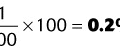CHAPTER 3 ASSESSMENT OF THE CARDIOPULMONARY PATIENT
PRETEST QUESTIONS
1. A patient coughs up yellow sputum after an IPPB treatment. Which one of the following statements is TRUE in regard to this sputum production?
2. The term used to describe a condition in which a patient has difficulty breathing while in a supine position is which of the following?
3. A patient enters the emergency department, and on initial examination the respiratory therapist observes paradoxical chest movement. Which of the following should the practitioner suspect?
4. Perfusion in the extremities may best be determined by which of the following methods?
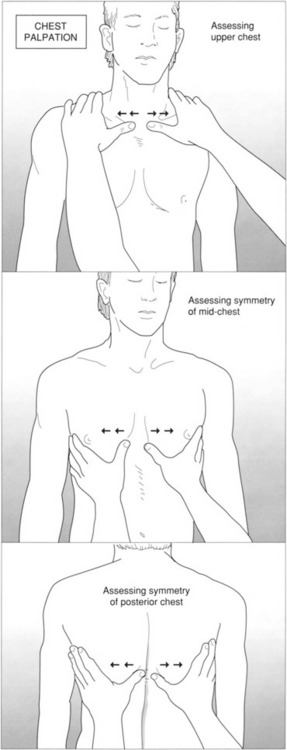
5. While palpating the chest, the respiratory therapist determines that there are decreased vibrations over the right lower lobe. This may be the result of which of the following?
6. A chest x-ray film obtained after ET intubation shows the tip of the ET tube is resting at the fourth rib. Which of the following actions should be taken?
7. A patient is suspected of having intrathoracic metastatic nodal disease. Which of the following imaging studies should the respiratory therapist recommend to determine, with the highest accuracy, whether disease is present?
8. Which of the following imaging studies may be useful in determining whether a pulmonary embolism is present?
REVIEW
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA1, IB5a-f
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA2, IB1c, IB5a-f, IIIE5a
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA2, IB1c, IB5a-e
![]() Foul-smelling sputum that often settles into several layers is characteristic of bronchiectasis. (See Chapter 12 on disorders of the respiratory system.)
Foul-smelling sputum that often settles into several layers is characteristic of bronchiectasis. (See Chapter 12 on disorders of the respiratory system.)
III. OTHER PHYSICAL ASSESSMENTS
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA2, IA6, IA8a-b, IB1a, IB2a-b, IB4a-c, IB7a-e, IB8, IC2, IIIA1b3, IIIE1
IV. ASSESSMENT OF LABORATORY TEST RESULTS
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA3, IC1, IIIE8
V. REVIEWING THE PATIENT CHART
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA1-8
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA1-8
VI. CLINICAL APPLICATION OF COMPUTERS
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIIA1-4
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IIIA1-2
VII. DEVELOPING RESPIRATORY CARE PLANS AND PROTOCOLS
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIIH6-8
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IIIH6-8
POSTCHAPTER STUDY QUESTIONS
1. What is yellow sputum indicative of?
2. What bacterial organism should be suspected if the patient’s sputum is green and foul smelling?
3. List nine causes of dyspnea.
4. What does the term orthopnea mean and in which patients is it most commonly found?
5. Describe Kussmaul respirations and in which patients this breathing pattern is most often seen.
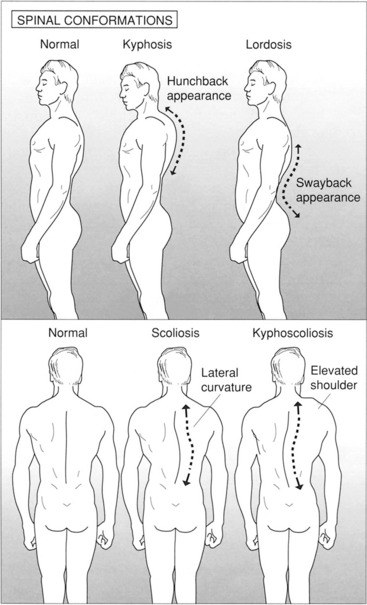
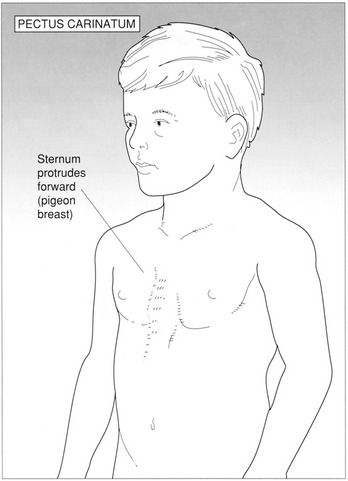
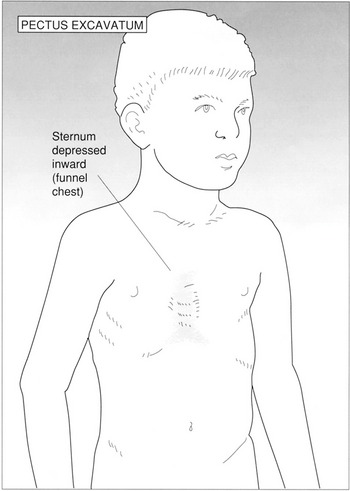
6. List three conditions in which asymmetrical chest movement may be observed.
7. Describe paradoxical respiration and name a condition in which it is most commonly observed.
8. Define pedal edema and what causes it.
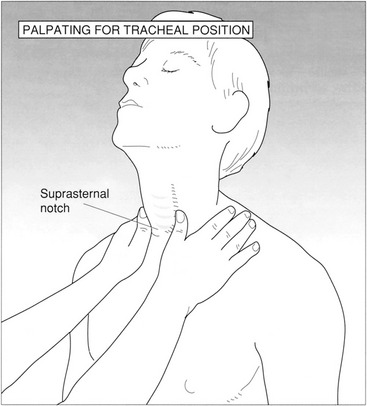
9. Name a condition that results in the trachea shifting toward the side of the body that the condition is affecting.
10. Name a condition that results in the trachea shifting away from the affected side.
11. Which muscles are used for normal ventilation?
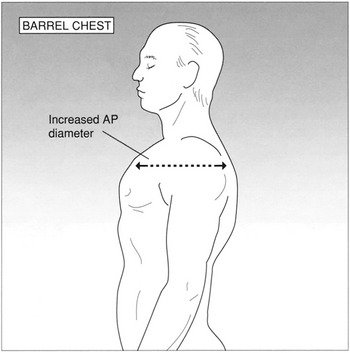
12. What causes the “barrel chest” appearance in patients with COPD?
13. Name two conditions in which a hyperresonant percussion note would be heard.
14. Name two conditions in which a dull percussion note would be heard.
15. List four conditions that result in heart murmurs.
16. List the normal values for the following electrolytes: sodium, potassium, and chloride.
17. Why would decreased sodium and potassium levels make weaning a patient from the ventilator more difficult?
18. What does an elevated BUN level indicate?
19. How does the respiratory system compensate when glucose levels increase in a diabetic patient?
20. List the normal levels for each of the following: RBC count, Hb level, Hct, and WBC count.
21. What do decreases in Hb level, Hct, and RBC count indicate?
22. Name two conditions that cause a decreased platelet count.
23. Patients with a decreased platelet count and increased PT are at a greater risk of what occurrence?
Farzan S. A concise handbook of respiratory diseases, ed 4. Stamford, CT: Appleton & Lange; 1997.
Hess D, Respiratory care principles and practice, ed 1, Philadelphia, Saunders, 2002.
Wilkins RL, Stoller JK, Kacmarek R. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 9. St Louis: Mosby; 2009.
Wilkins R, Dexter JR, Heuer AJ. Clinical assessment in respiratory care, ed 7. St Louis: Mosby; 2010.
Wyka K, Matthews P, Clark W. Foundations of respiratory care, ed 1. Albany: Delmar; 2002.