Biochemistry of the skin
Keratins
Keratins are high-molecular-weight polypeptide chains produced by keratinocytes (Fig. 1). They are the major constituent of the stratum corneum, hair and nails. The stratum corneum comprises 65% keratin (along with 10% soluble protein, 10% amino acid, 10% lipid and 5% cell membrane).
Melanins
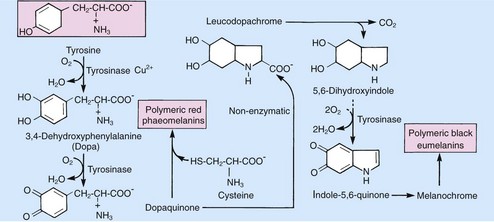
Melanin is produced from tyrosine (Fig. 2) in melanocytes and takes two forms:
 eumelanin, which is more common and gives a brown–black colour
eumelanin, which is more common and gives a brown–black colour
 phaeomelanin, which is less common and produces a yellow or red colour.
phaeomelanin, which is less common and produces a yellow or red colour.
Collagens
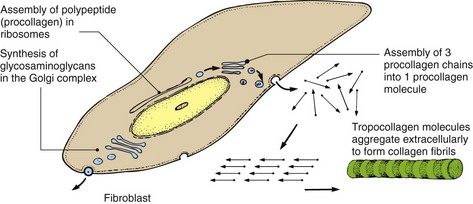
Collagens are synthesized by fibroblasts (Fig. 3) and are the major structural proteins of the dermis, forming 70–80% of its dry weight. The main amino acids in collagens are glycine, proline and hydroxyproline. Collagens are broken down, e.g. in wound healing, by collagenases, of which the matrix metalloproteinases are important. There are over 22 types of collagen; at least five are found in skin:
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
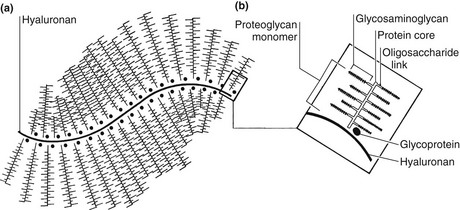
GAGs often exist as high-molecular-weight polymers with a protein core. These structures are known as proteoglycans (Fig. 4).
Skin surface secretions
The skin surface has a slightly acidic pH (between 6 and 7). Sebum (Table 1), sweat and the horny layer (including intercellular lipid) contribute to the surface conditions, which generally discourage microbial proliferation.
| Component | Sebum (%) | Epidermal lipid (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Glyceride/free fatty acid | 58 | 65 |
| Wax esters | 26 | 0 |
| Squalene | 12 | 0 |
| Cholesterol esters | 3 | 15 |
| Cholesterol | 1 | 20 |
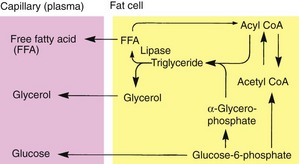
Subcutaneous fat
Triglyceride is synthesized from α-glycerophosphate and acyl coenzyme A (CoA). Triglyceride is broken down by lipase to give free fatty acid (FFA) – an energy source – and glycerol (Fig. 5).
Hormones and the skin
The skin is the site of production of one hormone (vitamin D), but it is often a target organ for other hormones and is frequently affected in endocrine diseases (Table 2).
| Hormone | Site of production | Effects |
|---|---|---|
|
Vitamin D |
Corticosteroids
Produce vasoconstriction
Reduce mitosis by basal cells
Generate anti-inflammatory effects on leucocytes
Inhibit phospholipase A
Gonads
Stimulate terminal hair growth and increased output of sebum
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Ovaries
Stimulates differentiation Alters calcium metabolism
Web resource
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22247/
Biochemistry
 Keratins are made up of polypeptide helical coils linked by covalent bonds. They form the horny layer, nails and hair.
Keratins are made up of polypeptide helical coils linked by covalent bonds. They form the horny layer, nails and hair.
 Melanin is a complex polymer synthesized from tyrosine. There are eu- and phaeo- types. Melanins absorb free radicals and energy including UV.
Melanin is a complex polymer synthesized from tyrosine. There are eu- and phaeo- types. Melanins absorb free radicals and energy including UV.
 Collagens are polypeptide polymers that constitute 75% of the dry weight of the dermis. They are synthesized by fibroblasts.
Collagens are polypeptide polymers that constitute 75% of the dry weight of the dermis. They are synthesized by fibroblasts.
 Glycosaminoglycans make up the ground substance of skin. They provide viscosity and hydration, and can exist as high-molecular-weight polymers.
Glycosaminoglycans make up the ground substance of skin. They provide viscosity and hydration, and can exist as high-molecular-weight polymers.
 Vitamin D: cutaneous UV activation produces the active form of vitamin D3 from the inactive 7-dehydrocholesterol via the precursor previtamin D3.
Vitamin D: cutaneous UV activation produces the active form of vitamin D3 from the inactive 7-dehydrocholesterol via the precursor previtamin D3.
 Androgen receptors in hair/sebaceous glands make these structures sensitive to the androgen surge of puberty.
Androgen receptors in hair/sebaceous glands make these structures sensitive to the androgen surge of puberty.