Aquatic Skin Disorders
Disorders
Treatment
1. Promptly wash with soap and water to remove toxins.
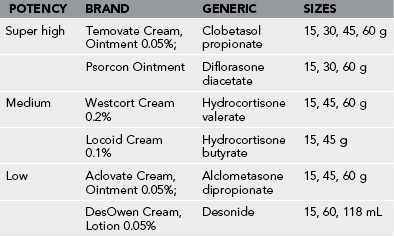
2. Treat a mild to moderate reaction with antihistamines and a topical medium-potency corticosteroid preparation (Table 55-1).
3. Treat a severe reaction with an oral corticosteroid, specifically prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 1 mg/kg for children, with a 2-week taper.
Sea Cucumber Dermatitis
Treatment
1. Promptly wash with soap and water to remove toxins.
2. Treat a mild to moderate reaction with a topical low- or medium-potency corticosteroid preparation (see Table 55-1).
3. Treat a severe reaction with an oral corticosteroid, specifically prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 1 mg/kg for children, with a 2-week taper.
Sea Moss Dermatitis (Dogger Bank Itch)
Treatment
1. Treat as for mild poison oak dermatitis (see Chapter 40).
a. Depending on the severity of the reaction, apply calamine lotion or a topical medium- or high-potency corticosteroid preparation.
2. Treat a severe reaction with an oral corticosteroid, specifically prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 1 mg/kg for children, with a 2-week taper.
Seaweed Dermatitis
Signs and Symptoms
1. In minutes to hours after exposure, a pruritic, burning, moist, and erythematous rash developing in bathing suit distribution, followed by bullous escharotic desquamation in the genital, perineal, and perianal regions (see Plate 44)
2. Lymphadenopathy, pustular folliculitis, and local infections
3. Oral and ocular mucous membrane irritation, facial rash, conjunctivitis
Treatment
1. Wash the skin vigorously with soap and water.
2. Apply a brief soak of isopropyl alcohol 40%.
3. Apply a topical corticosteroid preparation. This may need to be medium to high potency.
4. Treat a severe reaction with an oral corticosteroid, specifically prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 1 mg/kg for children, with a 2-week taper.
Protothecosis
Signs and Symptoms
1. Superficial cutaneous lesions present as papulonodules or verrucous plaques with or without ulcerations. Bullous lesions or, rarely, eczematous and cellulitis-like lesions may occur (see Plate 45).
2. Olecranon bursitis, with or without spontaneous drainage. A history of preceding trauma should suggest protothecosis.
3. Systemic infection may occur, particularly in immunosuppressed persons.
Aquagenic Pruritus
Signs and Symptoms
1. Intense disabling itching without visible cutaneous changes on exposure to water of any temperature
2. Reaction within minutes of exposure and lasting between 10 minutes and 2 hours
3. Lack of concurrent skin disease or drug exposure
4. Symptoms may occur only in areas exposed to water. Typically the head, palms, soles, and mucosa are spared
Schistosomiasis (Cercarial Dermatitis, “Swimmer’s Itch”)
Signs and Symptoms
1. Initial symptom: prickling sensation (sometimes burning and itching sensations)
2. Itching 4 to 60 minutes after the cercariae penetrate the skin, accompanied by erythema and mild edema
3. Subsidence of the initial urticarial reaction over 60 minutes, leaving red macules that become papular and more pruritic over the next 10 to 15 hours; discrete and highly pruritic papules 3 to 5 mm (0.1 to 0.2 inch) in diameter are surrounded by a zone of erythema (see Plate 48)
4. Vesicles, which may become pustules, frequently forming within 48 hours and possibly persisting for 7 to 14 days
5. Peak inflammatory response within 3 days and subsidence slowly over 1 to 2 weeks
Treatment
1. In a mild case, apply isopropyl alcohol 40% or equal parts of isopropyl alcohol and calamine lotion to control the itching.
2. Oral antihistamines may be helpful.
3. For a severe case, give an oral corticosteroid, specifically prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 1 mg/kg for children, with a 2-week taper.
4. Manage secondary bacterial infection, which is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus species, with a topical antiseptic ointment (mupirocin, bacitracin) or a systemic antibiotic (e.g., erythromycin, dicloxacillin).
Leeches
Treatment
1. To remove a leech, apply a few drops of brine, alcohol, or strong vinegar, or hold a flame near the site of attachment. Do not rip the leech off the skin because its jaws may remain and induce intense inflammation.
2. After removal of the leech, inspect the wound site closely for retained mouthparts.
3. Hasten hemostasis by the application of a styptic pencil, topical thrombin solution, oxidized regenerated cellulose absorbable hemostat, or “blood-stopper gauze” (e.g., QuikClot).
4. Clean wounds several times daily with an antiseptic. Treat any secondary infection that develops with an antibiotic.
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
Treatment
1. Use cryotherapy with ethyl chloride for a mild infestation, topical thiabendazole in a more refractory case, and oral thiabendazole (25 to 50 mg/kg) for 2 to 4 days in a more severe case. Alternative drugs are albendazole (400 mg/day PO for 7 days) or ivermectin (12-mg single dose).
2. Secondary infection may occur and require incision and drainage of pustules or furuncles and the use of topical and systemic antibiotics.
Soapfish Dermatitis
The soapfish (Rypticus saponaceus; Fig. 55-1) releases a soapy mucus when handled or disturbed.
Mycobacterium Marinum Infection
Signs and Symptoms
1. Development of localized area of cellulitis 7 to 10 days after sustaining puncture wound or laceration, particularly of the cooler distal extremity; may progress to localized arthritis, bony erosion, formation of subcutaneous nodules, and superficial desquamation
2. Development of red papule within 3 to 4 weeks after inoculation that transforms into hard purple nodule, with scaling, ulceration, and verrucous appearance; may enlarge to 6 cm (2.4 inches) in diameter, although 1 to 2 cm (0.4 to 0.8 inch) more common
3. New lesions developing in pattern that resembles sporotrichosis, with dermal granulomas in linear distribution (see Plate 50) along the superficial lymphatics
Treatment
1. Administer trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or ethambutol plus rifampin as first-line therapy.
2. Subsequent treatment is determined by culture and drug sensitivity testing. Effective antibiotics have included minocycline, tetracycline, levofloxacin, azithromycin, amikacin, amoxicillin/clavulanate, and tuberculostatic drugs.
Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae Infection
Signs and Symptoms
1. Appearance of violaceous, raised area within 2 to 7 days after inoculation
2. Enlarged area, accompanied by pain and itching
4. Hallmark lesion: purplish skin irritation or paronychia, with edema and small amount of purulent discharge
a. Surrounded by area of relative central fading, in turn surrounded by centripetally advancing, raised, well-demarcated, and marginated erythematous or violaceous ring (see Plate 34)
b. Lesion warm and tender, with progression up the dorsal edge of the finger into the web space and descent along the adjoining finger
5. Infection seldom affecting the palm; absence of pitting or suppuration
Aeromonas Hydrophila Infection
Signs and Symptoms
1. Within 24 hours, wound (particularly of puncture variety) that becomes cellulitic, with erythema, edema, and purulent discharge (see Plate 51)
a. Most frequently affects the lower extremity
b. Appearance indistinguishable from streptococcal cellulitis
2. Localized pain, lymphangitis, fever, chills
3. Rapidly advancing, gas-forming, soft tissue reaction, with bullae formation and necrotizing myositis
Treatment
1. Administer an antibiotic such as chloramphenicol, gentamicin, tobramycin, tetracycline, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (co-trimoxazole), ciprofloxacin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, moxalactam, imipenem/cilastatin, or meropenem.
2. For severe infection, administer IV antibiotics as soon as possible. Aggressive wound debridement may be necessary.
Vibrio Sp. Infection
For information on antibiotic prophylaxis against Vibrio spp. infection, see Chapter 52. For information on antibiotic therapy for established Vibrio sp. infection, see Chapters 52 and 54.
Reactions to Diving Equipment
Treatment
1. Treat acute facial dermatitis with cool compresses of Burow’s solution (aluminium acetate).
2. For a severe skin reaction, treat with an oral corticosteroid, specifically prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 1 mg/kg for children, with a 2-week taper.
3. For a serious intraoral reaction, use a twice-daily mouthwash of equal parts of antihistamine (diphenhydramine) elixir and magnesium salts (milk of magnesia). Coat individual sores twice daily and at bedtime with triamcinolone acetonide (0.1%) dental paste (Kenalog in Orabase) for 5 to 7 days.
Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)
Signs and Symptoms
1. Initial symptoms: itching, mild pain; rarely, decreased hearing
2. Possibly sensation of “fullness” in the affected ear
3. Pain that worsens as the inflammation progresses until it is uncomfortable to push on the tragus or pull on the earlobe
4. Severe infection: possible cellulitis, with purulent discharge (see Plate 53), occlusion of the ear canal, cervical lymphadenopathy, headache, nausea, fever, and sepsis
Treatment
1. The most important topical therapy is reacidification and desiccation of the ear canal, which can be accomplished with a 50 : 50 mixture of isopropyl alcohol 40% and acetic acid 5% (vinegar) or with Burow’s solution (Domeboro: aluminum sulfate and calcium acetate).
3. Administer appropriate pain medications.
4. For a mild infection (slight pain and discharge), use ear drops such as nonaqueous acetic acid (VoSol otic). Colistin sulfate has been recommended to combat Pseudomonas. Using acetic acid or acetic acid with hydrocortisone 1% (VoSol HC otic) avoids sensitization that may occur with neomycin-containing products.
5. If suppuration occurs, antibiotic ear drops such as hydrocortisone 1%, polymyxin B, and neomycin (Cortisporin otic) or ofloxacin otic are indicated.
6. If the ear canal is so swollen that drops will not penetrate the debris, place a gauze or foam wick and keep it soaked with the topical solution for 24 to 72 hours.
7. If adenopathy, profuse purulent discharge, or fever is present, give oral co-trimoxazole, ciprofloxacin, or amoxicillin/clavulanate.
Prevention
1. The most important preventive measure is to diminish moisture retention in the external ear canal.
2. Do not use cotton-tipped applicators to extract moisture because they can damage the ear canal lining or press cerumen deeply into the canal.
3. Acidifying and desiccating agents are effective prophylaxis.
4. Achieve prevention by briefly rinsing with common rubbing alcohol, vinegar, or a mixture of these after each entry into the water. Avoid petroleum jelly or other substances intended to form a watertight seal because they may act as a moist trap for debris.