186 Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Questions
What are the stages of atopic dermatitis?
There are three age-related stages, which are separated by remission.
Infantile stage (up to 2 years of age). Red, scaly, itchy crusted rash on both cheeks and extensors of the extremities. The napkin area is generally spared. Eczema of the scalp may also be seen
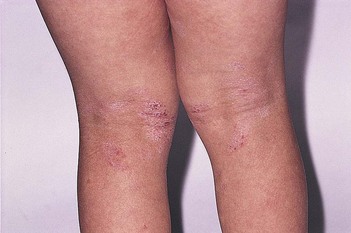
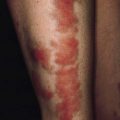
Childhood stage (2–12 years). There is papulation (rather than exudation) in the flexural areas including neck, cubital fossa, popiliteal fossa and volar aspect of wrists and ankles. The plaques show both excoriation and lichenification. In black children, there may be hypopigmentation
Adults (puberty onwards). The face is commonly involved and there is lichenification of flexures including wrists, hands, fingers, ankles, toes and feet, head and neck.
What are the criteria for diagnosis?
Hanifin and Rajka’s major criteria require three or more of the following:
How would you treat such patients?
• Foods (typically dairy products, peanuts, eggs and wheat) which cause itching should be avoided
• Patient should be instructed about skin care including avoiding frequent baths and scratchy fabrics, and regular use of emollients
• Adequate cutaneous hydration
• Antihistamines to control itching
• Corticosteroid lotion, cream or ointment: topical steroids are first-line drug therapy
• Phototherapy with psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) in those unresponsive to topical treatment
• Severe recalcitrant disease: ciclosporin, azathioprine, tacrolimus, mycophenolate, mofetil, pimecrolimus, Grenz-rays
• Investigational treatment: phosphodiesterase inhibitors, interleukin-2 and thymopentin.
What do you know about natural history of atopic dermatitis?
• Non-atopic dermatitis is the first manifestation of atopic dermatitis (as a result of genetically determined epidermal barrier dysfunction and the effect of environmental factors).
• Sensitization occurs subsequently (because of the genetic predisposition for IgE-mediated sensitization). This phenomenon is favoured by S. aureus enterotoxin products.
• Tissue damage and the release of structural proteins occurs finally (from scratching), which triggers an IgE response in patients with atopic dermatitis. This sensitization to self-proteins can be the result of the homology of allergen-derived epitopes and human proteins in the context of molecular mimicry.