1 Bone
Structure of bone
Compact bone
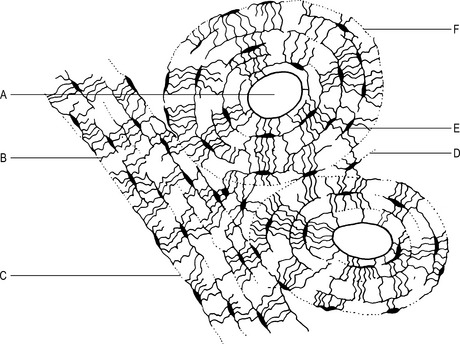
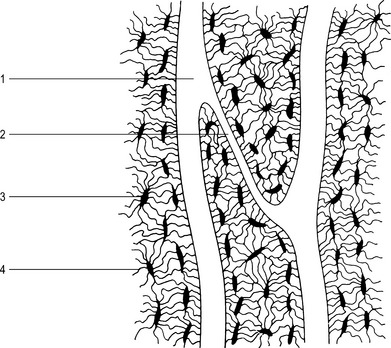
This type of bone is found mainly in the shafts of long bones where a strong, tubular structure is required. It consists of a number of cylindrical structures called haversian systems (Figs 1.1 and 1.2). Each system comprises:
Elsewhere the red bone marrow becomes inactive yellow marrow.
Ossification
Ossification is the formation of bone from connective tissue and requires:
Growth of the bone is influenced by the following hormones:
Intracartilaginous ossification
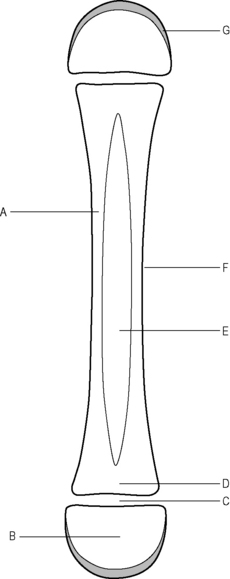
The process by which bone formation takes place, e.g. in a long bone (Fig. 1.3).
Primary centre of ossification
Osteoblasts ‘build the bone’ by laying down fibres, matrix and calcium.
Osteoclasts are responsible for forming the medullary canals and sinuses within the bone.
Types of bones
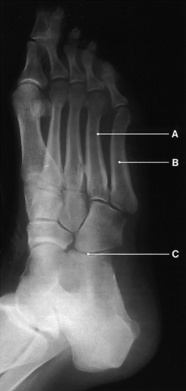
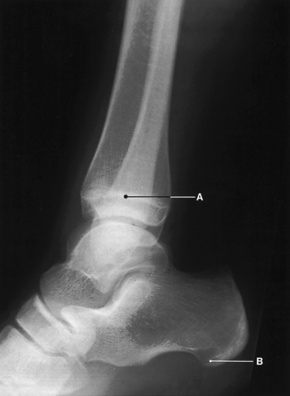
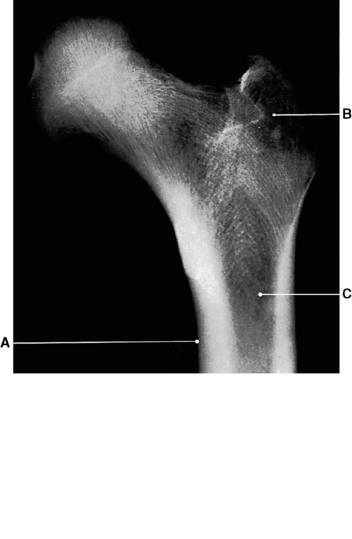
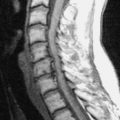
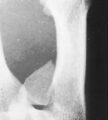
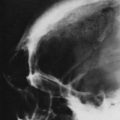
‘Normal’ radiographic bone appearances (Figs 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6)
Terminology
 an adjective derived from the name of the bone
an adjective derived from the name of the bone
 an adjective derived from the bone with which they articulate
an adjective derived from the bone with which they articulate
 an adjective derived from part of the bone with which they articulate
an adjective derived from part of the bone with which they articulate
 a descriptive term – see lists below (elevations, projections, holes and depressions).
a descriptive term – see lists below (elevations, projections, holes and depressions).