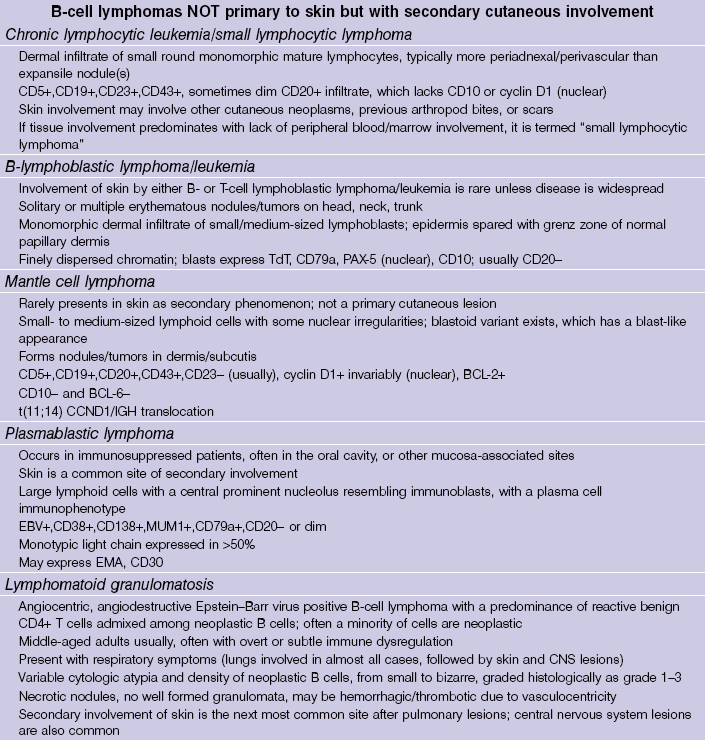
B-cell lymphoma and lymphocytic leukemia
Cutaneous B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia
Table 25-1
WHO classification of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma
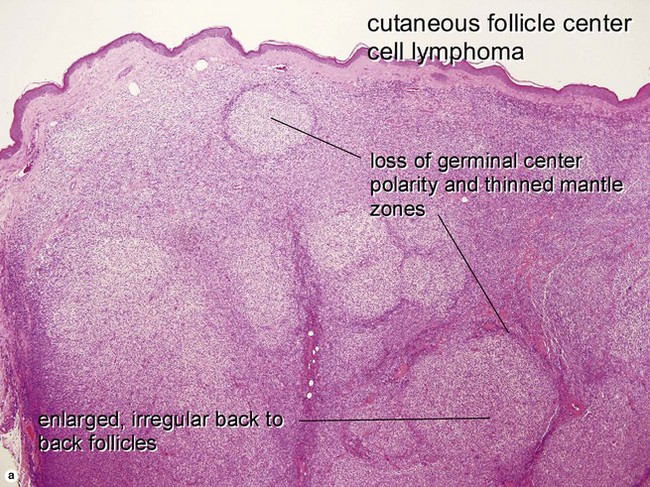
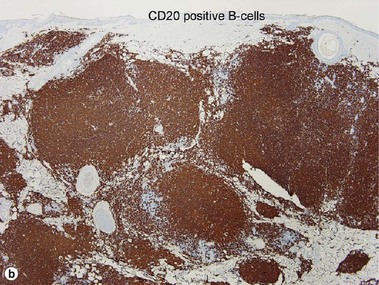
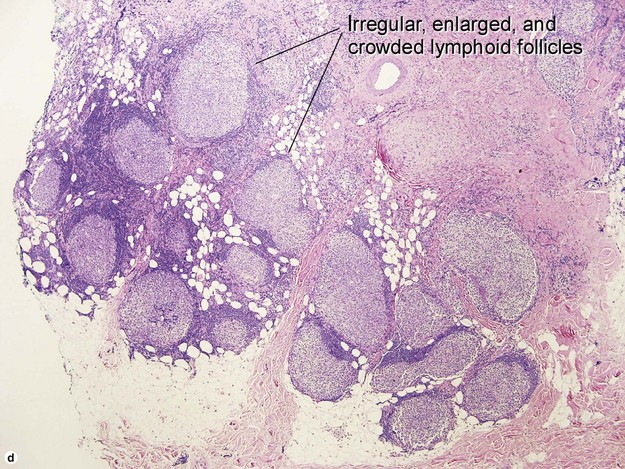
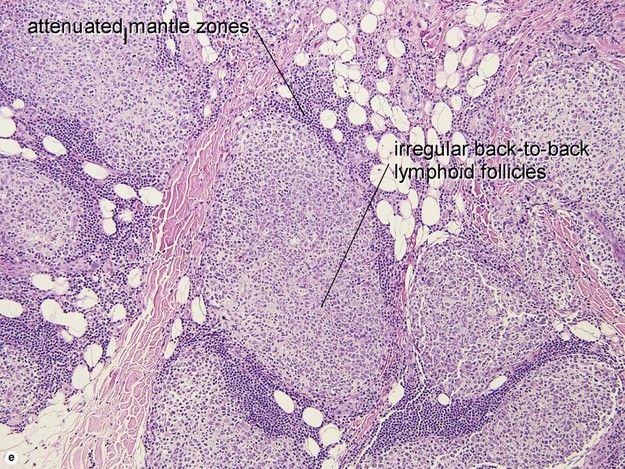
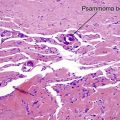
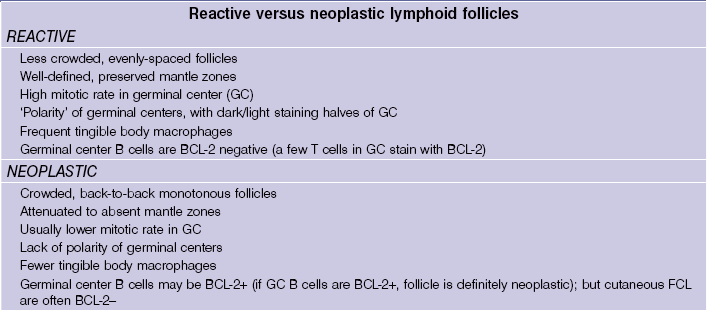
Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma
• Most common anatomic site is head/neck (often scalp), followed by trunk
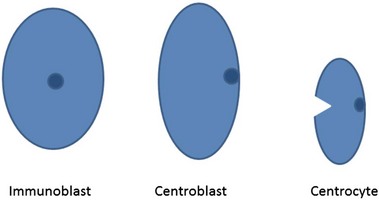
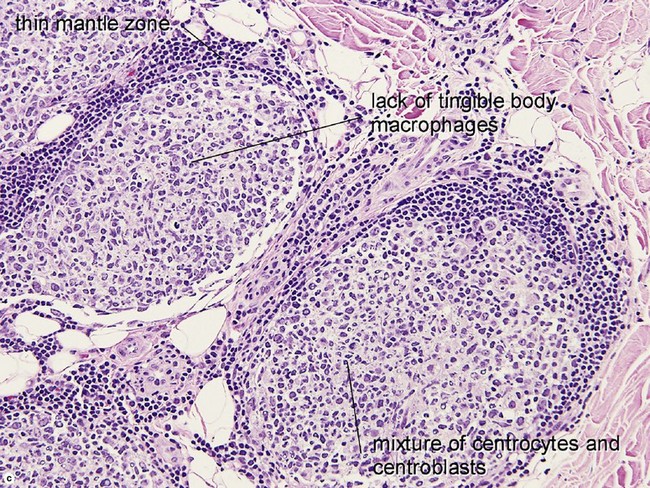
• Composed of neoplastic follicle center cells; i.e. centrocytes and centroblasts in various proportions
• Centrocytes are small with cleaved nuclei
• Centroblasts are larger, with non-cleaved nuclei and 1–3 nucleoli attached to inside of nuclear membrane
• If diffuse growth pattern with sheets of centroblasts, is classified as diffuse large B-cell rather than follicular lymphoma
• Otherwise, numbers of centrocytes and centroblasts do not matter as primary FCL is NOT graded
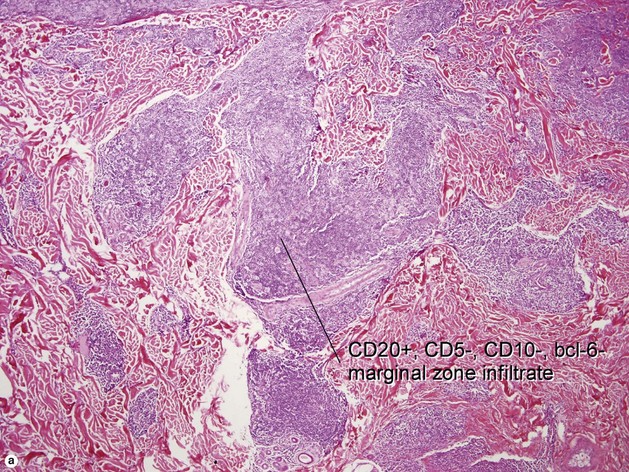
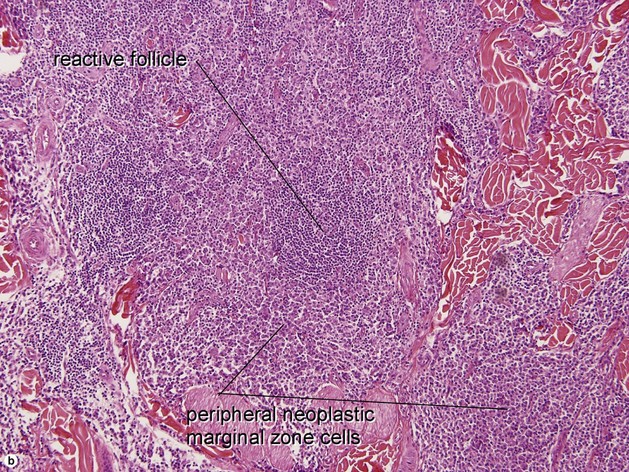
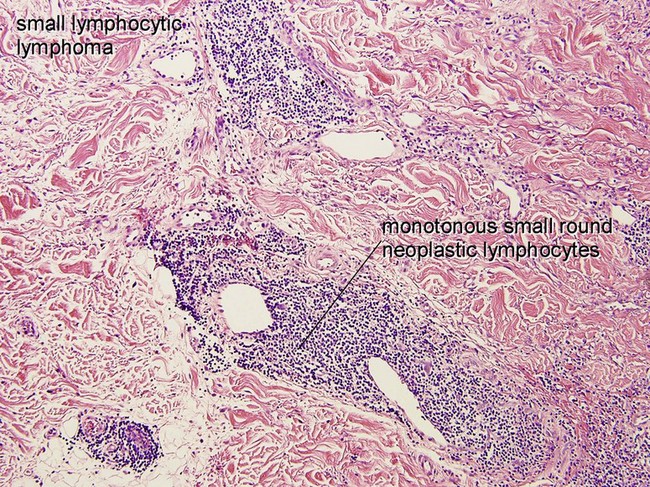
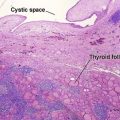
Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma (Cutaneous MALT-type lymphoma)
• Includes entities previously classified as:
• Primary cutaneous plasmacytoma without underlying myeloma
• Primary cutaneous immunocytoma
• Erythematous to purple nodules/tumors most often on trunk and extremities, often single or few lesions
• Proliferation of small marginal zone centrocyte-like B cells, usually surrounding benign reactive germinal centers
• Immunophenotype: CD20+, CD79a+, BCL-2+, CD5−, CD10−, BCL-6−
• Approximately 70% show evidence of monoclonal light chain restriction
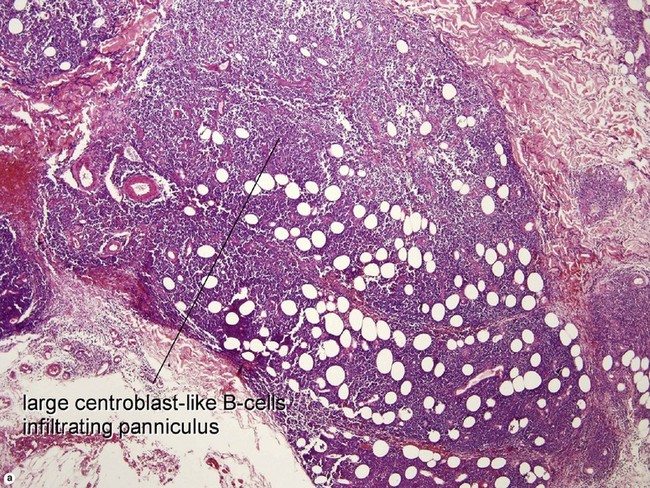
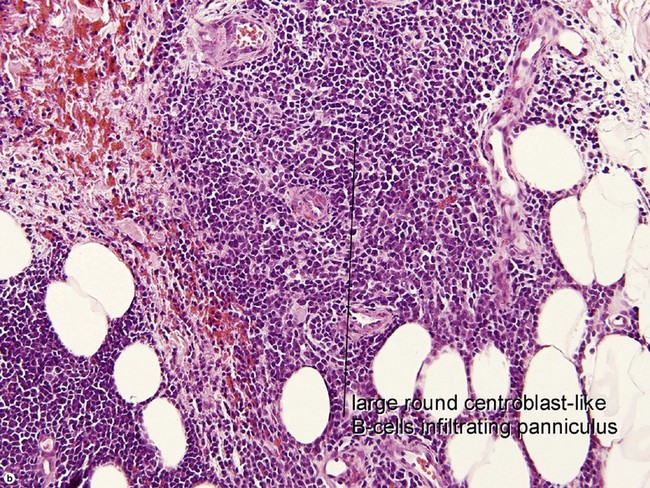
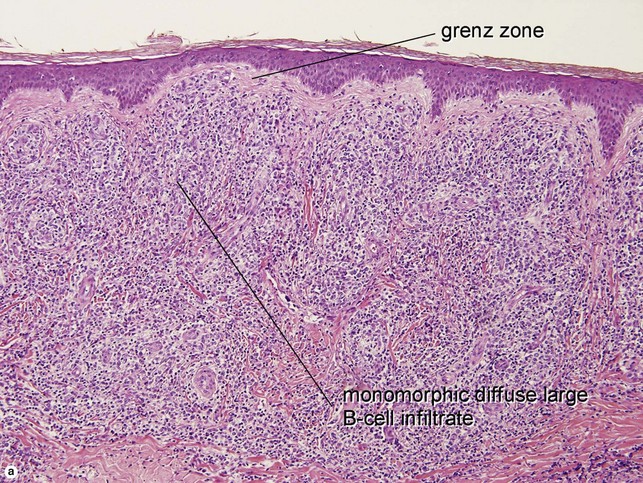
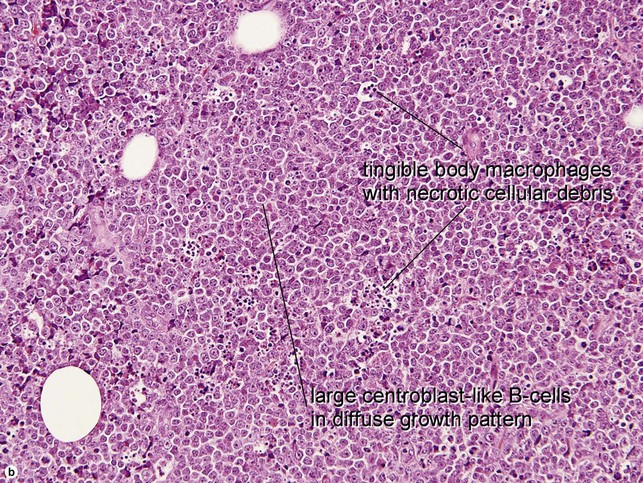
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type
• 80% of cases occur in patients ≥70 years
• Diffuse proliferation of monotonous large transformed B cells
• Activated B-cell immunophenotype, with strong BCL-2+ cells which are MUM-1/IRF4+, CD19+, CD20+, CD79a+, BCL-6 variable
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, other
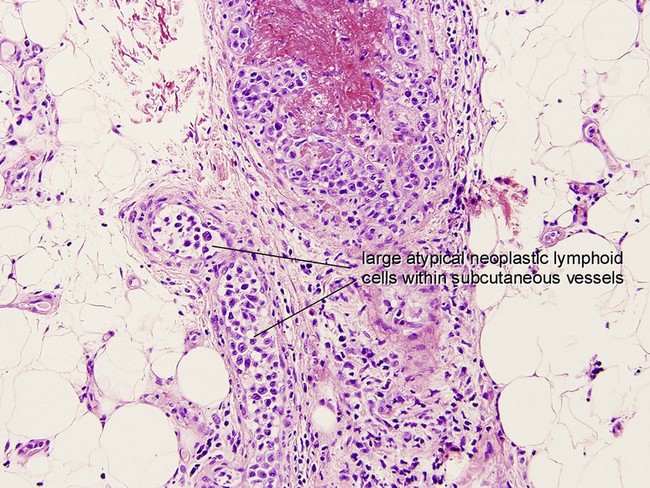
• Includes intravascular/angiotropic B-cell lymphoma and other non-leg type diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with only skin involvement
Adapted from World Health Organisation Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th edition, 2008.
Table 25-2
WHO Classification of B-cell Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues



Unified system accepted globally by hematopathologists, dermatopathologists, oncologists, other clinicians Formally incorporates previous 2004 WHO-EORTC classification scheme entities
Baldassano, MF, Bailey, EM, Ferry, JA, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia and cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma: comparison of morphologic and immunophenotypic features. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999; 23(1):88–96.
Bradford, PT, Devessa, SS, Anderson, WF, et al. Cutaneous lymphoma incidence patterns in the United States: a population based study of 3884 cases. Blood. 2009; 113:5064–5073.
Caro, W, Helwig, E. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia. Cancer. 1969; 24:487–502.
De Laval, L, Harris, NL, Longtine, J, et al. Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas of follicular and marginal zone types. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001; 25(6):732–741.
Demierre, M, Kerl, H, Willemze, R. Primary cutaneous B cell lymphomas: a practical approach. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2003; 17:1333–1350.
Kiyohara, T, Kumakiri, M, Kobayashi, H, et al. Cutaneous marginal zone B cell lymphoma: a case accompanied by massive plasmacytoid cells. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 48:S82–S85.
LeBoit, PE, McNutt, NS, Reed, JA, et al. Primary cutaneous immunocytoma: a B cell lymphoma that can easily be mistaken for cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994; 18:969–978.
Ritter, J, Adesokan, P, Fitzgibbon, J, et al. Paraffin section immunohistochemistry as an adjunct to morphologic analysis in the diagnosis of cutaneous lymphoid infiltrates. J Cutan Pathol. 1994; 21:481–493.
Roglin, J, Boer, A. Skin manifestations of intravascular lymphoma mimic inflammatory diseases of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 157:16–25.
Sander, C, Kaudewitz, P, Schirren, C, et al. Immunocytoma and marginal zone B cell lymphoma (MALT lymphoma) presenting in skin-different entities or a spectrum of disease? J Cutan Pathol. 1996; 23:59a.
Sokol, L, Naghashpour, M, Glass, F. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: recent advances in diagnosis and management. Cancer Control. 2012; 19(3):236–244.
Swerdlow, SH, Campo, E, Harris, NL, et al. World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: World Health Organization; 2008.
Van Maldegem, F, van Dijk, R, Wormhoudt, TA, et al. The majority of cutaneous marginal zone B cell lymphomas express class-switched immunoglobulins and develop in a T-helper type 2 inflammatory environment. Blood. 2008; 112:3355–3361.
Willemze, R, Jaffe, ES, Burg, G, et al. WHO-EORTC Classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005; 105:3768–3785.