CHAPTER 25 Arthroscopic Resection of Arthrosis of the Proximal Hamate
Rationale and Basic Science
Pain in the ulnar aspect of the wrist is a common symptom in the field of hand surgery. This presenting complaint has a large number of possible etiologies, however, and the treatment for any given etiology is largely dependent on the diagnosis. Although treatment options for isolated tears of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) or the lunotriquetral (LT) ligament have been studied for many years, there is very little research on outcomes for patients with arthritic change of the proximal pole of the hamate. This is surprising, given that the proximal hamate is one of the most frequent sites of arthrosis in the wrist.1,2
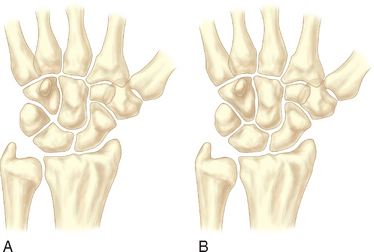
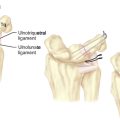
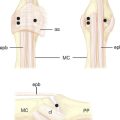
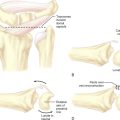
In 1990, two unrelated anatomical studies closely characterized the lunate articular anatomy.1,3 These descriptions referred to the distal joint morphology of the lunate in the midcarpal joint and two types were described (Figure 25.1). A type I lunate is one in which the distal lunate articulation makes contact with only the capitate. It was observed in approximately 30% of specimens. A type II lunate is one with an obvious distal lunate medial facet that articulates with the proximal pole of the hamate in addition to the regular facet that articulates with the capitate. The size of this medial facet ranges between 1 and 6 mm in width. This type II variant was observed in up to 70% of specimens. A type I lunate has no contact with the proximal pole of the hamate regardless of wrist position, whereas a type II lunate has a variable amount of contact between the hamate and medial lunate facet—primarily when the wrist is in an ulnarly deviated position.
Cadaver studies have revealed that cartilage erosion of the proximal pole of the hamate is the most common arthrotic condition within the wrist.1,2 An increasing rate of degeneration is noted with increased age. When proximal hamate arthrosis is present, it is noted almost exclusively in specimens with type II lunates. This appears to be directly related to the increased midcarpal motion observed in patients with type II lunates during radioulnar hand movements, and is presumed to be a result of overloading of the proximal hamate over the long term.4,5 Patients with symptomatic proximal hamate arthrosis typically complain of ulnar-sided wrist pain, especially with gripping. This appears to correlate with radiographic studies that clearly show increasing contact areas between the hamate and lunate with ulnar deviation. The larger the medial facet of the lunate the more likely arthrosis is to develop. The cartilage degeneration is most evident dorsally on the hamate, and matching degeneration on the medial facet of the lunate is observed up to 50% of the time.
Clinical and cadaveric studies have also demonstrated a strong association between arthrosis at the proximal hamate and tears in the lunotriquetral interosseous ligament (LTIL). Complete or partial disruption of the LTIL has been documented almost 90% of the time when arthrosis of the proximal hamate is identified. Because of this strong association, we have proposed the term HALT (hamate arthrosis lunotriquetral ligament tear) wrist to describe this common clinical condition. There has been little crossover of this anatomical and biomechanical data to the clinical arena, however. The role a torn LTIL may play in the development of hamate arthrosis has not been delineated. A prospective longitudinal study would be required to delineate whether LT instability predisposes wrists with type II lunates to increased or earlier degeneration of the proximal hamate.
Published clinical studies examining the treatment regimens for hamate arthrosis are limited. Thurston and Stanley reported on four patients with arthrosis of the proximal pole of the hamate who were treated by proximal hamate excision. All of the patients were reported to have done well after surgery.6 Harley et al. reviewed a much larger series of patients who were treated by arthroscopic excision of the proximal hamate and found favorable results in the majority of patients.7 A biomechanical arm of this latter study evaluated the unloading effect of proximal hamate resection. Cadaver wrists with type II lunates were mounted on a custom vice and testing stand.
Indications
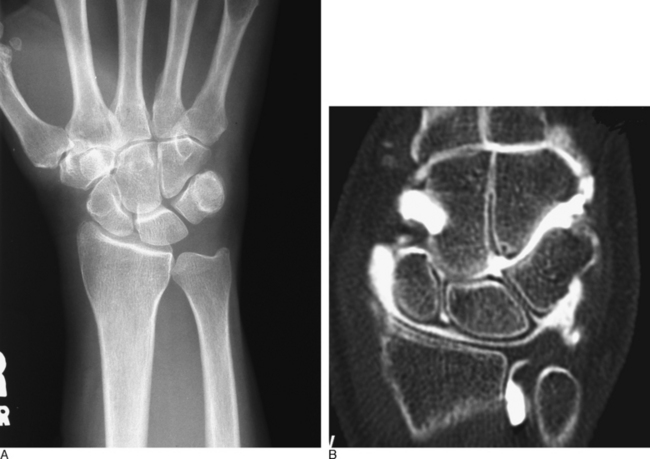
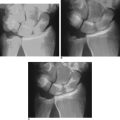
Plain radiographic studies of the affected wrist should be compared to the opposite asymptomatic wrist. Cystic change within the proximal hamate, or a sharp and sclerotic proximal hamate margin, can aid in the identification of this condition preoperatively. However, in most instances plain radiographic studies are noncontributory (Figure 25.2). Furthermore, it is important to realize that plain radiographs are not always diagnostic of a type II lunate morphology.8 MRI scans of the wrist that demonstrate edema within the proximal hamate are suggestive of this condition. Likewise, a wrist CT-arthrogram study that outlines a thinned proximal hamate cartilage surface and/or reveals a sclerotic subchondral ridge can also assist in making the diagnosis preoperatively. Unfortunately, neither of these two expensive diagnostic modalities consistently identifies this condition.
Contraindications
Contraindications to arthroscopic resection of the proximal hamate are few. Any symptomatic patient with advanced chondromalaciac changes identified at the time of arthroscopy can derive significant benefits from a proximal pole resection. Proximal hamate arthrosis represents a spectrum of pathological changes. Resection of the proximal hamate in a patient with grade I or II change is usually contraindicated (Table 25.1). A gray area exists for those patients with limited or focal grade III or IV chondromalacia.
| Type I | Localized softening, discoloration; no break in the surfaces |
| Type II | Softening, discoloration; small areas of fibrillation or irregular surface |
| Type III | Fibrillation and fissures extend to subchondral bone surface; “crabmeat” appearance |
| Type IV | Areas with complete loss of articular cartilage; exposed subchondral bone |
Surgical Technique
The involved wrist and forearm are prepped and draped and placed in some type of traction device. A tourniquet is elevated after exsanguination. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not required for an isolated proximal hamate resection. A standard arthroscopic survey of the radiocarpal and midcarpal joints is then performed, and all cartilage surfaces and ligamentous structures are assessed. The usual working portals include the 3-/,4 and 4-/,5 portals as well as midcarpal-radial (MCR) and midcarpal-ulnar (MCU) portals. In the radiocarpal joint, close attention must be paid to the articular surface of the lunate as well as to the TFCC. If a TFCC perforation is present, the distal ulnar chondral surface of the ulnar head can also be assessed. The LTIL is best seen through the 4-/,5 portal. The 6-U portal is frequently utilized for instrumentation to help probe or debride a torn LTIL.
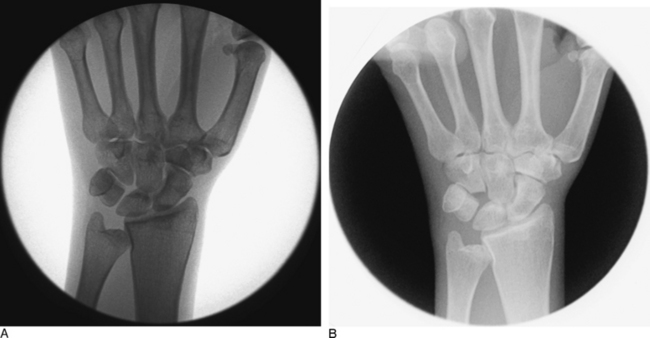
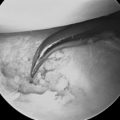
When the surgeon is satisfied with the arthroscopic decompression of the hamatolunate articulation, an intra operative fluoroscopic assessment is performed to confirm the adequacy of the proximal hamate resection (Figure 25.3). Whereas this often requires some maneuvering of both the surgeon and the instruments, the fluoroscopic pictures provide an important secondary means of evaluation. If the radiographs confirm that the resection is satisfactory, all portals are closed with skin tapes, local anesthetic is infiltrated into the joint and the surrounding subcutaneous tissues, and a light compressive bandage is applied for 10 days.
1 Viegas SF, Wagner K, Patterson R, Peterson P. Medial (hamate) facet of the lunate. J Hand Surg. 1990;15A:564-571.
2 Viegas SF, Patterson RM, Hokanson JA, Davis J. Wrist anatomy: Incidence, distribution, and correlation of anatomic variations, tears, and arthrosis. J Hand Surg. 1993;18A:463-475.
3 Burgess RC. Anatomic variations of the midcarpal joint. J Hand Surg. 1990;15A:129-131.
4 Nakamura K, Beppu M, RM P, Hanson C, Hume P, Viegas S. Motion analysis in two dimensions of radial-ulnar deviation of type I versus type II lunates. J Hand Surg. 2000;25A:877-888.
5 Nakamura K, Patterson R, Moritomo H, Viegas S. Type I versus type II lunates. J Hand Surg. 2001;26A:428-436.
6 Thurston AJ, Stanley JK. Hamato-lunate impingement. Arthroscopy. 2000;16:540-544.
7 Harley BJ, Palmer AK, Boles SD, Werner FW. Arthroscopic resection of arthrosis of the proximal hamate: A clinical and biomechanical study. J Hand Surg. 2004;29A:661-667.
8 Sagerman SD, Hauck RM, Palmer AK. Lunate morphology: Can it be predicted with routine X-ray films? J Hand Surg. 1995;20A:38-41.