Ovarian Calcifications
Synonyms/Description
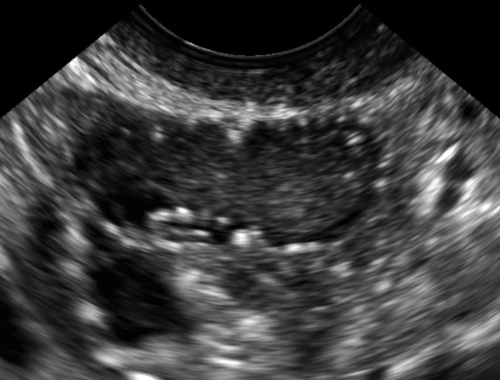
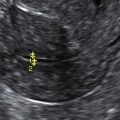
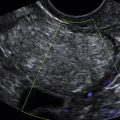
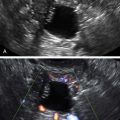
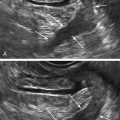
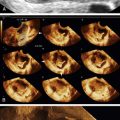
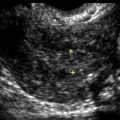
Echogenic foci or “bright spots” of the ovary
Most commonly thought to represent calcified corpora albicans
Etiology
In a study by Brown and colleagues, small ovarian calcifications (1 to 3 mm) were found in more than half of women examined with transvaginal ultrasound who were scheduled to undergo oophorectomy for unrelated diagnoses. The mean number of echogenic foci per ovary was 8.7 (range, 1 to 30). In 23 ovaries with sonographically detected echogenic foci, the location was peripheral in 17 ovaries, central in 1, and both central and peripheral in 5. Histology identified a potential cause of the echogenic foci in 17 of the 23 ovaries (74%). The most frequent sole histologic finding was a corpus albicans with hemosiderin (26% of cases). Inclusion cysts were also frequently seen along with a corpus albicans. The foci were not associated with either endometriosis or malignancy.
Brown and colleagues also studied larger calcifications on the ovary (greater than 5 mm; range, 5 to 13 mm) in patients with otherwise normal ovaries who did not undergo surgery and found that they were stable over time (mean, 3 years).
Ultrasound Findings
These are small echogenic foci, often without acoustic shadowing, that usually appear along the peripheral aspect of normal ovaries, especially in older women. If there is an associated mass in the ovary and the calcifications are part of the mass, they should be interpreted as such.
Differential Diagnosis
Ovaries that have small punctate echogenic foci without a mass are considered normal. A single larger calcification without a mass could conceivably represent a small dermoid or just a scar, but is also likely not to be clinically significant. If there is an associated mass, the differential diagnosis includes many different ovarian tumors either benign or malignant, and the possible diagnoses relate to the appearance and texture of the mass rather than the presence of small calcifications.
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Isolated punctate echogenic foci in an otherwise normal ovary are typically incidental findings. No treatment is recommended for this benign finding.