CHAPTER 4 Applied Anatomy
Right Upper Lobectomy
Anterior Hilum
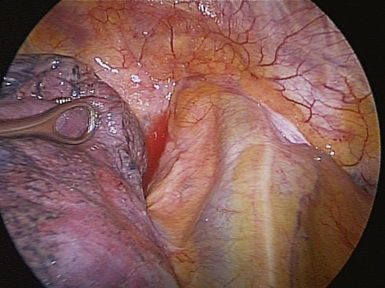
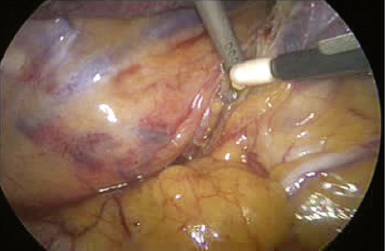
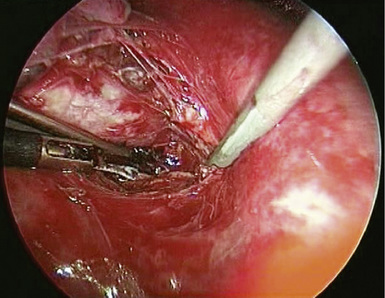
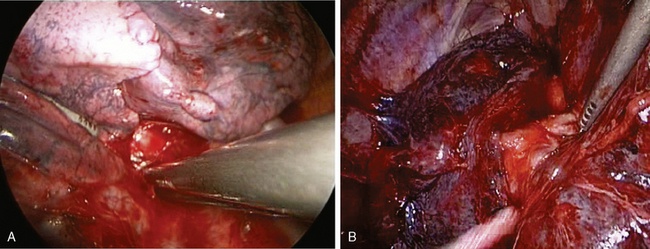
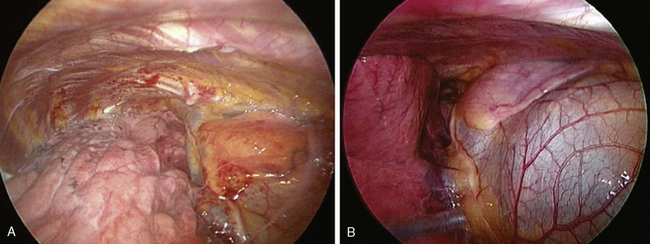
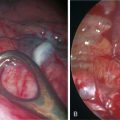
♦ The phrenic pedicle travels in a superoinferior direction on the superior vena cava and heart (Figure 4-1). Identify this structure so that it is not inadvertently injured in dissection of the superior pulmonary vein (SPV) (Figure 4-2). Using blunt dissection, the phrenic nerve and its vessels can be swept anteriorly away from the pulmonary vein (Figure 4-3).
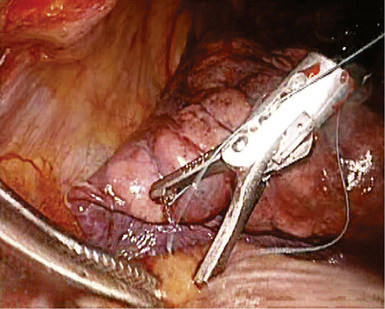
♦ The important structures are the SPV, which is most anterior; the right pulmonary artery, which is posterior and often superior to the SPV; and the right upper lobe bronchus, which is the most posterior structure and often can be identified after the SPV and the truncus anterior branch of the pulmonary artery are divided (Figure 4-4).
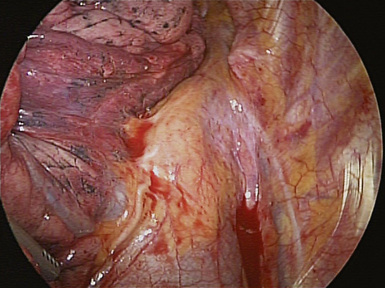
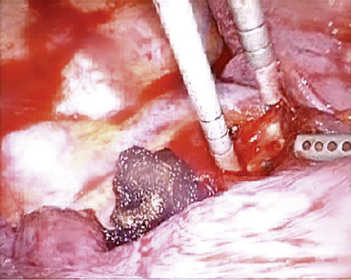
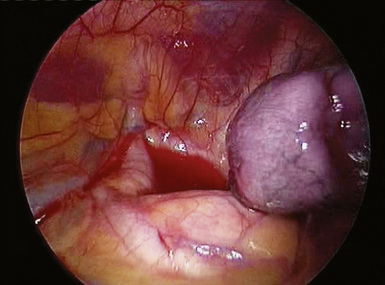
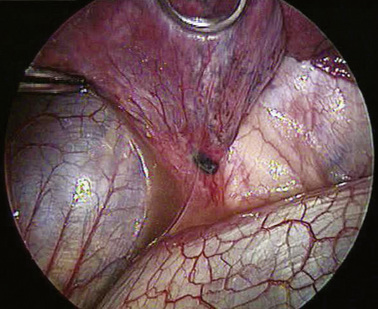
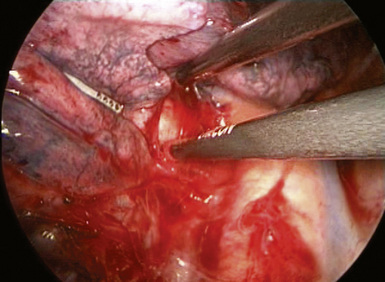
♦ With retraction of the lung inferiorly from the posterior incision, the azygous vein can be identified passing to the superior vena cava from a posterior direction (Figure 4-5). It is positioned just superior to the truncus anterior branch of the pulmonary artery and the right mainstem bronchus. It should be dissected bluntly away from these structures. Mobilizing the azygous vein allows complete node dissection (Figure 4-6). If there are any problems with visualization of the nodes, the vein can be readily divided with the endovascular stapler.
Posterior Hilum
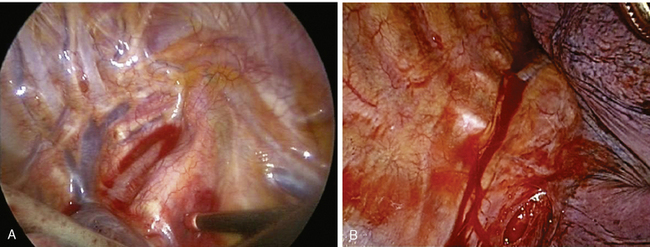
♦ After opening the posterior mediastinal pleura with the harmonic scalpel or cautery device, you can see the subcarinal space with the right mainstem bronchus and bronchus intermedius traveling in an oblique direction toward the lung (Figure 4-7).
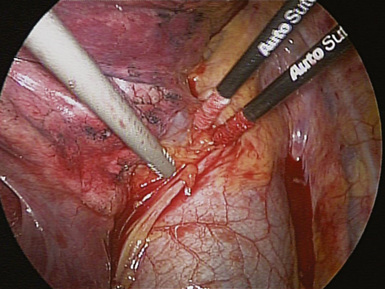
♦ The azygous vein travels up the posterior chest wall before turning anterior at the level of the carina (Figure 4-8). With gentle blunt dissection, free the vein from the right mainstem bronchus.
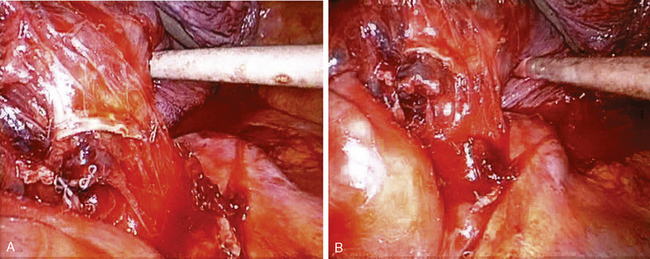
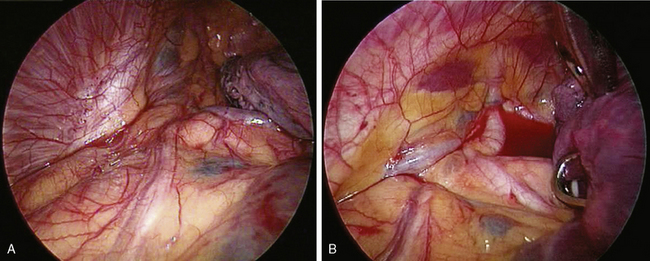
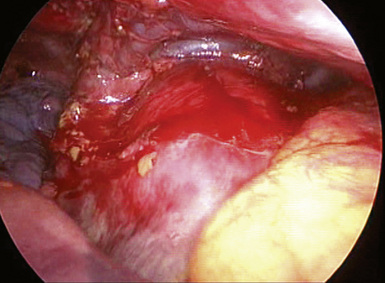
♦ During the subcarinal node dissection, the entire subcarinal space is well visualized. The esophagus lies anterior to the left mainstem bronchus (Figure 4-9). After the nodes are completely resected, hemostasis is straightforward and can be accomplished with surgical cellulose and pressure. Use thermal energy discretely to avoid injury to the membranous right mainstem bronchus or the esophagus.
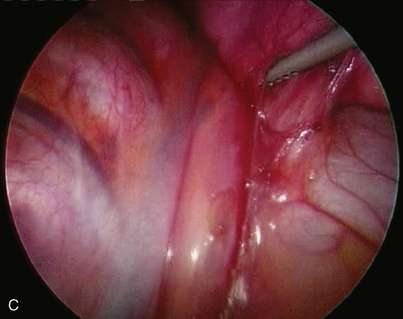
♦ Sweeping mediastinal pleura up toward the lung permits visualization of the right upper lobe bronchus taking off at a 90-degree angle from the right mainstem bronchus (Figure 4-10).
♦ The thoracic duct lies posterior to the esophagus and is rarely an issue, although with extensive node dissection in the subcarinal space, significant thoracic duct radicals can be disrupted. Use clips on any lymphatic vessels of significant size (>2 mm).
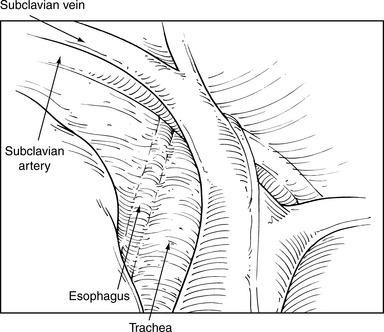
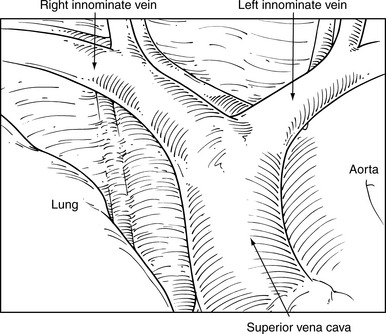
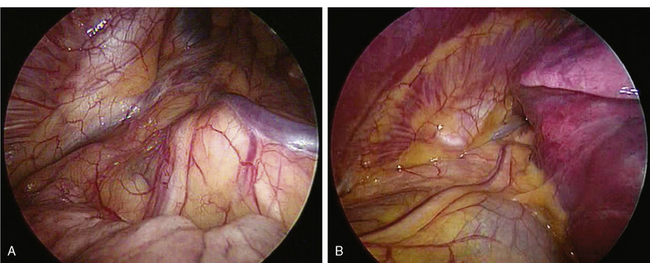
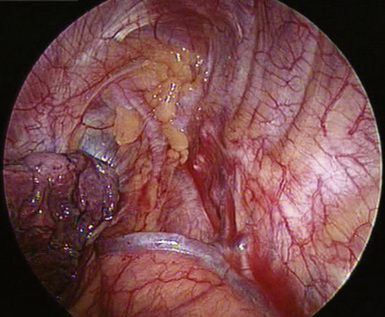
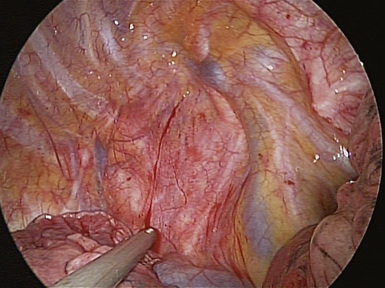
♦ Extensive paratracheal node dissection extends to the apex of the right chest. Identify the right subclavian artery and vein (Figure 4-11). Avoid extensive thermal dissection in this region to avoid injury to the right recurrent nerve. Medially and anteriorly, the left innominate vein joins the right innominate vein to form the superior vena cava (Figure 4-12). It should be identified during the high paratracheal node dissection. The pericardium can be seen at the base of the paratracheal node dissection after the nodes are removed.
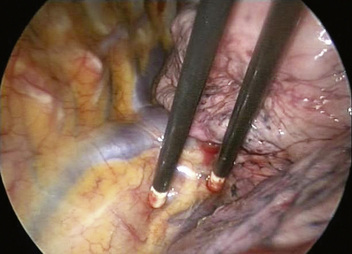
Figure 4-8 The azygous vein travels superiorly lateral to the right border of the thoracic vertebral bodies.
Right Middle Lobectomy
♦ The phrenic nerve courses in an inferior direction over the base of the middle lobe pulmonary vein (Figure 4-13). Similar to the dissection for the upper lobectomy, bluntly sweep away the nerve to avoid injury to it. The middle lobe pulmonary vein usually drains into the left atrium with the superior pulmonary vein but can drain separately or, rarely, with the inferior pulmonary vein. The middle lobe vein is composed of two segmental veins, with one anterior to the other or, less commonly, with one superior to the other.
♦ Unlike with the upper lobe, the bronchus sits posterior to the vein with the middle lobe pulmonary arteries posterior to the bronchus or slightly superior to the bronchus (Figure 4-14). This relationship is important because after dividing the middle lobe vein, the next step is to divide the middle lobe bronchus. In passing the right-angle clamp around the bronchus, be aware of the artery’s location to avoid injuring it with the clamp. The artery may be swept away from the bronchus bluntly before passing the clamp.
Right Lower Lobectomy
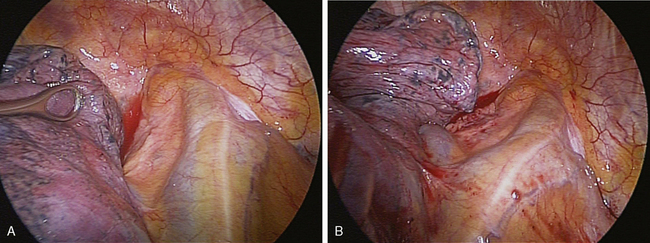
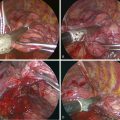
♦ The initial view for the lower lobectomy involves the posterior hilum (Figure 4-15). You should understand the relationships among the inferior pulmonary vein, the ongoing pulmonary artery, and lower and middle bronchi. Dissection on the superior and inferior border of the inferior pulmonary vein from the posterior hilum defines this vein and identifies the lower lobe bronchus and ongoing pulmonary artery, which lie immediately superior to the superior border of the inferior vein. The diaphragm may impede the view and may be retracted with an endokittner through the camera port or with an EndoStitch device.
♦ Identify the superior segmental pulmonary artery, which is the most posterior branch of the right pulmonary artery (Figure 4-16). After dividing this branch, you can divide the basilar trunk without concern.
♦ Consider the relationship between the lower lobe bronchus and middle lobe bronchus (Figure 4-17), and identify the takeoff of the middle lobe bronchus to avoid kinking the middle lobe bronchus in dividing the lower lobe bronchus. The anesthesiologist can perform bronchoscopy before the division of the lower lobe bronchus to ensure there is no distortion of the middle lobe bronchus.
♦ Avoid injury to the phrenic nerve in the region of the inferior pulmonary vein because it can sometimes pass very close to the inferior border of the vein before arborizing on the central tendon of the diaphragm (Figure 4-18). Exuberant use of the cautery can cause an injury in this location.
Left Upper Lobectomy
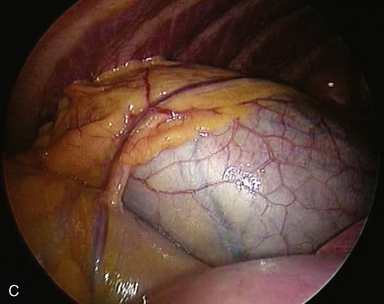
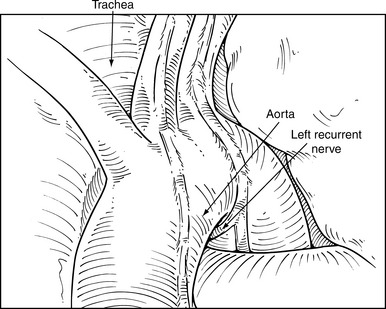
♦ Notice several anatomic structures: the aortic arch, the subclavian artery (Figure 4-19), the aortic pulmonary window (Figure 4-20), the aortic phrenic nerve (Figure 4-21), the left vagus nerve with its accompanying recurrent laryngeal nerve (Figure 4-22), and the esophagus.
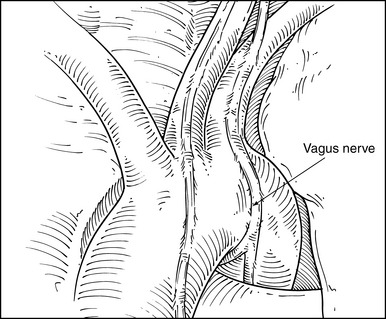
♦ The best way to assess level 5 (see Figure 4-20) and level 6 lymph nodes (Figure 4-23) is from a left thoracoscopic approach at the outset of a lobectomy. Bluntly sweep these nodes away from the recurrent laryngeal nerve at its takeoff from the vagus nerve at the level of the aortic arch. During proximal node dissection superior to the arch, be aware of the vagus nerve (Figure 4-24) because any injury at this level affects the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which takes off distal to this level. Medially at this level, the left innominate vein passes obliquely toward the midline to form the superior vena cava.
♦ Similar to the right side, the phrenic nerve courses from superior to inferior along the anterior hilum of the lung and should be swept away bluntly at the time of the dissection of the upper pulmonary vein and branches of the pulmonary artery to the upper lobe (see Figure 4-21).
♦ For left-sided pulmonary surgery, the surgeon must have a good understanding of the left pulmonary artery. It is short, and if there are any issues with dissection of the branches of the pulmonary artery, the surgeon should obtain proximal control before any bleeding occurs. Tamponade bleeding with a sponge stick through the anterior incision, although this makes it difficult to gain proximal control because of the short vessel length. If using an intrapericardial approach to the left main pulmonary artery, be careful not to compress or impede the outflow track of the right ventricle.
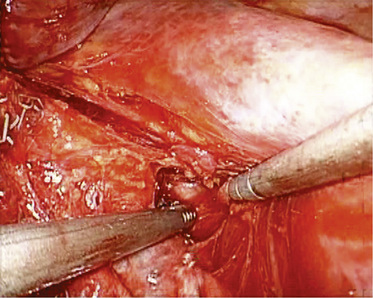
♦ In posterior hilar dissection, identify the posterior pulmonary arterial branches, and dissect out the level 10, 7, 8, and 9 lymph nodes. The esophagus is deep to the aorta at this level (Figure 4-25). The longitudinal muscle fibers are easy to identify. In dissecting the level 7 lymph nodes from the left side, gently retract the aorta and esophagus posteriorly to open up the subcarinal space (Figure 4-26). If there is bleeding in this region during dissection, the best initial approach is to pack the area with surgical cellulose to permit a better visualization of the source, which usually is a nodal artery that can be clipped or cauterized. Spare the vagus nerve, which passes from a superior to inferior direction in the posterior direction just medial to the aorta and along the esophagus, by sweeping it posteriorly along the surface of the aorta. Some of the branches to pulmonary hilum may be divided sharply to facilitate this.
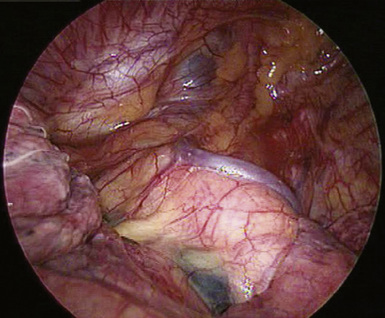
Figure 4-23 Level 6 lymph nodes can be visualized by retracting the left upper lobe anteriorly and slightly inferiorly.
Left Lower Lobectomy
♦ The diaphragm obscures the view of the inferoposterior hilum. Retract it with an Endokittner or EndoStitch device in the posterior aspect of the central tendon (Figure 4-27).
♦ After the inferior pulmonary ligament is released, the inferior vein is exposed. It is identified by the almost constant appearance of a level 9 lymph node at its inferior border (Figure 4-28). When this is observed, the vein is immediately superior to it. Because the esophagus can be adherent inferior and posterior to the vein, keep the dissection just inferior to the lower edge of the lung when releasing the ligament.
♦ Similar to the procedure for the right side, you should understand the relationships among the inferior pulmonary vein, the bronchus, and the pulmonary artery where it passes from its posterior location into the fissure. It is easier to identify the left pulmonary artery entering the fissure than the right, because its course is more direct into the fissure (Figure 4-29) and the middle lobe does not obscure its path. The takeoff of the superior segmental pulmonary artery is easy to identify (Figure 4-30). Often, the vagus nerve courses very close to the posterior aspect of the left lower lobe bronchus and vein. You can sweep it posteriorly to preserve it.
♦ The anatomy of the left lower lobe is consistent, and there is no middle lobe on the left, making this perhaps the easiest of the major lobes to resect using a VATS.
Esophageal Resection
♦ The esophagus runs from the thoracic inlet to the esophageal hiatus in a direct superoinferior direction (Figure 4-31).
♦ It usually is best to approach the esophagus from the right side when resecting it above its midportion because of the aortic arch on the left side (Figure 4-32).
♦ The airway lies anterior to the esophagus, and the aorta is located posteriorly. The thoracic duct runs posterior to the esophagus beginning at the esophageal hiatus, and it crosses to the left side at the level of the carina (T4). The vagal nerves run on the left and right sides of the esophagus.
♦ You can dissect the esophagus circumferentially using blunt dissection and electrocautery or harmonic energy.
♦ Because of the proximity of the esophagus to the right and left mainstem bronchi, the surgeon should avoid injury to the membranous airways by staying in an appropriate plane and not straying with the dissection when using electrocautery.
♦ When dissecting the esophagus from the aorta, use clips or the harmonic scalpel to secure the aortoesophageal branches. The more inferior branches usually are larger and require more attention. In this location, there may be large thoracic duct branches that should be similarly clipped. If there is any question about this approach, prophylactic use of an EndoStitch device is reasonable and can be accomplished by suturing all tissue between the aorta and azygous vein at the most inferior aspect of the chest.
Thymectomy
♦ The thymus gland is a midline structure located in the anterior mediastinum. It extends into the neck and can be accessed from the right side of the chest.
♦ The phrenic nerve outlines the lateral extent of the dissection (Figure 4-33). The left phrenic nerve can be identified from the right side in most cases. All tissue medial to this, including that in the anteroposterior window, must be removed. If visualization is difficult, a left-sided camera port may be placed.
♦ The right internal mammary vein drains into the right innominate vein and can be divided just before its entrance into the innominate vein to open up the space between the anterior and superior mediastinum.
♦ Two to three draining thymic veins drain from the body of the thymus into the left innominate vein, running in an inferosuperior direction (Figure 4-34). They should be divided between clips or with the harmonic scalpel.
♦ The diaphragm outlines the inferior extent of the dissection, and all associated fat should be removed with the thymus to remove any ectopic thymic tissue. The cervical poles of the thymus can be seen extending into the neck and can be teased out from the right VATS approach. Draining vessels can be clipped or cauterized.