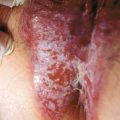
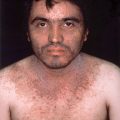
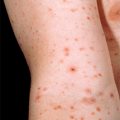
Chapter 25 Bullous viral eruptions
Table 25-1. Recommendations for Systemic Antiviral Treatment of Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infection*
| DRUG | RECOMMENDED DOSAGE | |
|---|---|---|
| Genital HSV | ||
| Primary/first episode | Acyclovir Valacyclovir Famciclovir |
400 mg PO tid or 200 mg PO 5 times per day for 7–10 days (mild to moderate) 5 mg/kg IV q8h for 5 days (severe) 1 g PO bid for 7–10 days 250 mg PO tid for 10 days |
| Recurrent episode (start at prodrome) | Acyclovir Valacyclovir Famciclovir |
400 mg PO tid or 200 mg PO 5 times per day for 5 days 500 mg PO bid for 3 days 1 g daily for 5 days 1 g PO bid for 1 day 125 mg PO bid for 5 days |
| Chronic suppression | Acyclovir Valacyclovir Famciclovir |
400 mg PO bid or 200 mg PO tid; adjust up or down according to response (>6 outbreaks per year) 500 mg PO qd (<10 outbreaks per year) 1 g PO qd (10 or more outbreaks per year) 250 mg PO bid (6 or more outbreaks per year) |
| Orofacial HSV | ||
| Primary/first episode | Acyclovir Valacyclovir Famciclovir |
15 mg/kg 5 times per day for 7 days 1 g bid for 7 days 500 mg bid for 7 days |
| Recurrent (start at prodrome) | Acyclovir Valacyclovir Famciclovir |
400 mg PO 5 times per day for 5 days 2 g PO bid for 1 day 1500 mg as single dose |
| Chronic suppression | Acyclovir Valacyclovir |
400 mg PO bid–tid 500 mg to 1 g PO qd |
| Orolabial or Genital HSV in Immunosuppressed Patients | ||
| Recurrent/suppressive | Acyclovir Valacyclovir Famciclovir |
400 mg PO 3 times per day or 5–10 mg/kg IV q8h 500 mg to 1 g PO bid 500 mg PO bid |
Bid, Twice daily; IV, intravenous; PO, by mouth; qd, daily; tid, three times a day.
* Dose should be adjusted in the presence of renal insufficiency.
Gupta R, Warren T, Wald A: Genital herpes, Lancet 370:2127–2137, 2007.
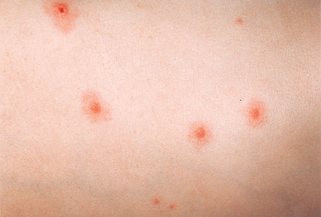
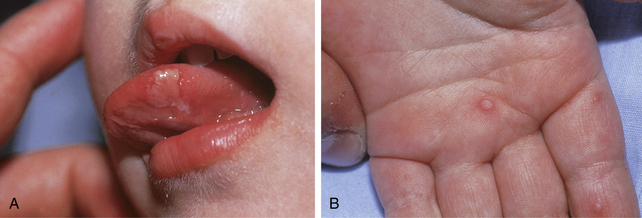
Figure 25-3. Varicella with skin lesions at all stages of development.
(Courtesy of Joseph G. Morelli, MD.)
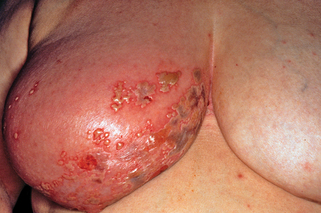
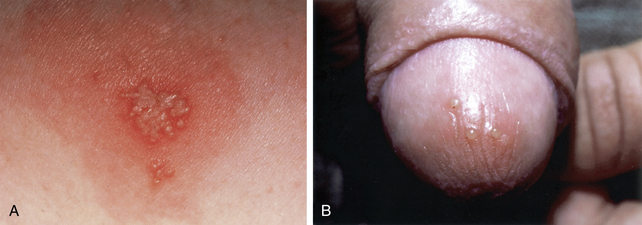
Figure 25-4. Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution.
(Courtesy of the Fitzsimons Army Medical Center teaching files.)
Whitley RJ: A 70-year-old woman with shingles: review of herpes zoster, JAMA 302:73–80, 2009.
Table 25-2. Recommendations for Systemic Antiviral Treatment of Varicella-Zoster Virus*
IV, Intravenous; PO, by mouth; tid, three times a day.
* Dose should be adjusted in the presence of renal insufficiency.
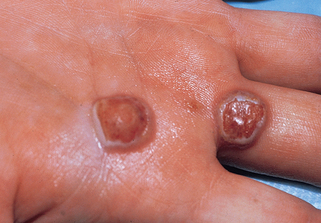
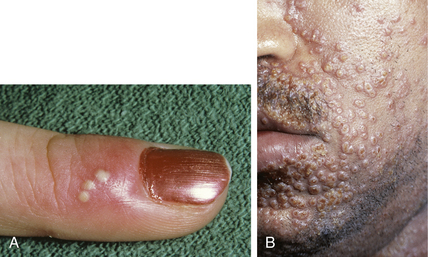
Figure 25-6. Classic lesions of orf demonstrating a central ulceration and necrotic vesiculobullous edge.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Orf virus infection in humans—New York, Illinois, California, and Tennessee, 2004–2005, MMWR 55(3):65–68, 2006.