Barcia, SM, et al. Pulmonary interstitial emphysema in adults: a clinicopathologic study of 53 lung explants. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014; 38(3):339–345.
Frutos-Vivar, F, et al. [Prognosis for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in mechanically ventilated patients.]. Med Intensiva. 2006; 30(2):52–61.
Anzueto, A, et al. Incidence, risk factors and outcome of barotrauma in mechanically ventilated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2004; 30(4):612–619.
Bejvan, SM, et al. Pneumomediastinum: old signs and new signs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 166(5):1041–1048.
Satoh, K, et al. CT appearance of interstitial pulmonary emphysema. J Thorac Imaging. 1996; 11(2):153–154.
Tocino, I, et al. Barotrauma. Radiol Clin North Am. 1996; 34(1):59–81.
Gammon, RB, et al. Clinical risk factors for pulmonary barotrauma: a multivariate analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995; 152(4 Pt 1):1235–1240.
Cho, KC, et al. Extraluminal air. Diagnosis and significance. Radiol Clin North Am. 1994; 32(5):829–844.
Levine, MS, et al. Diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum on supine abdominal radiographs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991; 156(4):731–735.
 Extraluminal ectopic gas in subcutaneous soft tissues and muscles, lung interstitium, retroperitoneum, intraperitoneal spaces, and bowel wall
Extraluminal ectopic gas in subcutaneous soft tissues and muscles, lung interstitium, retroperitoneum, intraperitoneal spaces, and bowel wall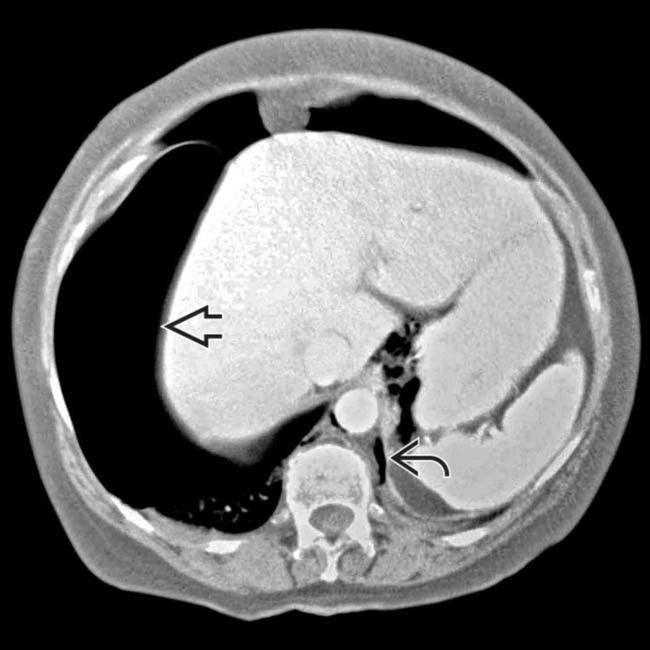
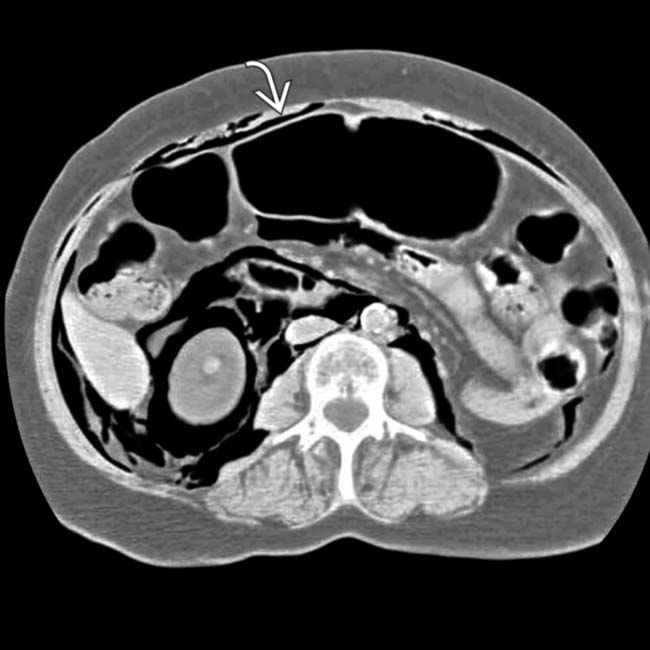
 on the right side and a smaller pneumothorax on the left. Gas dissects under pressure along the peridiaphragmatic fat
on the right side and a smaller pneumothorax on the left. Gas dissects under pressure along the peridiaphragmatic fat 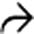 .
.
 to outline bowel loops. There was no intraabdominal injury.
to outline bowel loops. There was no intraabdominal injury.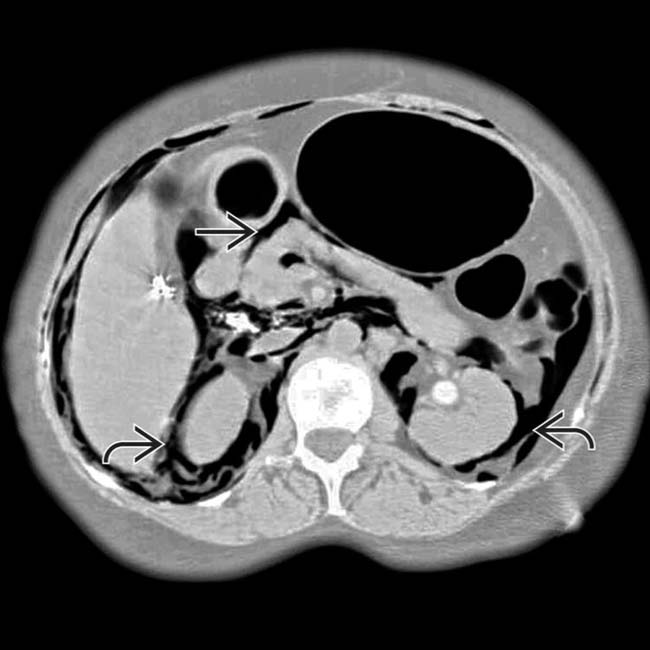
 and mesentery
and mesentery  .
.
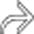 . In some cases, gas can dissect into the bowel wall, simulating pneumatosis from bowel ischemia.
. In some cases, gas can dissect into the bowel wall, simulating pneumatosis from bowel ischemia.




























