Culver, EL, et al. Systematic review: management options for primary sclerosing cholangitis and its variant forms – IgG4-associated cholangitis and overlap with autoimmune hepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 33(12):1273–1291.
Czaja, AJ. Cryptogenic chronic hepatitis and its changing guise in adults. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56(12):3421–3438.
Jothimani, D, et al. Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis: a review of current and evolving therapies. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26(4):619–627.
Lohse, AW, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 2011; 55(1):171–182.
Mayo, MJ. Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011; 27(3):224–230.
Mieli-Vergani, G, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 8(6):320–329.
Potts, JR, et al. Optimizing management in autoimmune hepatitis with liver failure at initial presentation. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17(16):2070–2075.
Vergani, D, et al. Pharmacological management of autoimmune hepatitis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011; 12(4):607–613.
Strassburg, CP. Autoimmune hepatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 24(5):667–682.
Bilaj, F, et al. MR imaging findings in autoimmune hepatitis: correlation with clinical staging. Radiology. 2005; 236(3):896–902.
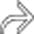 , a nonspecific sign often seen in acute hepatitis, among other causes.
, a nonspecific sign often seen in acute hepatitis, among other causes.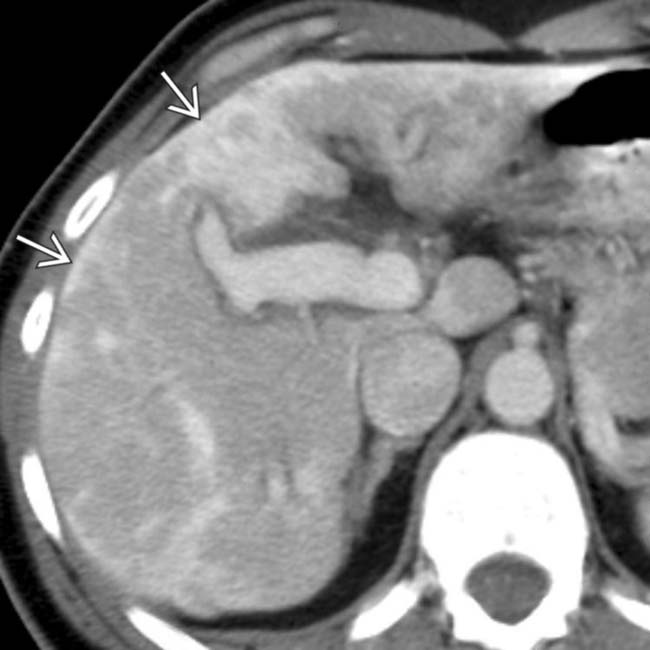
 , representing confluent fibrosis and is usually seen in advanced and more chronic liver damage. Liver biopsy showed acute and advanced liver injury due to autoimmune hepatitis (AIH).
, representing confluent fibrosis and is usually seen in advanced and more chronic liver damage. Liver biopsy showed acute and advanced liver injury due to autoimmune hepatitis (AIH).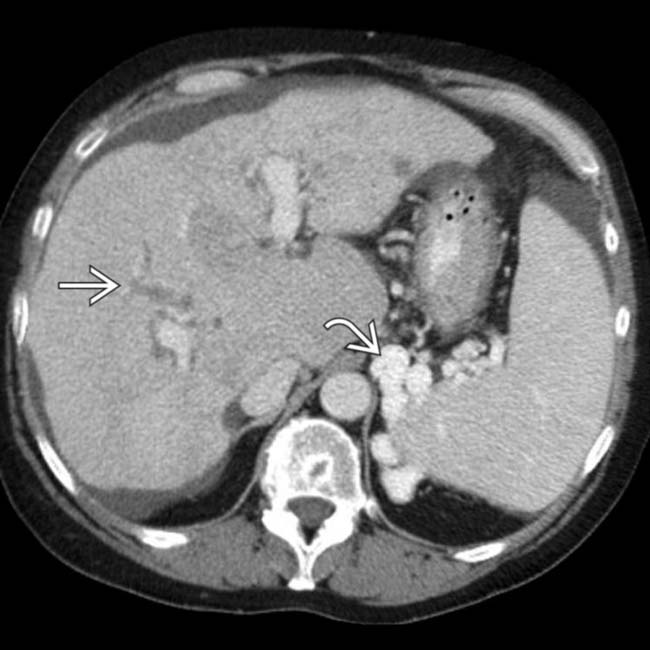
 . The intrahepatic ducts
. The intrahepatic ducts  are dilated with an abnormal arborization, suggestive of PSC.
are dilated with an abnormal arborization, suggestive of PSC.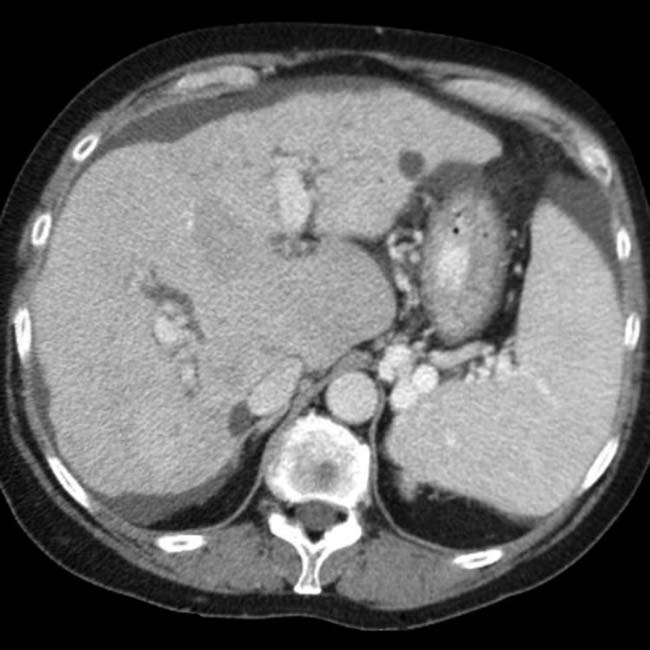
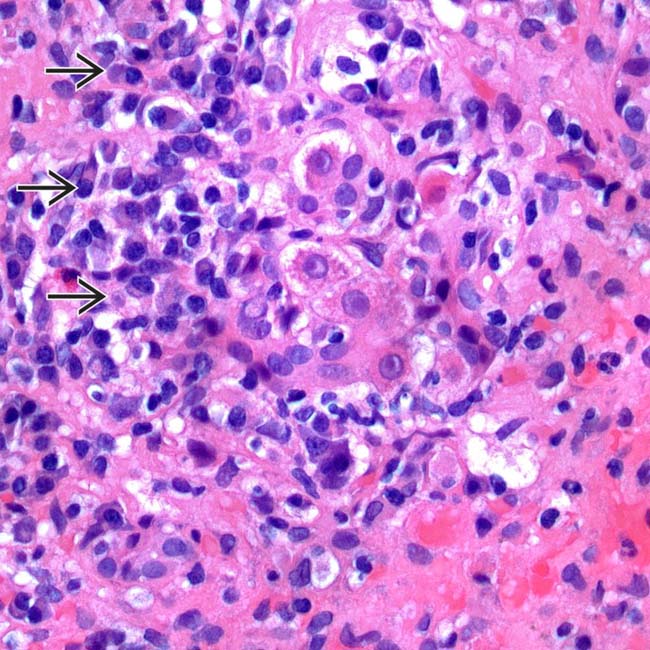
 in a case of autoimmune hepatitis. (Courtesy L. Yerian, MD.)
in a case of autoimmune hepatitis. (Courtesy L. Yerian, MD.)










































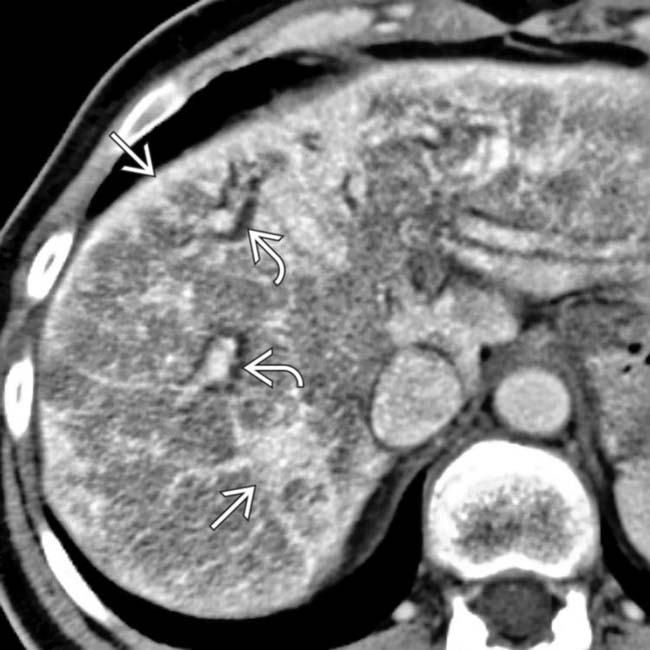
 , with subcapsular + parenchymal hyperdense bands
, with subcapsular + parenchymal hyperdense bands  that represent fibrosis.
that represent fibrosis.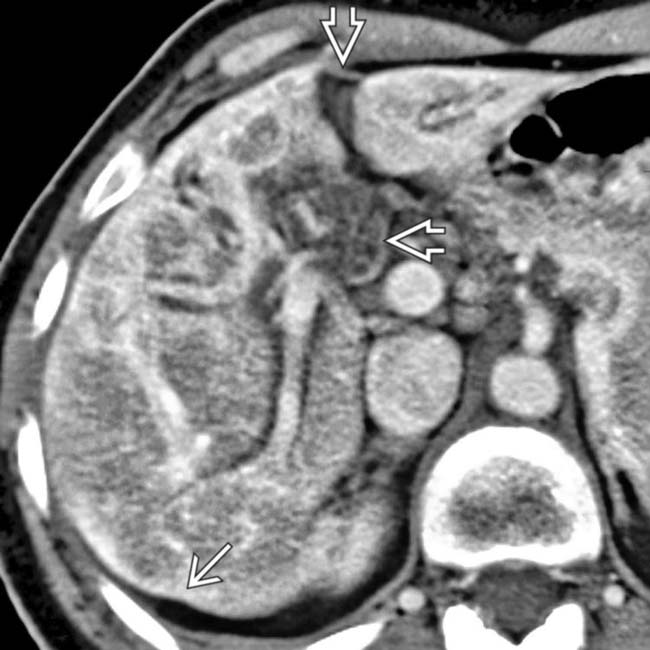
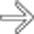 , a finding usually associated with confluent fibrosis & indicative of chronic liver injury. Also note the widened fissures
, a finding usually associated with confluent fibrosis & indicative of chronic liver injury. Also note the widened fissures  , typical of cirrhosis but not specific for AIH.
, typical of cirrhosis but not specific for AIH.
