15 Brainstem Summary
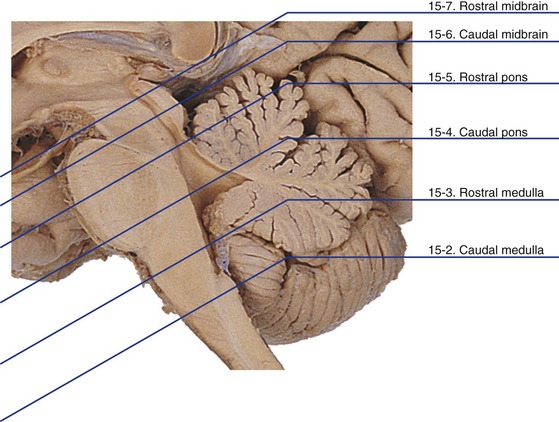
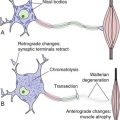
The previous four chapters presented various aspects of the brainstem and its cranial nerves bit by bit. This chapter summarizes the major points, using as a vehicle the same series of drawings of brainstem sections used in Chapter 11, but with additional structures and brief descriptions added. A few of the structures (e.g., substantia nigra) are dealt with more fully in later chapters.
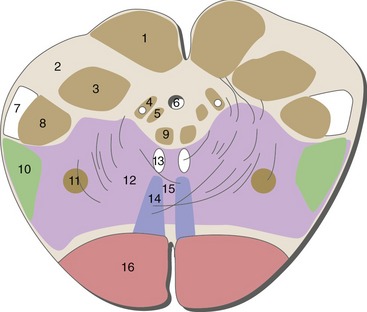
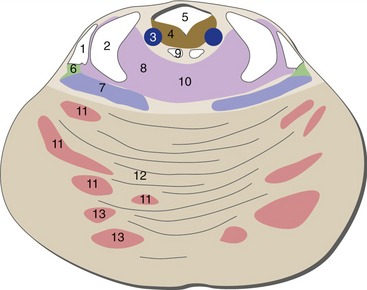
Caudal Medulla
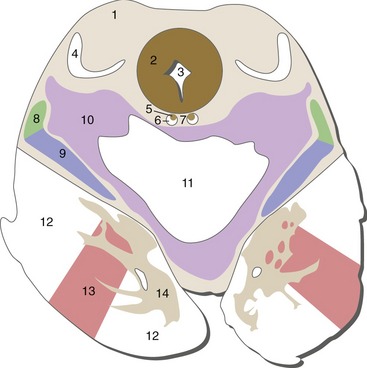
Rostral Medulla
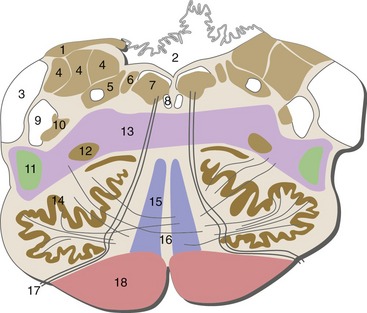
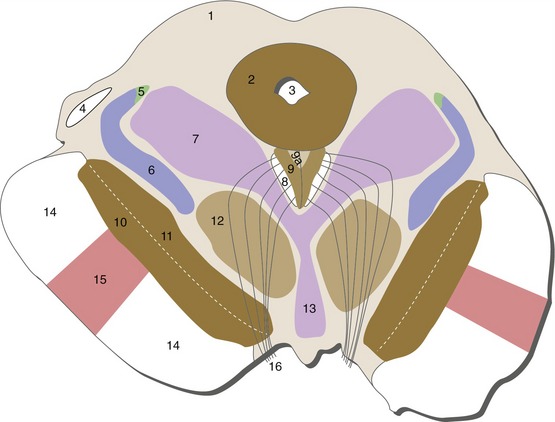
Caudal Pons
Important brainstem structures between Figures 15-4 and 15-3, near the pontomedullary junction: cochlear nuclei (just beginning in Fig. 15-3), the second-order neurons of the auditory pathway; inferior cerebellar peduncle enters the cerebellum; attachment points of the abducens, facial, and vestibulocochlear nerves.
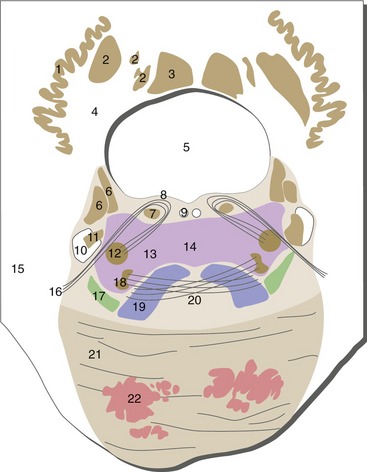
Rostral Pons
Important brainstem structures between Figures 15-5 and 15-4: trigeminal main sensory nucleus (midpons), the second-order neurons for large-diameter trigeminal afferents; trigeminal motor nucleus (midpons), the lower motor neurons for muscles of mastication.
Caudal Midbrain
Important brainstem structures between Figures 15-6 and 15-5: Trochlear nerves decussate and exit from the dorsal surface of the brainstem (pons-midbrain junction).