Chapter 39 Biofeedback
OVERVIEW.
Biofeedback is a treatment that uses a device that provides visual and auditory representations of physiologic events that are not normally perceived by the individual. With training, biofeedback permits the individual to voluntarily control responses. An example is the use of EMG signals to help patients initiate or control motor activity (e.g., activate muscle contraction or reduce muscle tension).1
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
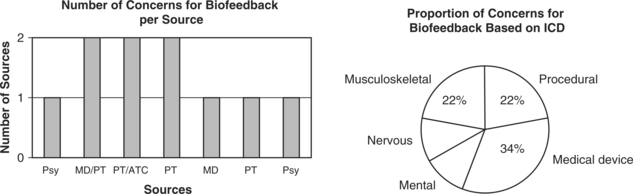
F00-F99 MENTAL AND BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS
G00-G99 DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
M00-M99 DISEASES OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
1 Bottomley JM. Quick reference dictionary for physical therapy. Thorofare (NJ): Slack, 2000.
2 Green JA, Shellenberger R. Biofeedback therapy. In: Jonas WB, Levin JE, editors. Essentials of complementary and alternative medicine. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999.
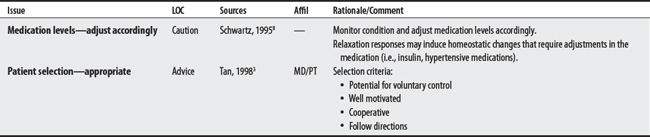
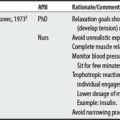
3 Tan JC. Practical manual of physical medicine and rehabilitation: diagnostic, therapeutic, and basic problems. St. Louis: Mosby, 1998.
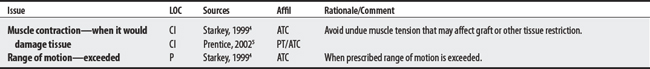
4 Starkey C. Therapeutic modalities. Philadelphia: FA Davis, 1999.
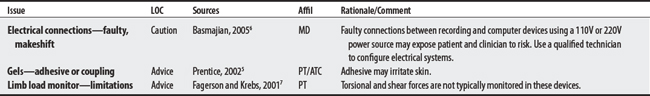
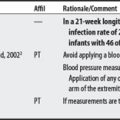
5 Prentice WE. Therapeutic modalities for physical therapists, ed 2. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002.
6 Basmajian JV. Biofeedback in physical medicine and rehabilitation. Delisa JA, editor. Physical medicine and rehabilitation: principles and practices, ed 4, vol 1. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005.
7 Fagerson TL, Krebs DE. Biofeedback. In O’Sullivan SB, Schmitz TJ, editors: Physical rehabilitation: assessment and treatment, ed 4, Philadelphia: FA Davis, 2001.
8 Schwartz MS. Biofeedback: a practitioner’s guide, ed 2. New York: Guilford, 1995.