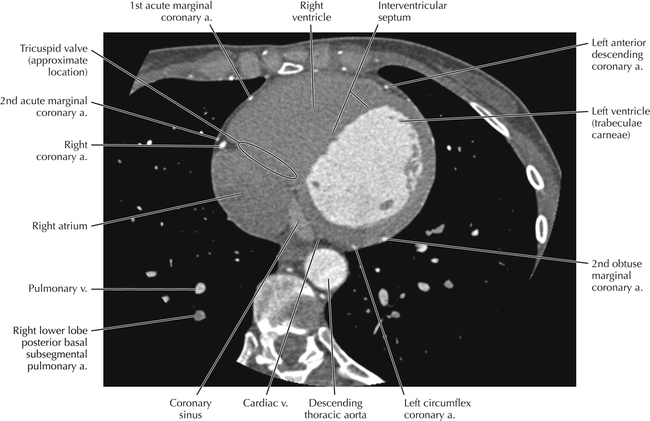
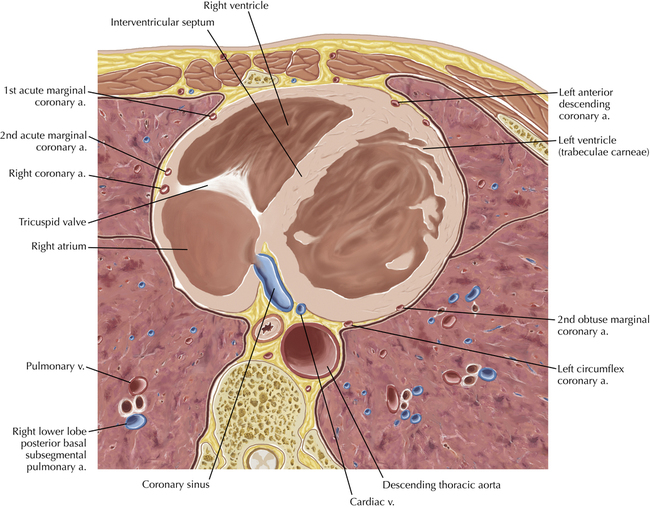
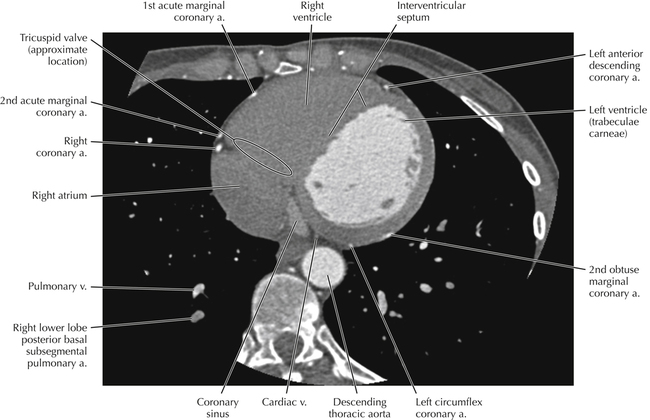
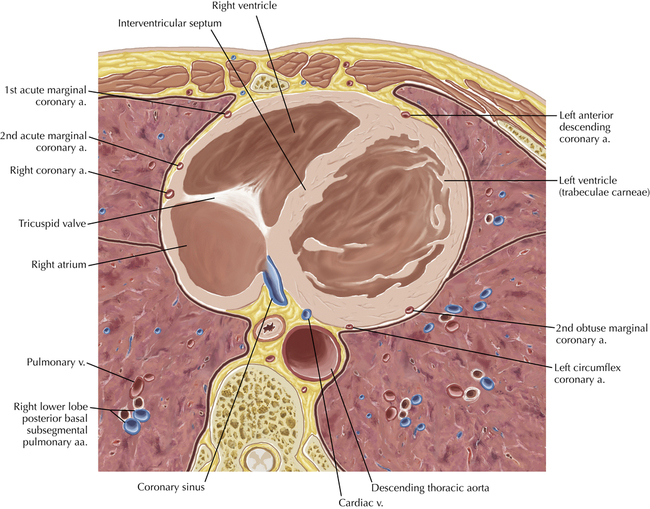
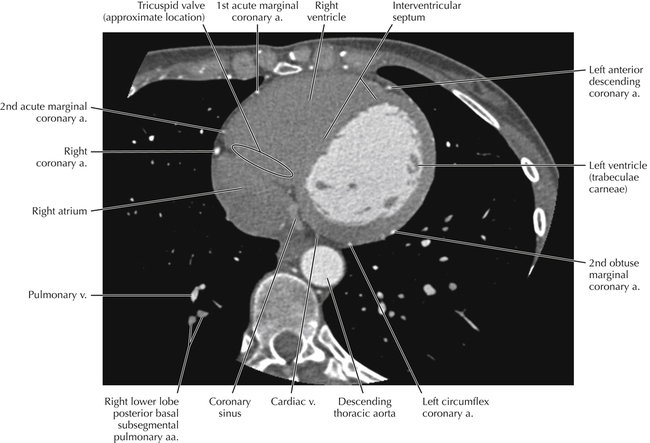
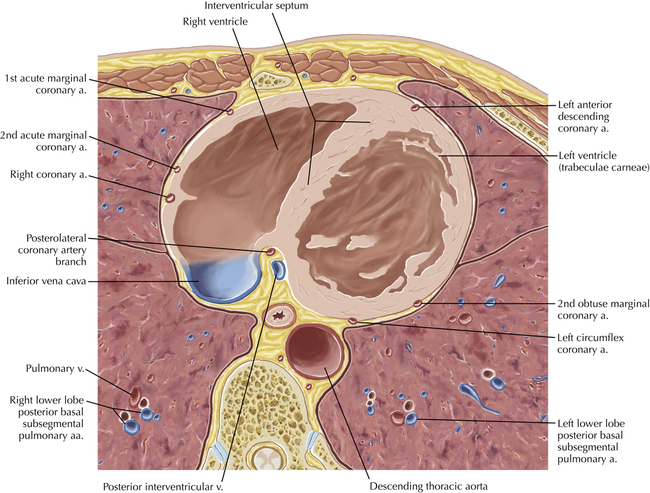
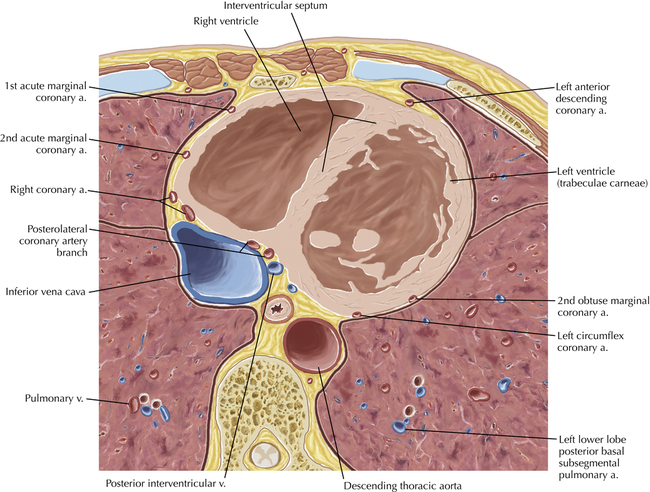
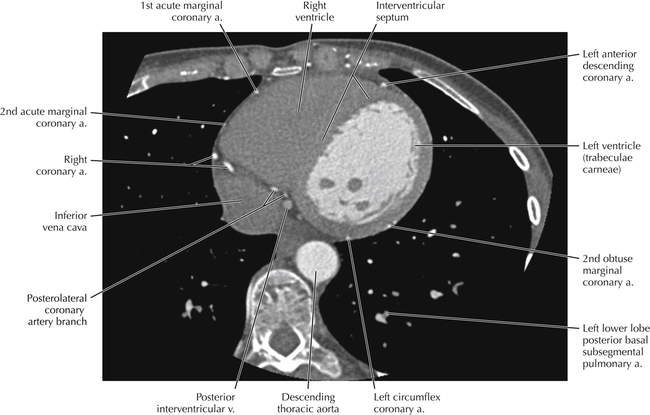
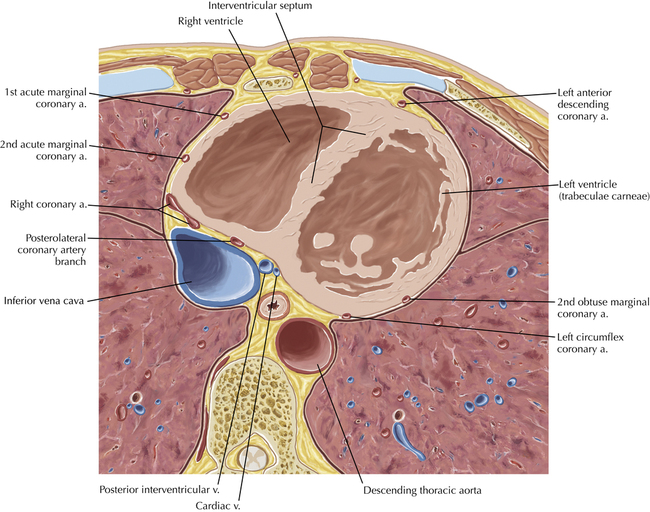
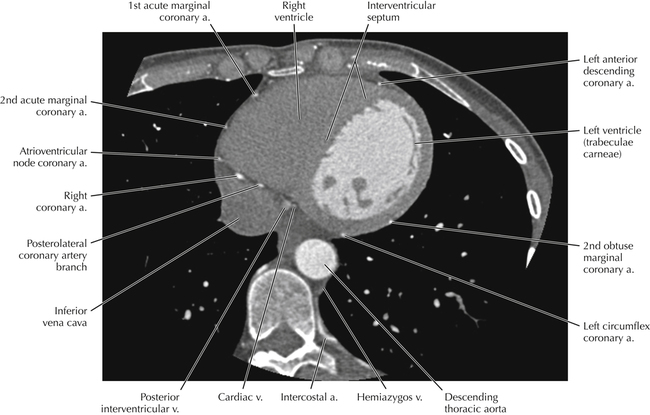
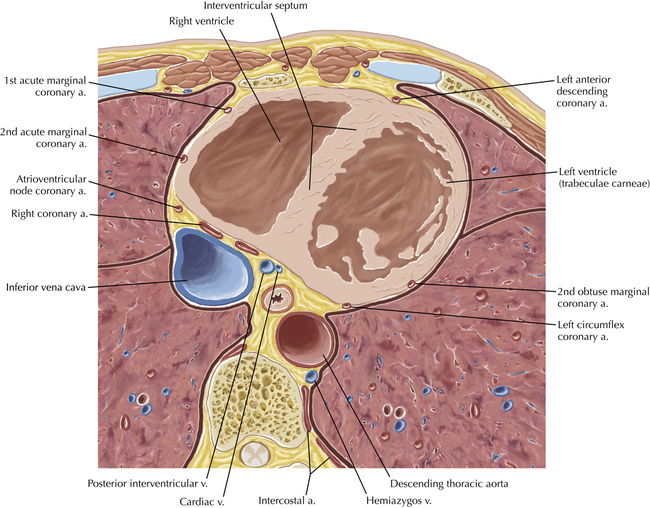
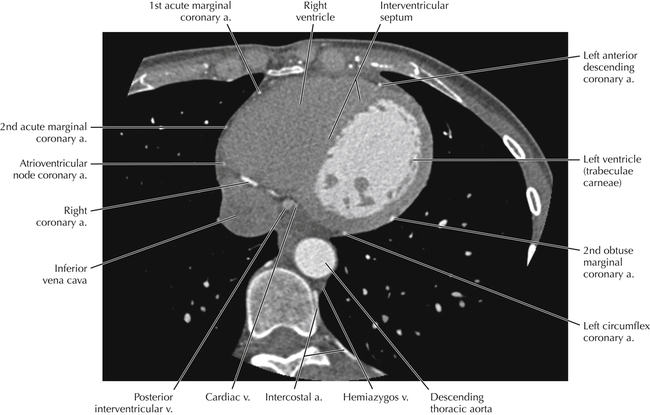
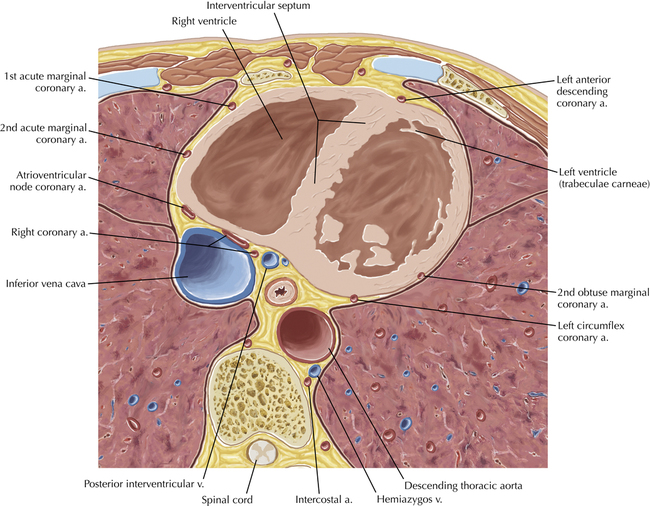
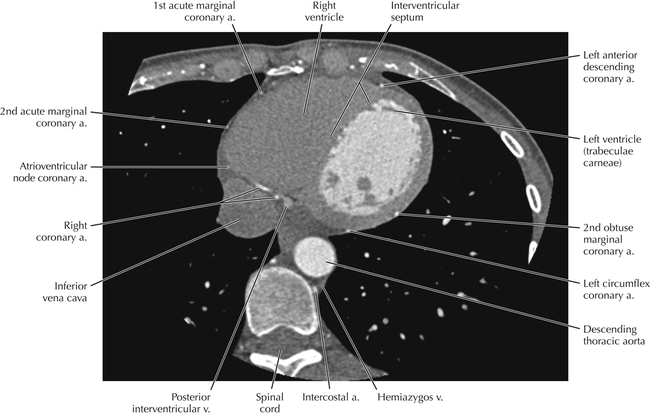
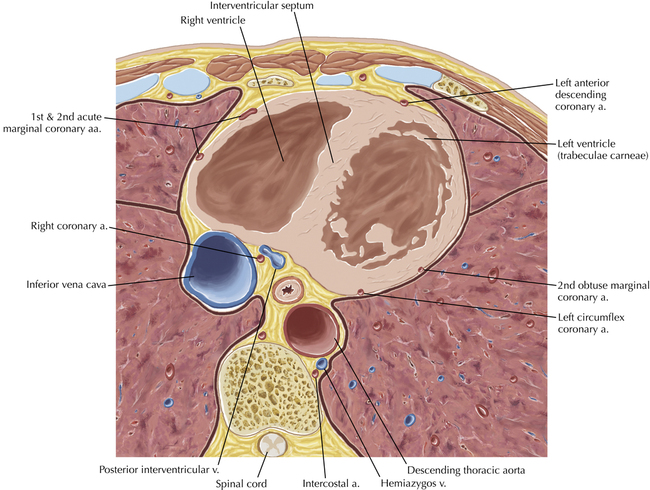
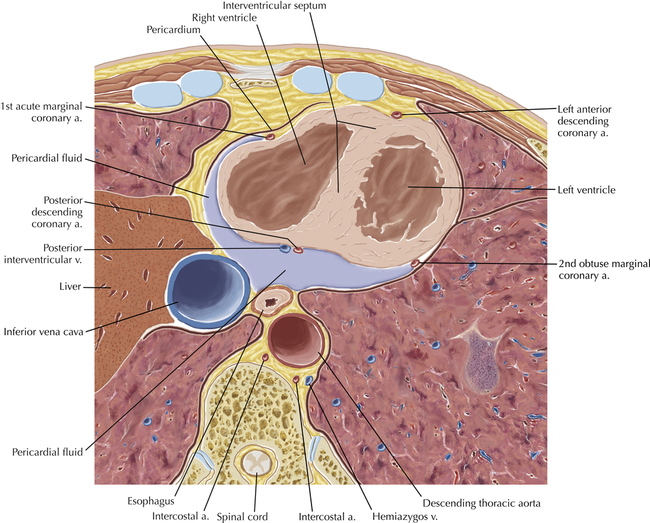
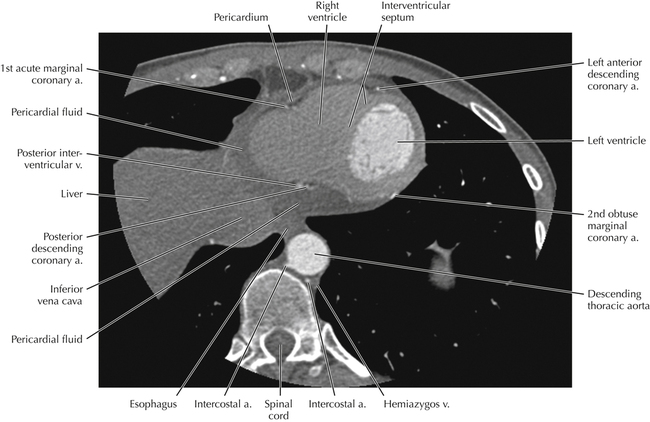
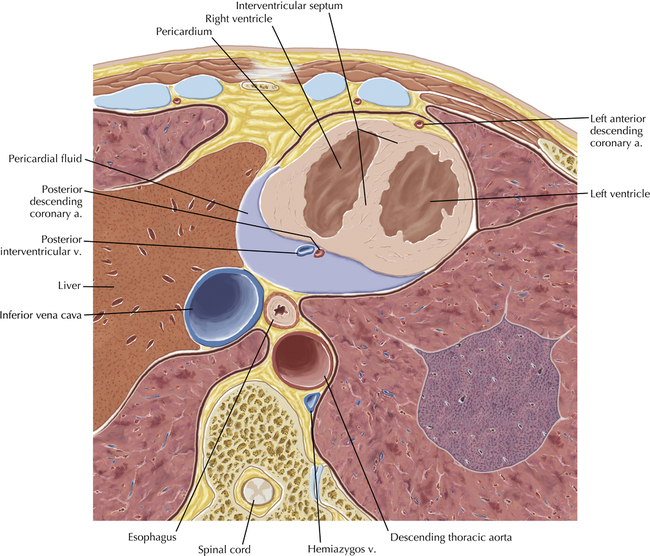
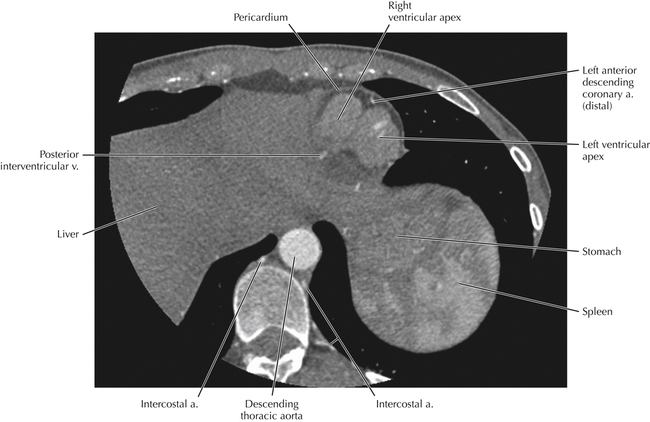
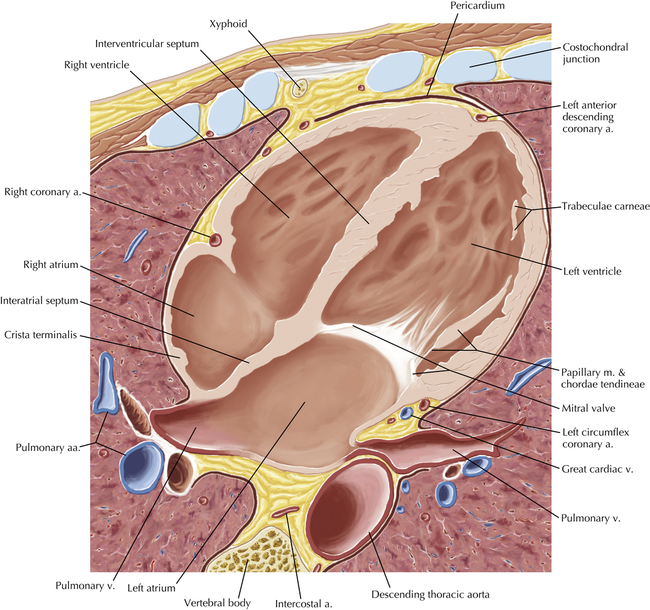
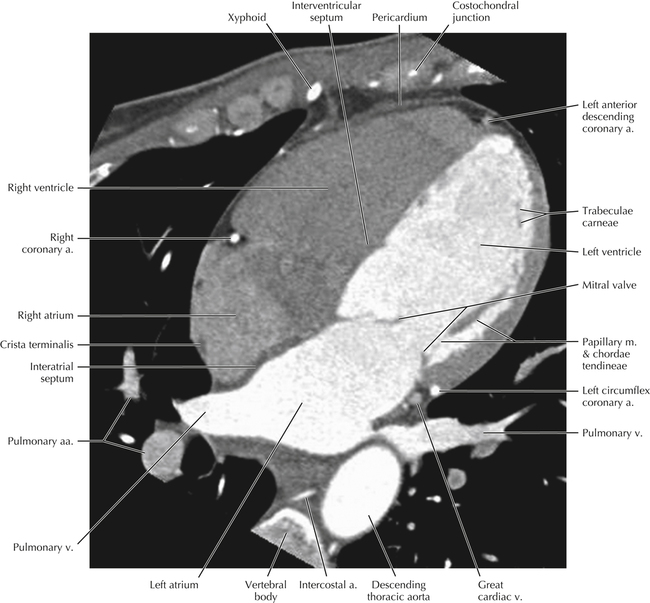
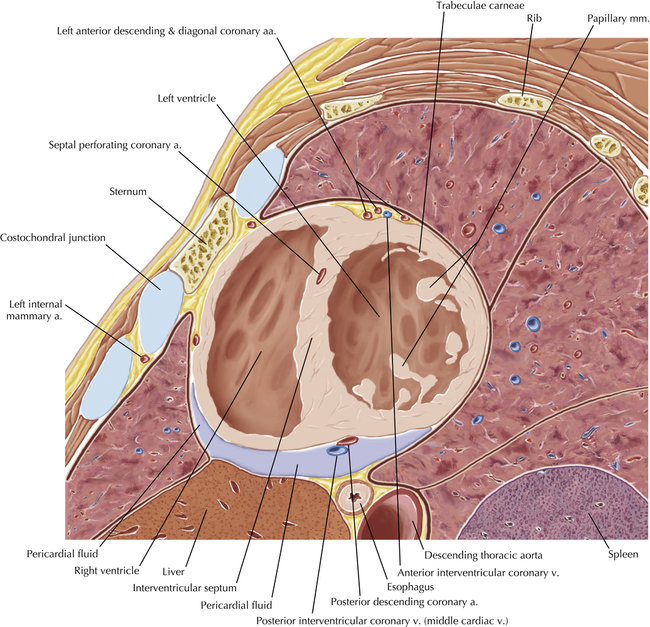
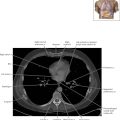
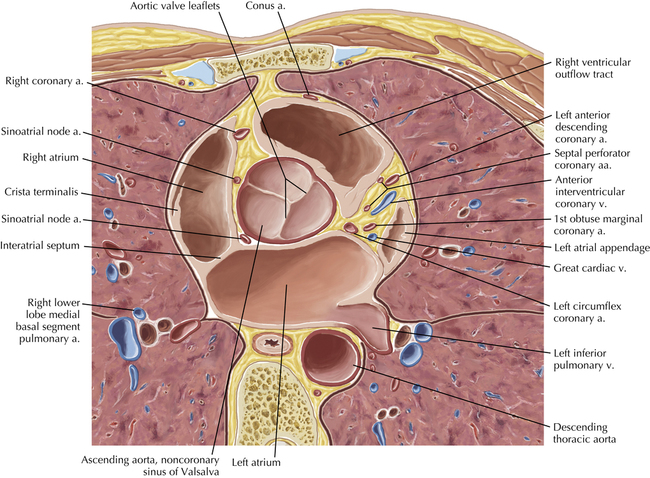
The sinoatrial nodal coronary artery is visible. The sinoatrial node is the source of the cardiac impulse and is typically located at the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium, in the superior end of the crista terminalis. The sinoatrial nodal artery usually arises as a single branch from the right coronary artery, as in this patient (see Axials 20 to 25), or, less commonly, the sinoatrial nodal artery may arise from the left circumflex coronary artery. The sinoatrial nodal artery may be followed superiorly toward the location of the sinoatrial node.
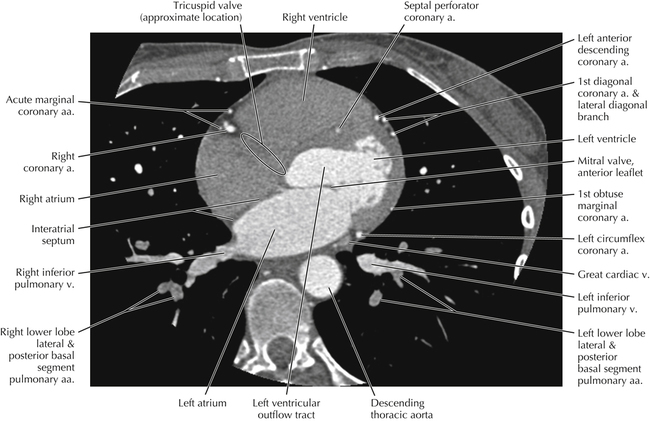
Cardiac CT Axial 28
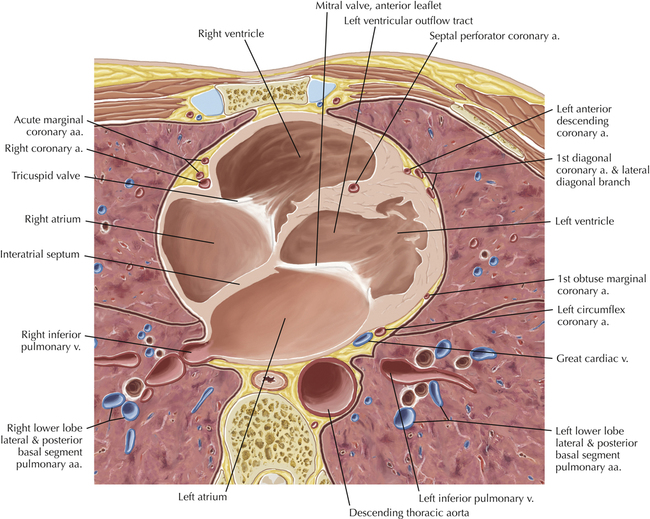
Normal Anatomy
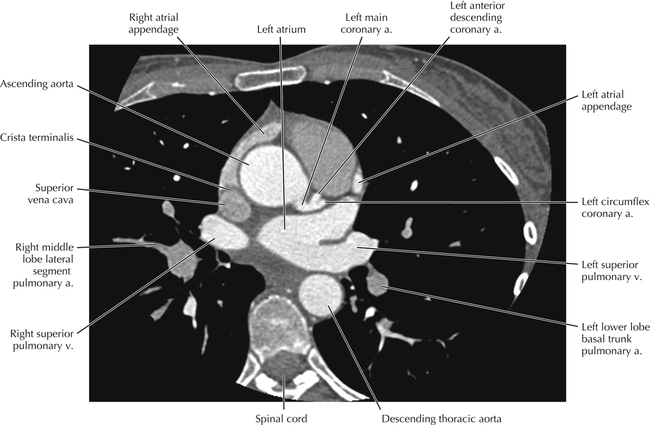
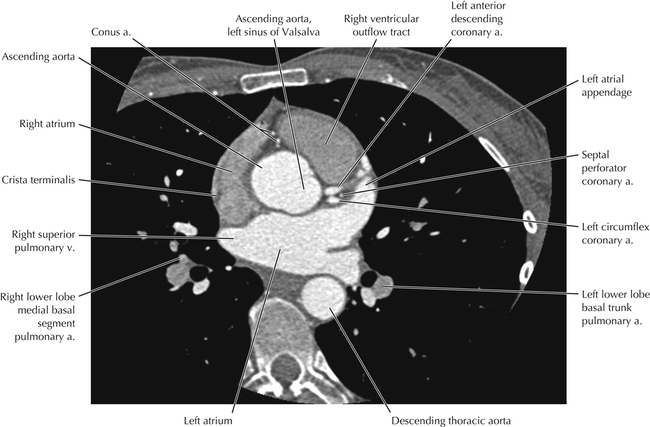
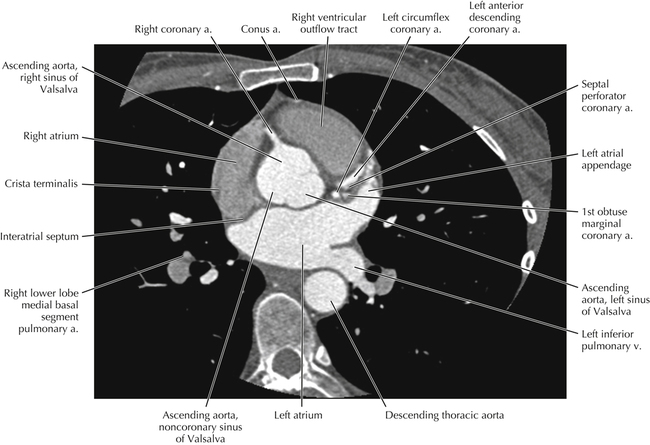
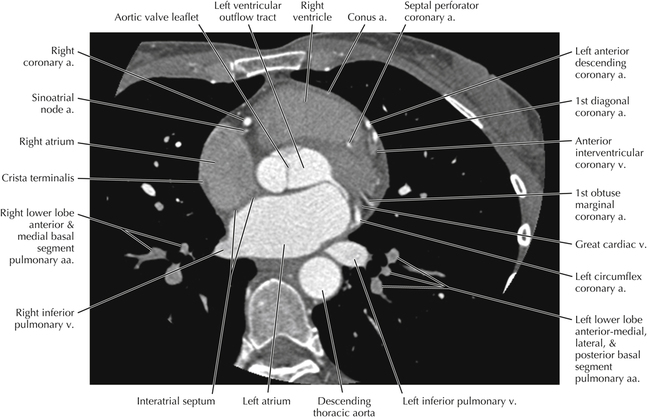
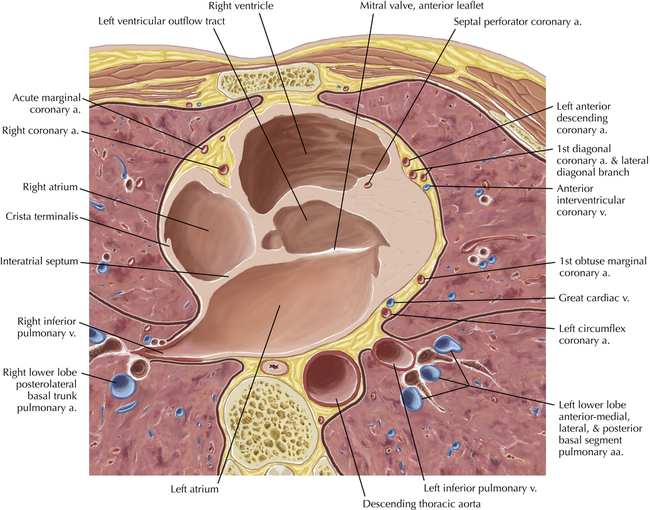
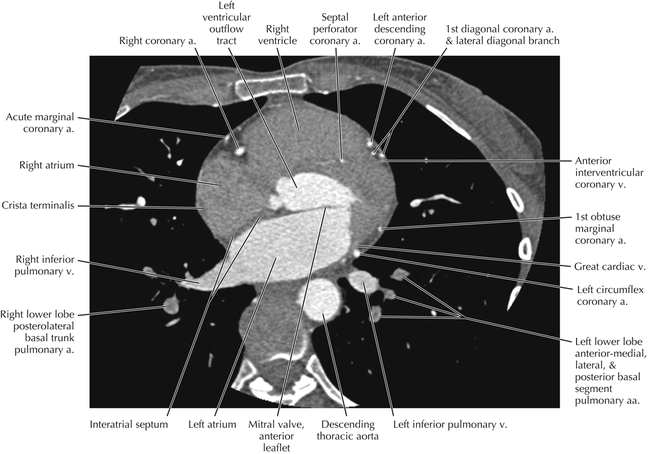
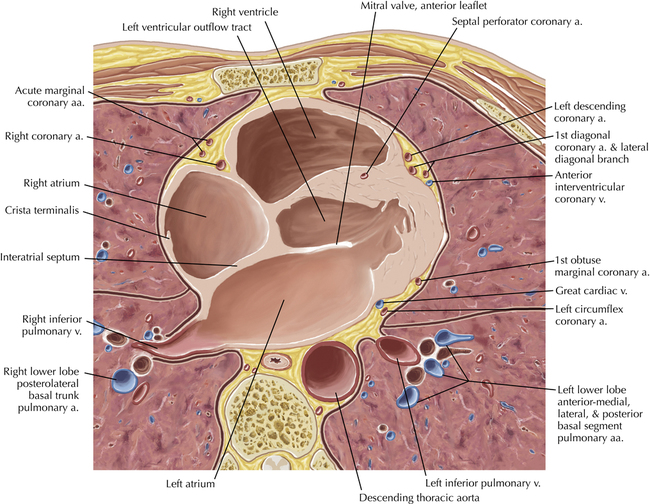
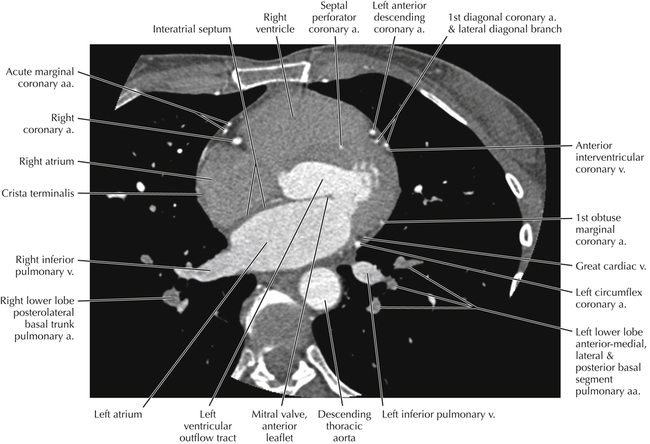
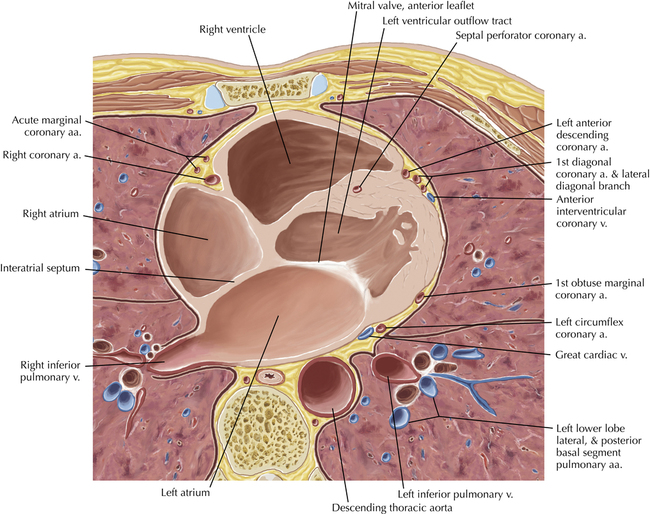
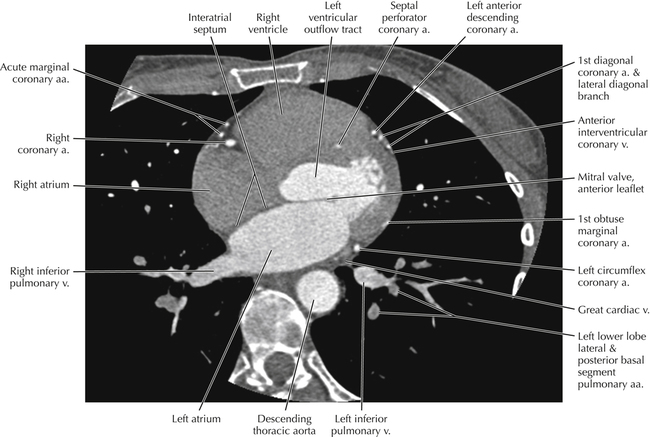
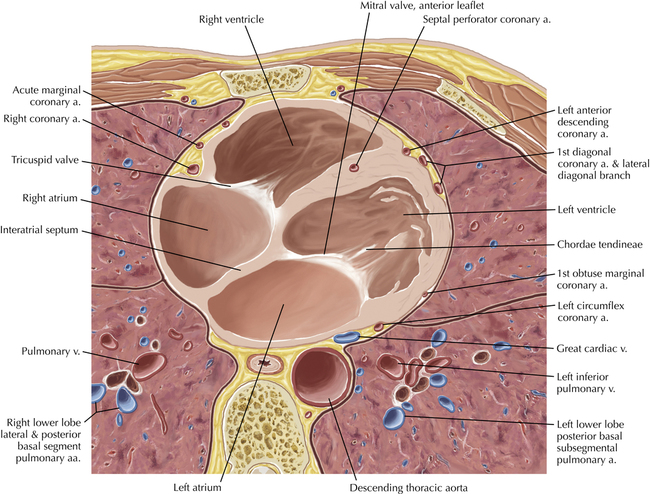
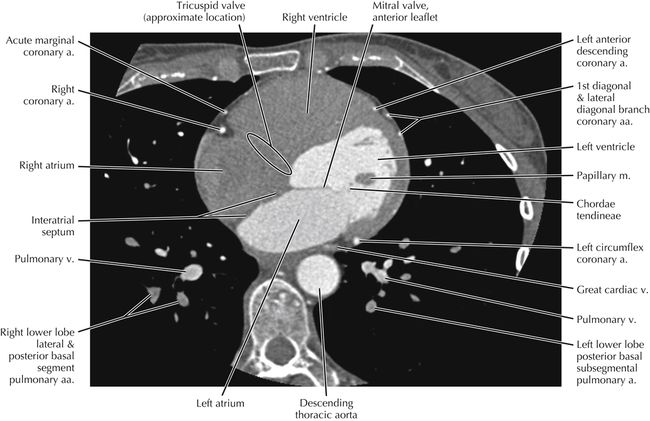
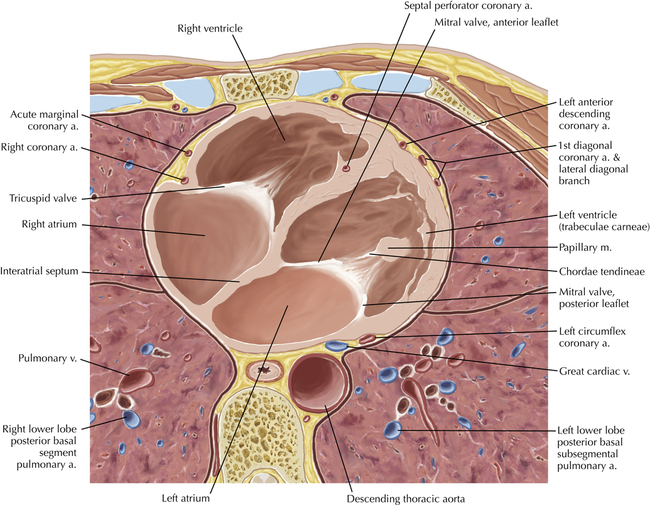
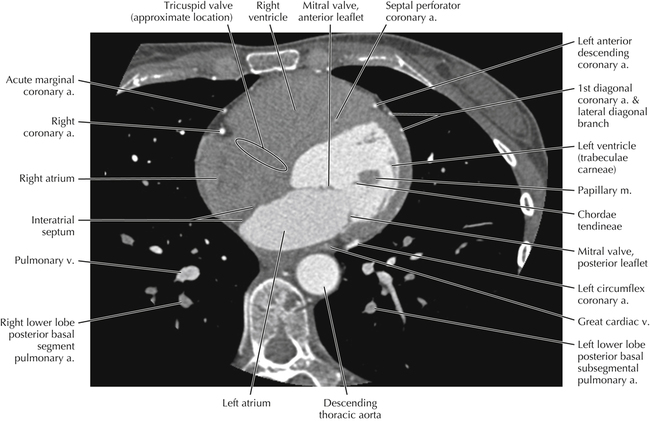
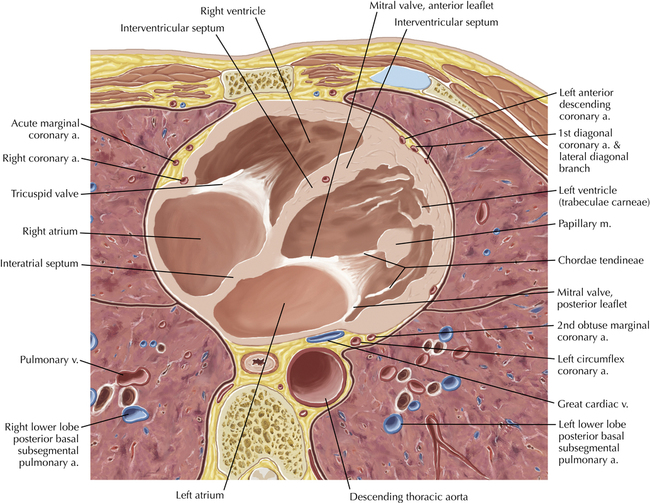
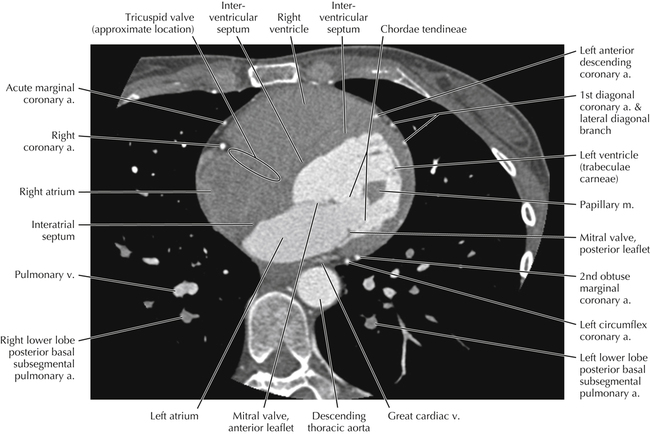
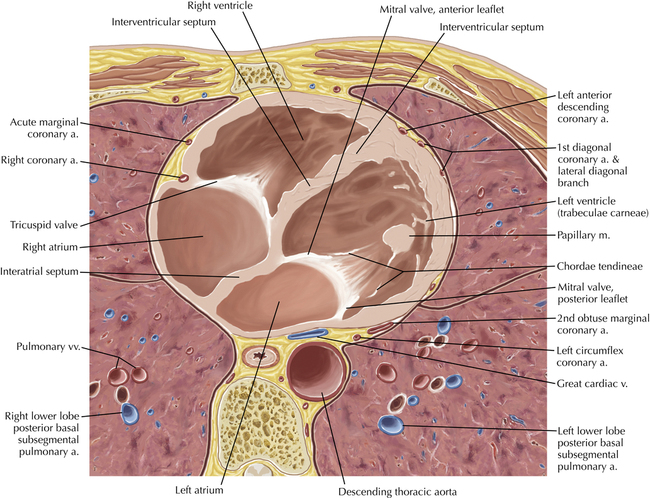
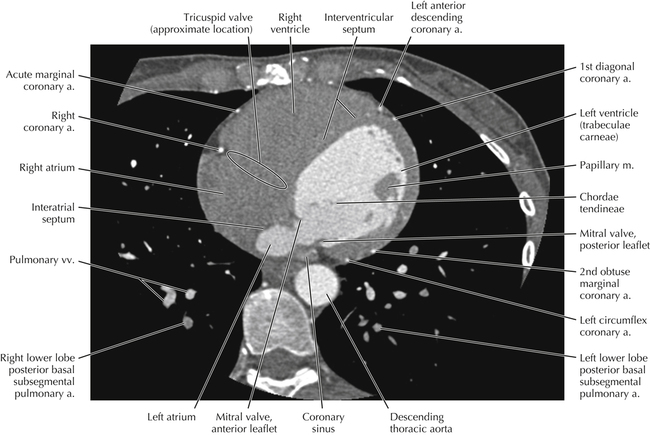
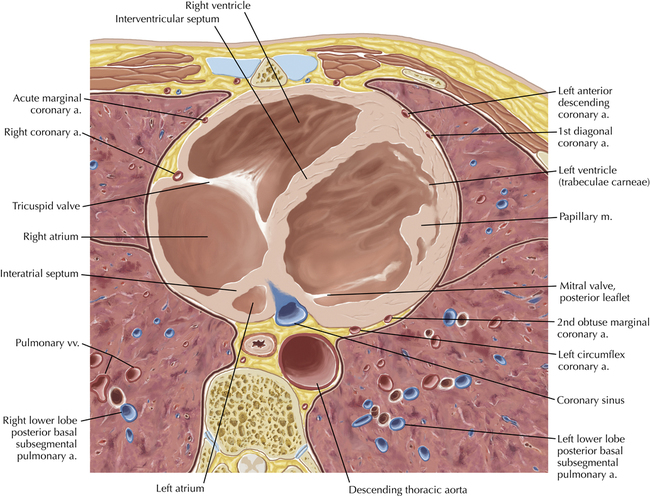
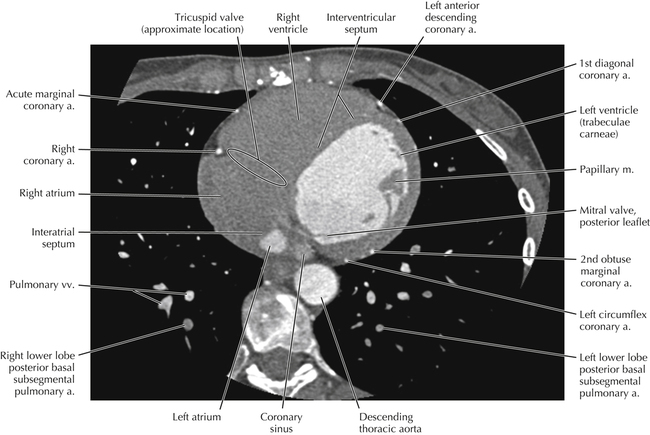
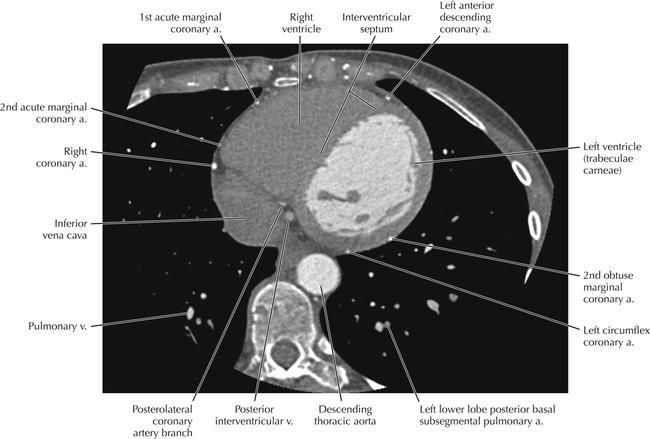
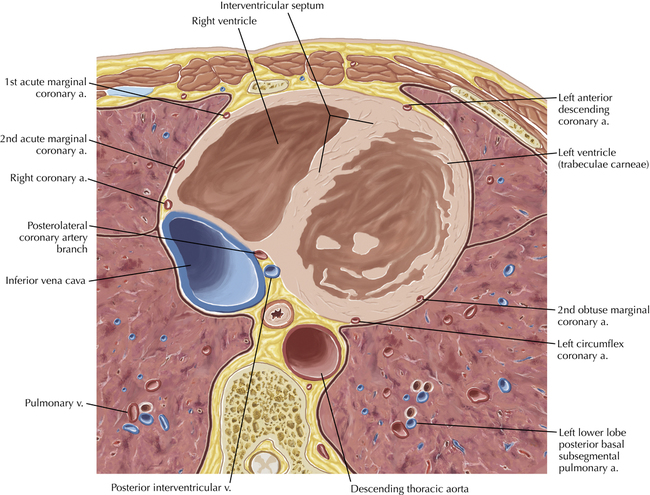
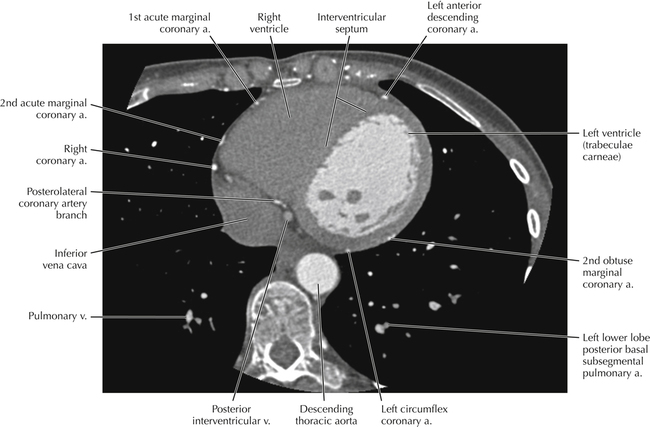
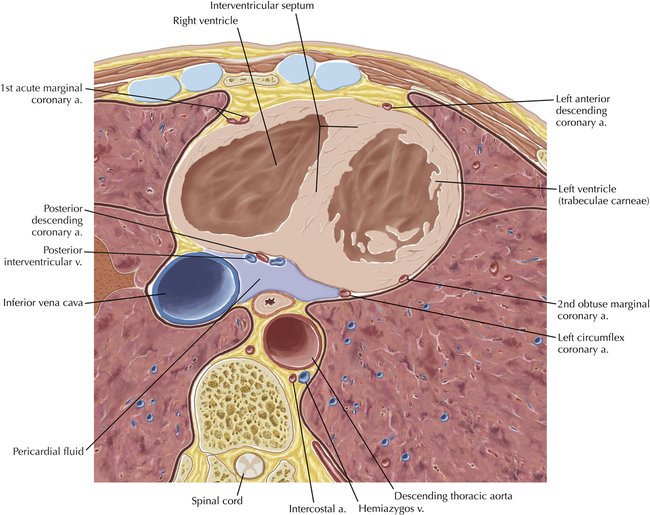
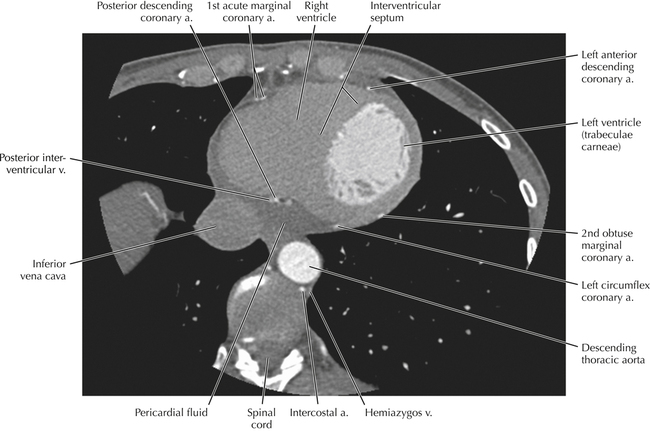
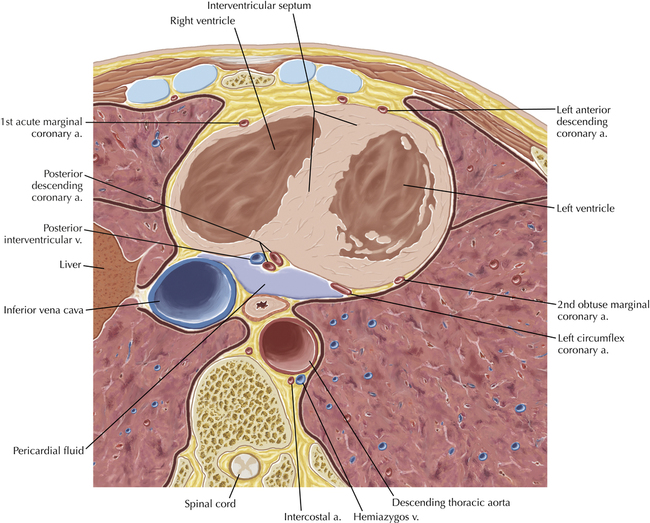
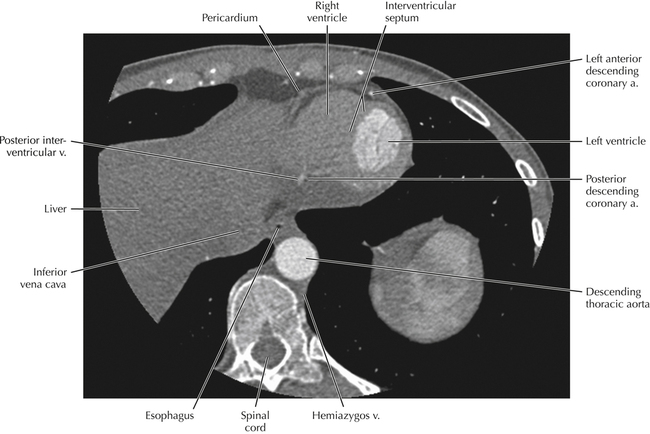
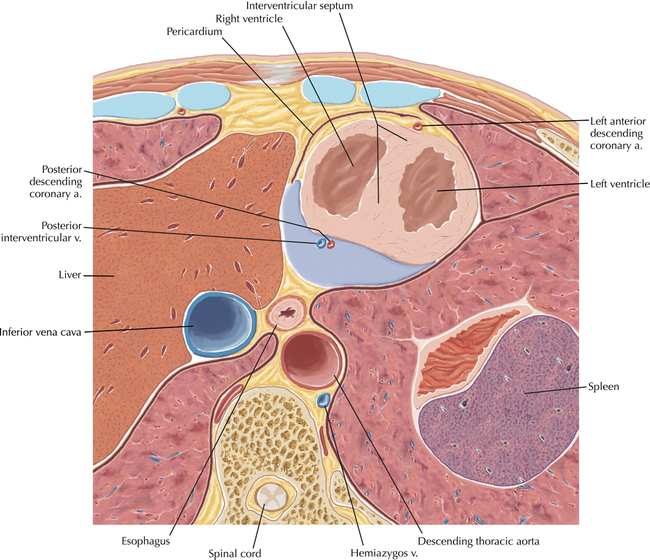
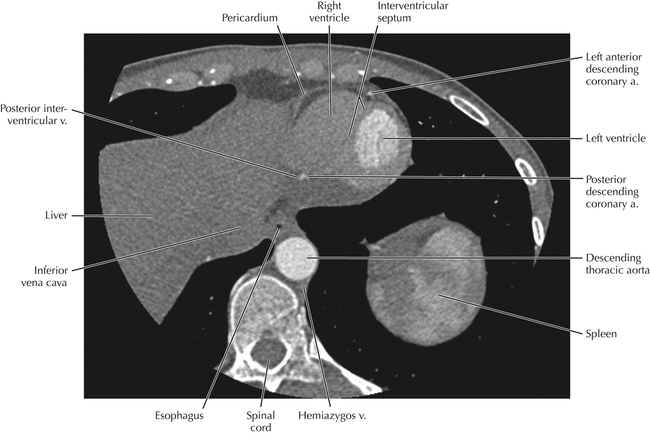
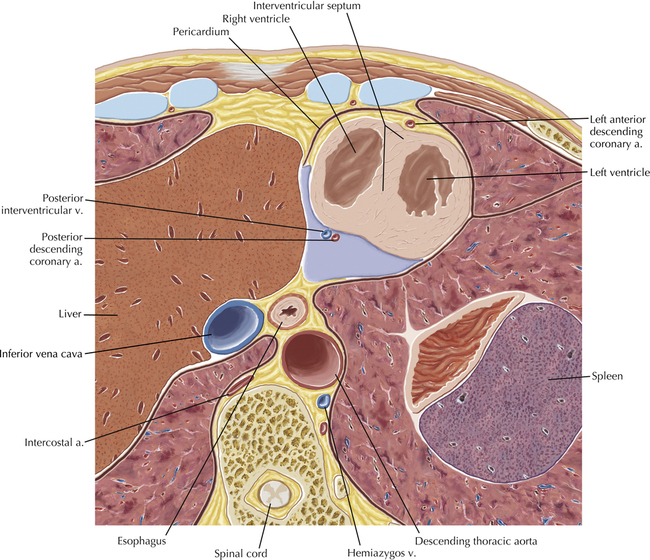
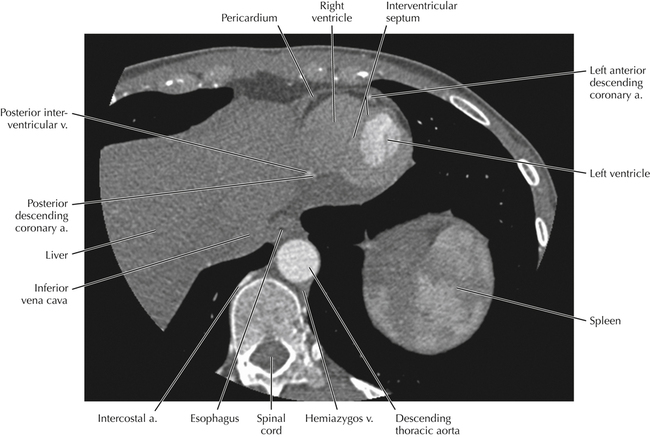
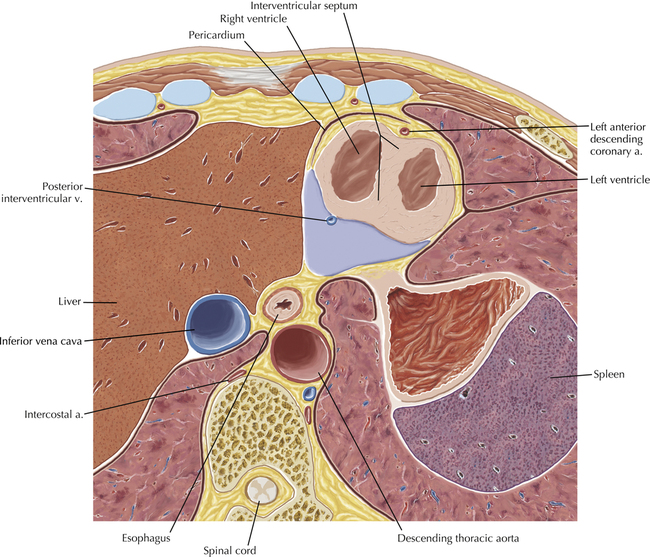
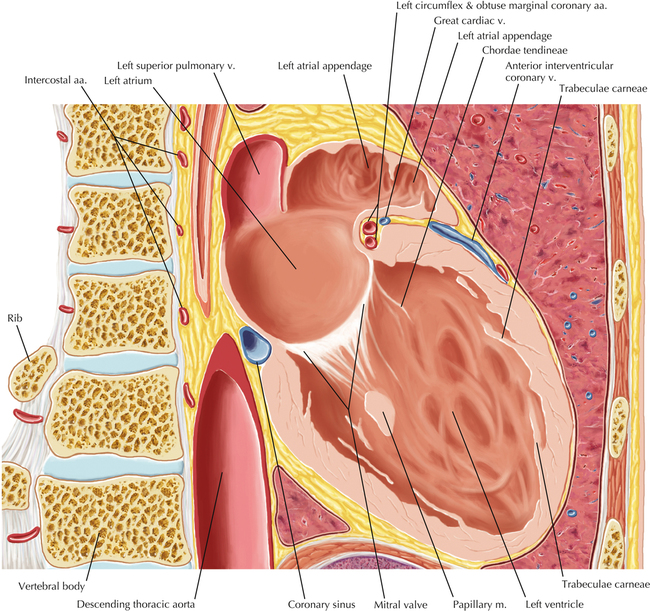
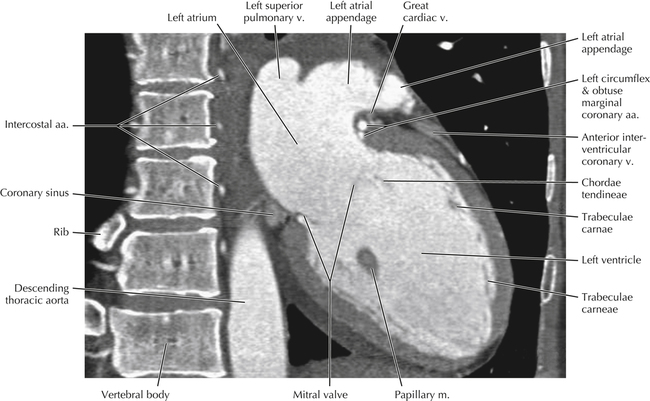
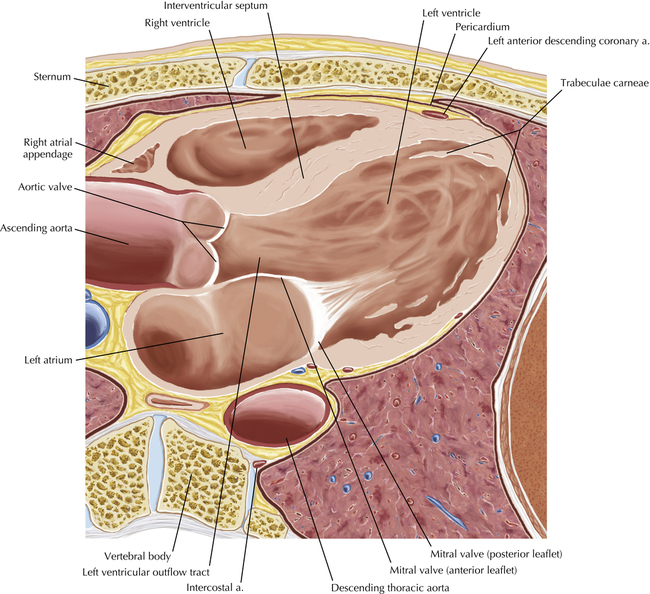
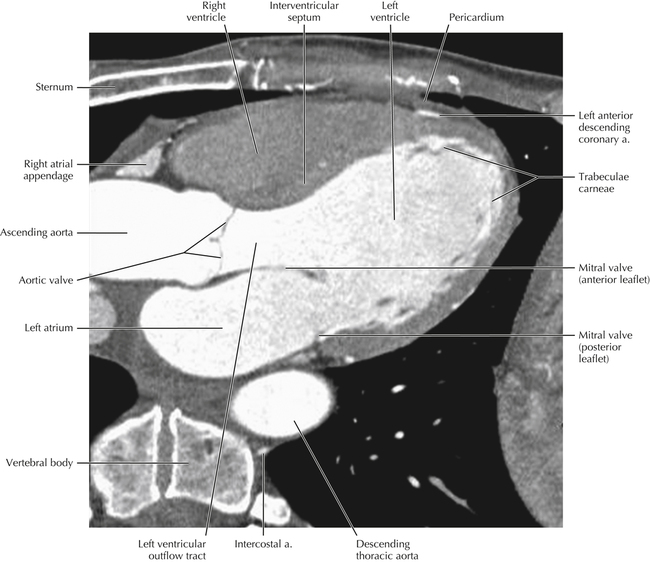
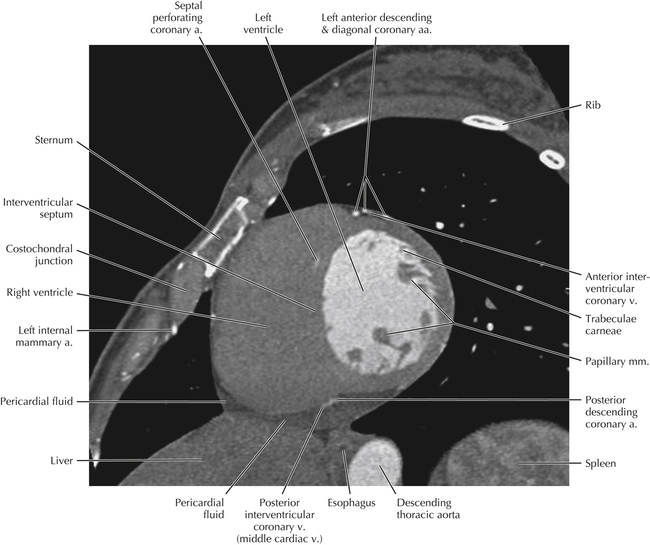
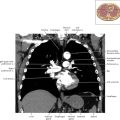
The left ventricular outflow tract is shown, demonstrating that the inflow (mitral valve) and outflow tracts of the left ventricle are closely related to one another. This contrasts with the right ventricle, in which the inflow portions (tricuspid valve) and outflow portions (right ventricular outflow tract, infundibulum, and pulmonic valve) are widely separated. Note that the left ventricular outflow tract is smooth, and that the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve is closely related to the aortic valvular apparatus (see Axials 22 to 25).