Sausage-like enlargement of pancreas (with smooth contour) and loss of normal pancreatic lobulations
 MRCP: Multiple discontiguous MPD/bile duct strictures which resolve after secretin (duct penetrating sign)
MRCP: Multiple discontiguous MPD/bile duct strictures which resolve after secretin (duct penetrating sign)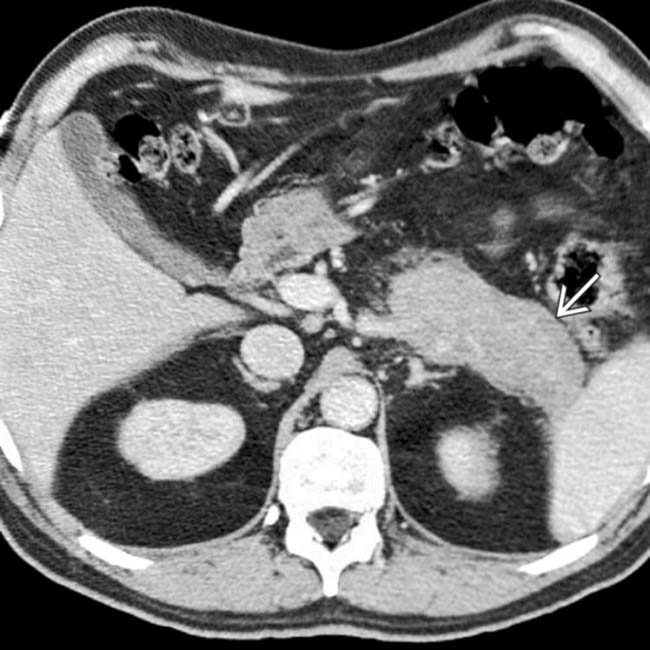
 around the pancreas, with relatively little spread into adjacent tissues, compatible with autoimmune pancreatitis. All symptoms and signs resolved with steroid therapy.
around the pancreas, with relatively little spread into adjacent tissues, compatible with autoimmune pancreatitis. All symptoms and signs resolved with steroid therapy.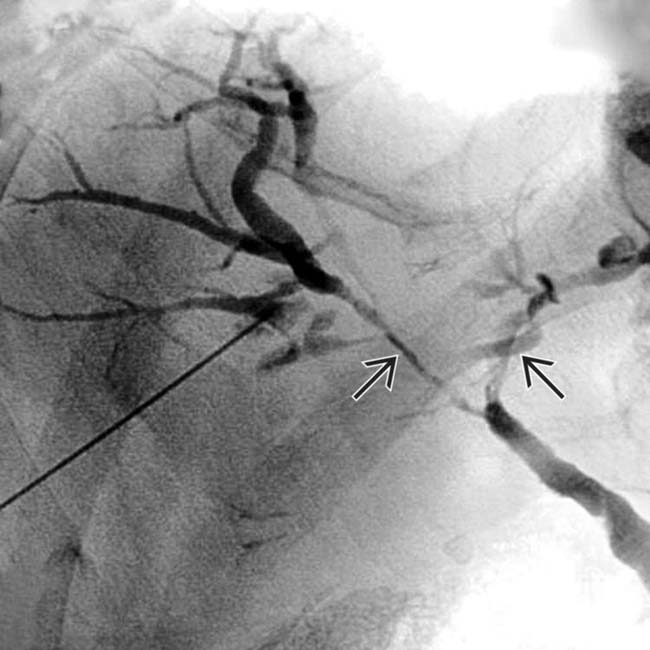
 indistinguishable from those of primary sclerosing cholangitis.
indistinguishable from those of primary sclerosing cholangitis.
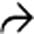 around its margin.
around its margin.
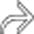 around the enlarged pancreatic margin. Note the presence of biliary dilatation
around the enlarged pancreatic margin. Note the presence of biliary dilatation  in this patient with a history of biliary strictures, often associated with autoimmune pancreatitis.
in this patient with a history of biliary strictures, often associated with autoimmune pancreatitis.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• Diffuse form
 Diffuse sausage-like enlargement of pancreas (with smooth contour) and loss of pancreatic lobulations
Diffuse sausage-like enlargement of pancreas (with smooth contour) and loss of pancreatic lobulations
 Diffuse sausage-like enlargement of pancreas (with smooth contour) and loss of pancreatic lobulations
Diffuse sausage-like enlargement of pancreas (with smooth contour) and loss of pancreatic lobulationsPATHOLOGY
General Features
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
• Most common signs/symptoms
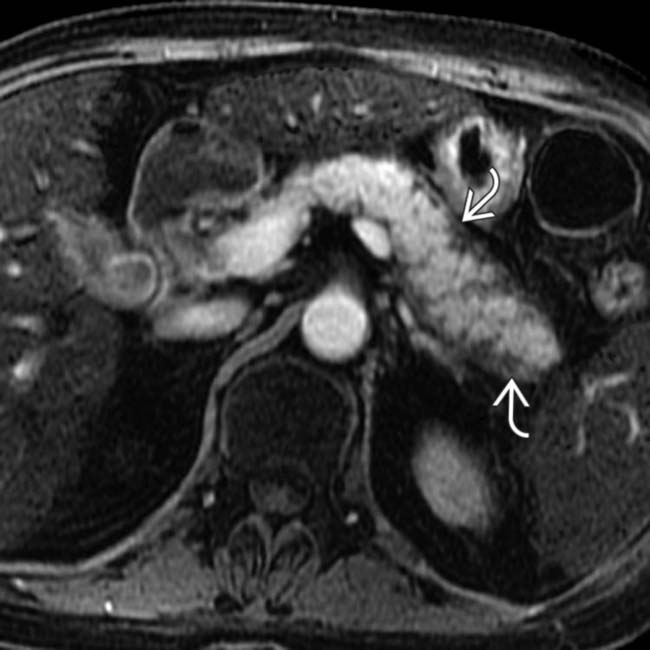
 around the margin of the pancreas.
around the margin of the pancreas.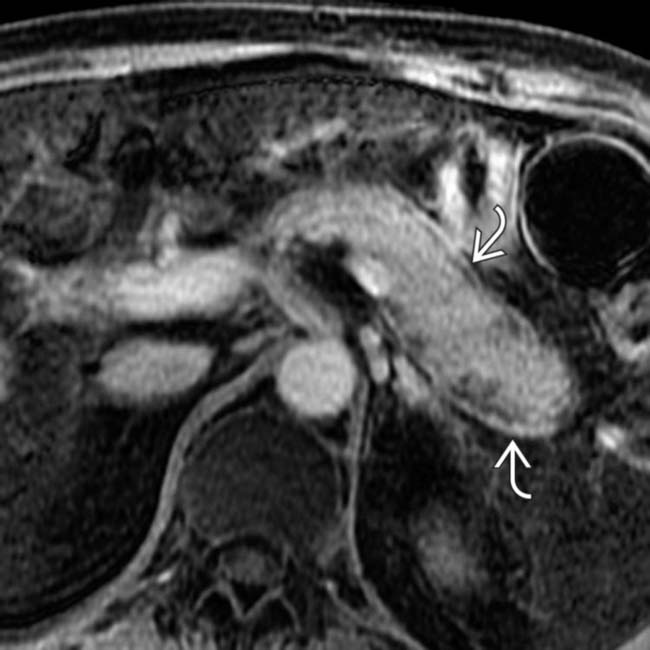
 now shows avid delayed enhancement, a characteristic feature of autoimmune pancreatitis.
now shows avid delayed enhancement, a characteristic feature of autoimmune pancreatitis.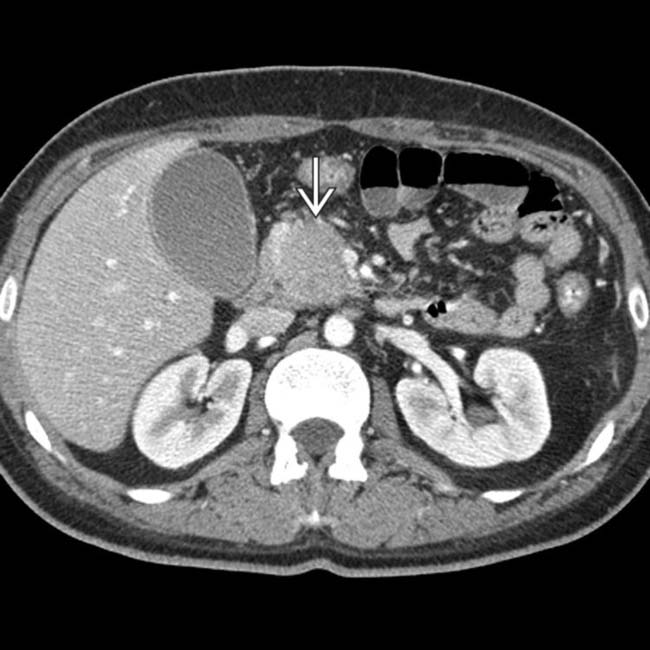
 .
.
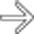
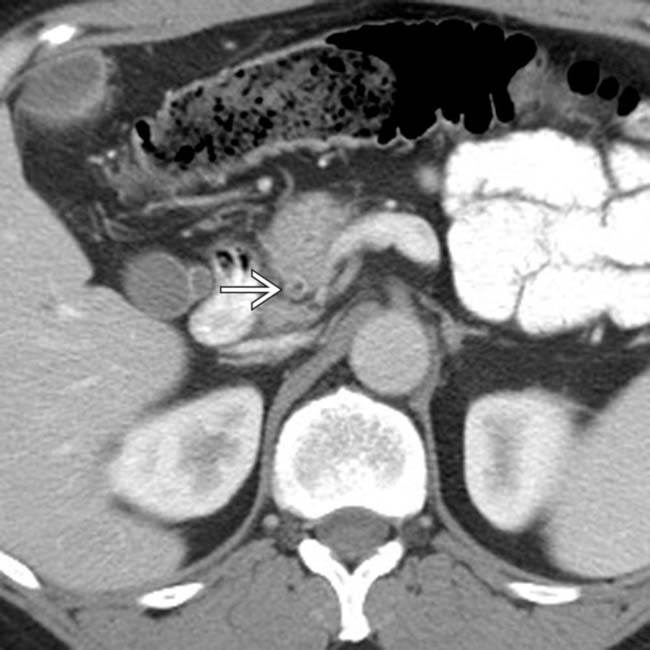
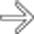
 in the pancreatic head, a tapered stricture of the common bile duct
in the pancreatic head, a tapered stricture of the common bile duct  , and a normal pancreatic duct
, and a normal pancreatic duct  . Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of the pancreatic head mass revealed autoimmune pancreatitis. The lack of dilatation of the pancreatic duct was an important clue to the diagnosis.
. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of the pancreatic head mass revealed autoimmune pancreatitis. The lack of dilatation of the pancreatic duct was an important clue to the diagnosis.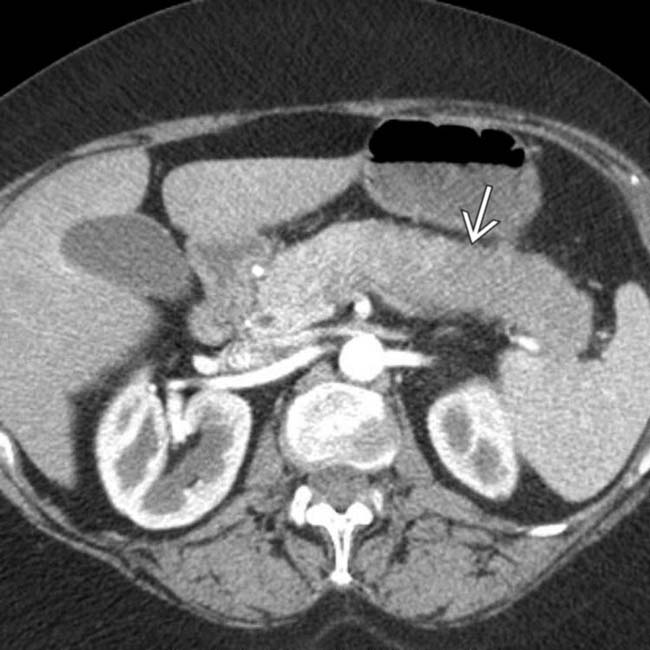
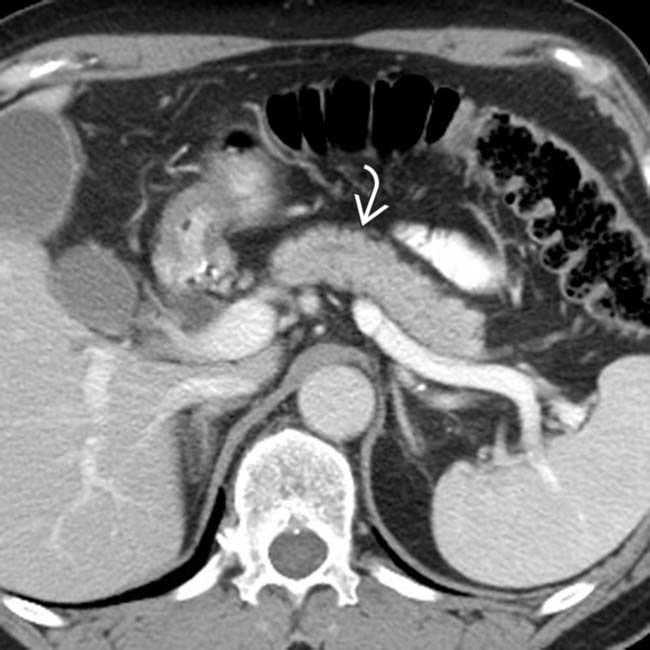
 . The pancreatic duct in this segment is not identified and there is little surrounding inflammation.
. The pancreatic duct in this segment is not identified and there is little surrounding inflammation.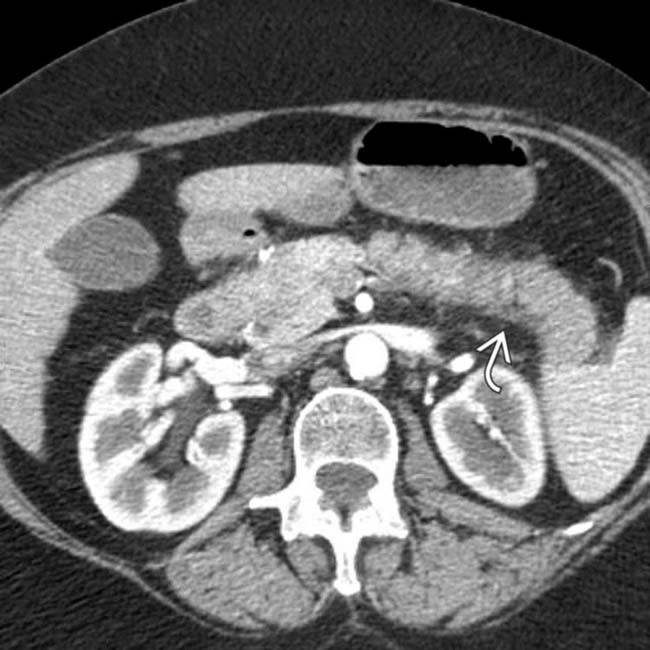
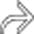 , typical of autoimmune pancreatitis.
, typical of autoimmune pancreatitis.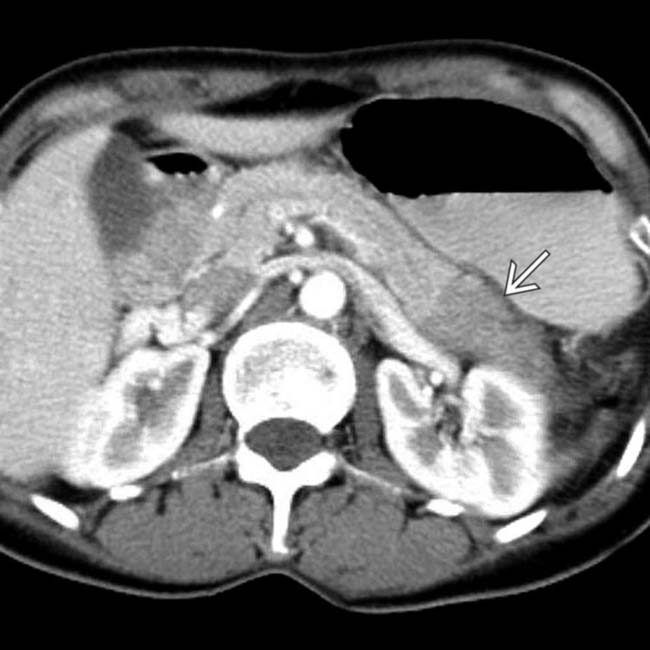
 in the tail of the pancreas. Serologic testing (IgG4) suggested the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and steroid therapy was started.
in the tail of the pancreas. Serologic testing (IgG4) suggested the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and steroid therapy was started.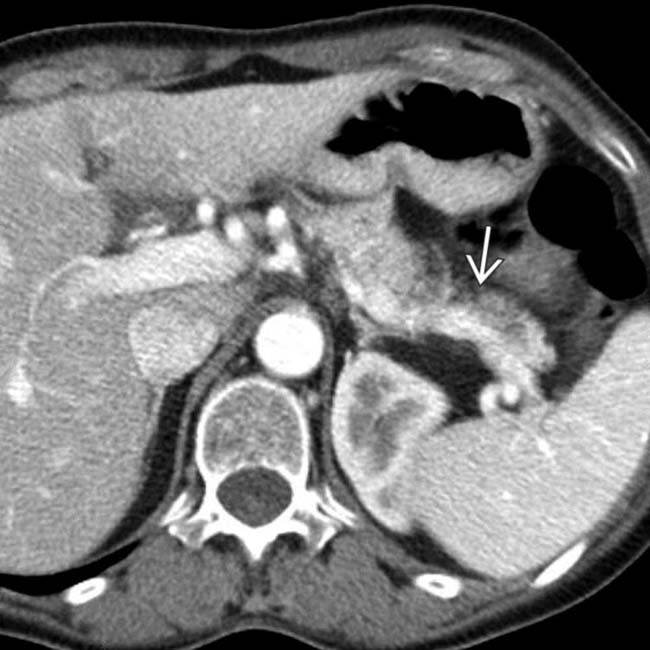
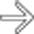 and slight atrophy of the affected pancreatic tail segment.
and slight atrophy of the affected pancreatic tail segment.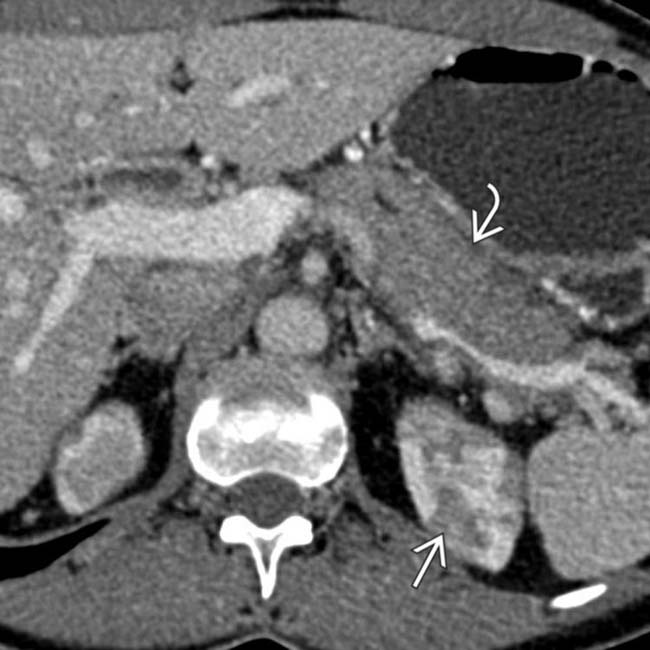
 in a patient with an elevated IgG4, compatible with autoimmune pancreatitis. Note the low-density wedge-shaped lesions
in a patient with an elevated IgG4, compatible with autoimmune pancreatitis. Note the low-density wedge-shaped lesions  in the left kidney.
in the left kidney.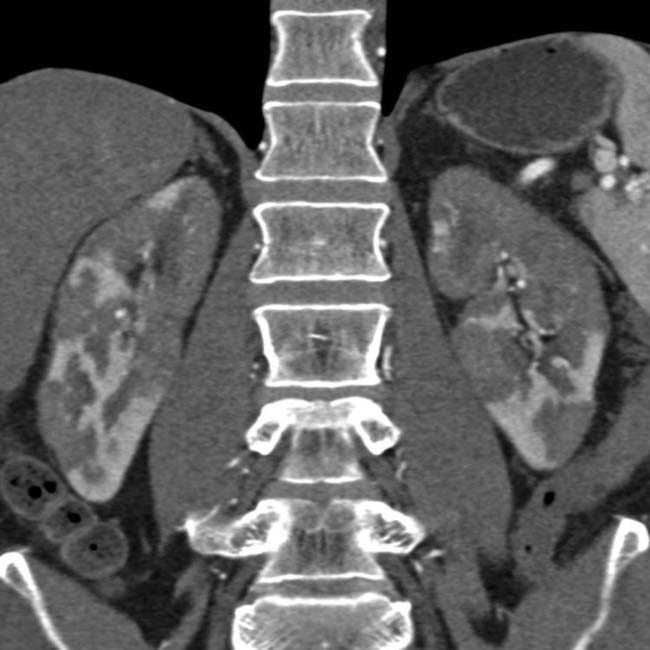
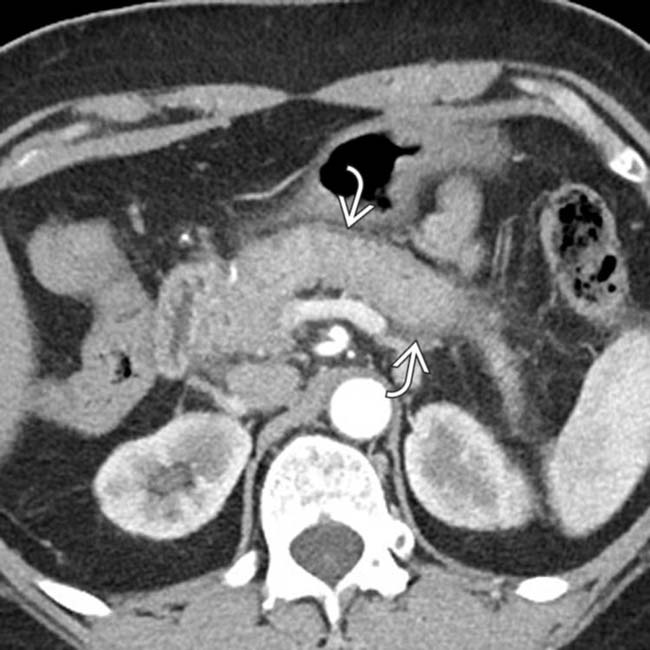
 . This was thought to likely represent autoimmune pancreatitis, and the patient was found to have elevated IgG4.
. This was thought to likely represent autoimmune pancreatitis, and the patient was found to have elevated IgG4.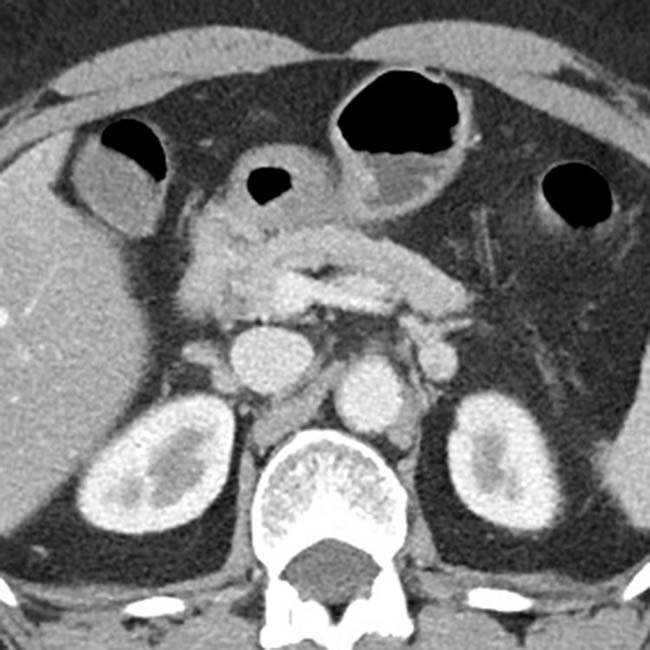
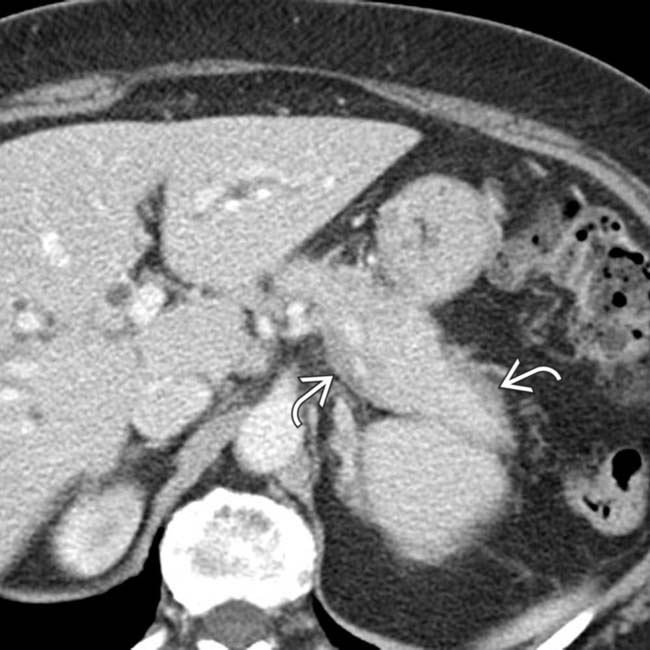
 surrounding the gland.
surrounding the gland.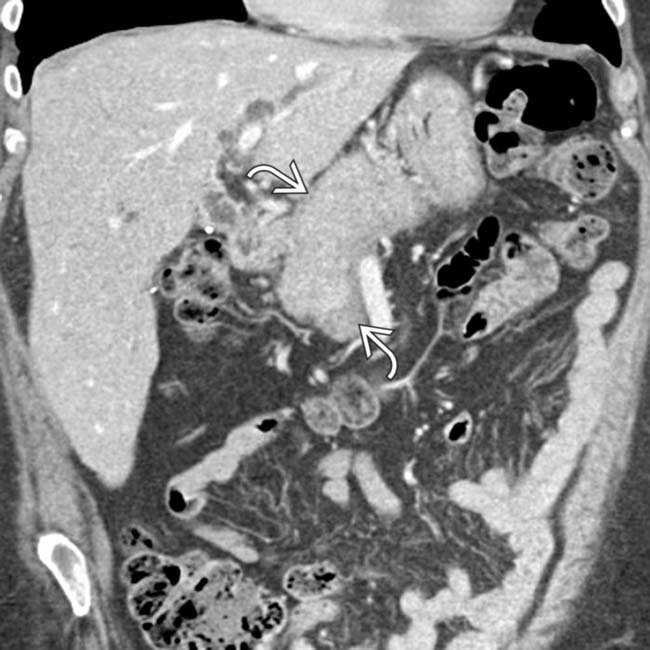
 . This constellation of findings is highly suggestive of autoimmune pancreatitis.
. This constellation of findings is highly suggestive of autoimmune pancreatitis.













































































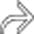 .
.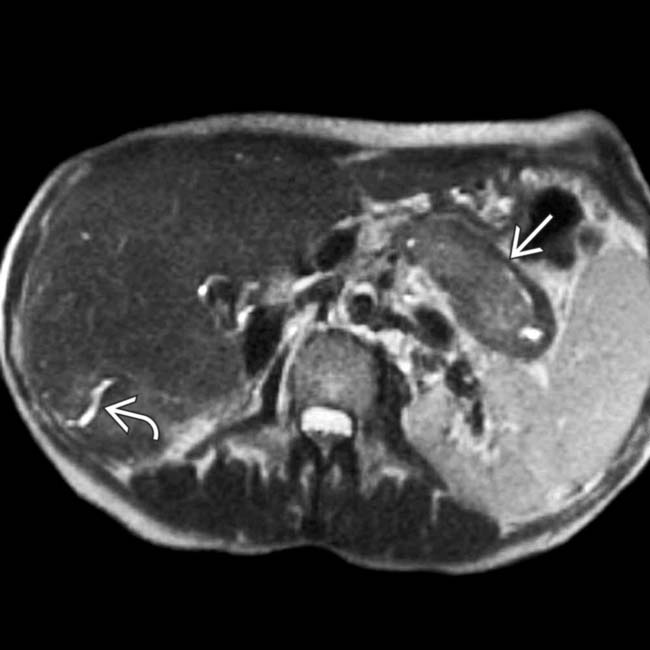
 around the pancreas, typical features of autoimmune pancreatitis. Multifocal, irregular dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts is also seen
around the pancreas, typical features of autoimmune pancreatitis. Multifocal, irregular dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts is also seen 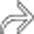 .
.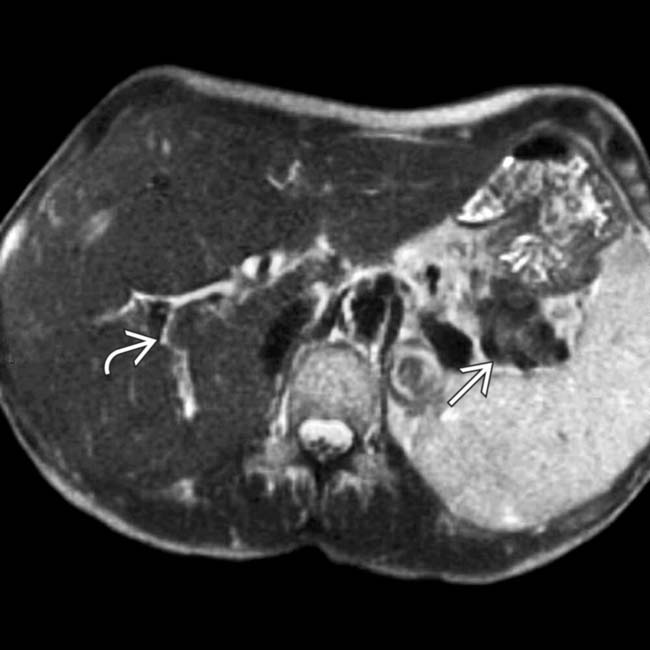
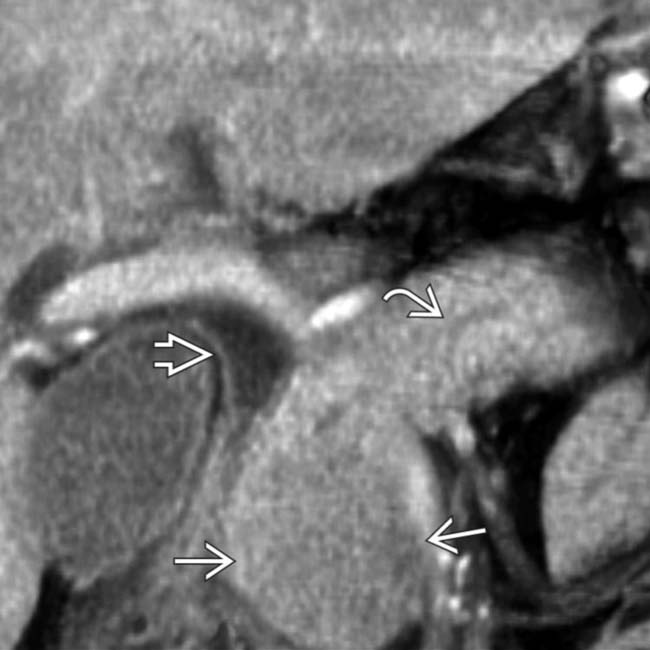
 and a hypointense halo
and a hypointense halo  around the tail of the pancreas.
around the tail of the pancreas.


