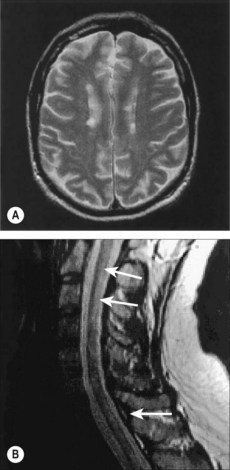
36 Bilateral spastic paralysis (spastic paraplegia)
Salient features
History
• Ask about onset, duration and course of symptoms
• Back pain: whether localized
• Numbness and parasthesia particularly below the level of lesion
• Weakness: whether gradual or sudden
• Sphincter control and bladder sensation
• Functional status: wheelchair transfers, walking aids, orthotic shoes and whether house has been modified for the patient’s disability
• Take a family history (hereditary spastic paraplegia)
• Take a history of birth anoxia (cerebral palsy)
• History of urinary infections, pressure sores and deep venous thromboses.
Examination
• Increased tone in both lower limbs
• Weakness in both lower limbs
• Tell the examiner that you would like to do the following:
• Try to localize the level of lesion using the following:
Questions
Advanced-level questions
What do you know about transverse myelitic syndrome?
| Total cord transection | Incomplete cord compression | |
|---|---|---|
| Paraplegia in flexion | + | + |
| Paralysis | Symmetrical | Asymmetrical |
| Flexor–withdrawal reflex | + without return (withdrawal phase only) | Associated with return to original position |
| Other | Vasomotor and sphincter changes | Variable area of anaesthesia that is not consistent with motor loss |