Animal Attacks
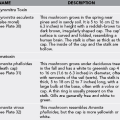
Recommended oral antibiotics for prophylaxis of domestic animal and human bite wounds are listed in Appendix J.
Wound Care
1. Irrigate the wound, preferably using normal saline solution. Alternatively, use boiled or otherwise treated and potable water (see Chapter 20 for more irrigation discussion).
2. If possible, add a germicidal agent to the irrigating solution. In order of preference, use 1% povidone-iodine solution (not “scrub”), 1% benzalkonium chloride, or ordinary hand (camping) soap. In a heavily contaminated wound, a 5% to 10% povidone-iodine solution may be used.
3. Complete the irrigation with a germicide-free solution (e.g., plain water) to rinse all irritating chemicals from the wound. Use 2% benzalkonium chloride to cleanse wounds inflicted by animals suspected of being rabid (see Chapter 43).
4. Clean the wound, if necessary, by swabbing with a soft, clean cloth or sterile gauze. Follow with a repeat irrigation.
5. Determine whether the injury is high or low risk for infection to make decisions about closure, need for antibiotics, and evacuation (Box 42-1).
6. If the wound edges are macerated, crushed, or extremely contaminated, perform sharp debridement.
7. If the wound must be closed to control bleeding, to allow dressing, or to facilitate evacuation, do so in a manner that allows drainage. Use tape, surgical adhesive strips, or loose approximating sutures or staples in preference to a tight closure.
a. High-risk wounds should be irrigated, debrided, and if possible left open for closure later. Do not primarily close bite wounds older than 6 to 12 hours (limbs) or 12 to 24 hours (face).
b. Immobilize high-risk wounds of the hand with a bulky mitten dressing in an elevated position, and start the patient promptly on an antibiotic (see Appendix J).
8. Cover the wound with a sterile dressing or a clean, dry cloth. Apply a topical antiseptic ointment, such as bacitracin/polymyxin B (Polysporin) or bacitracin, to abrasions and shallow wounds. Do not plug deep puncture wounds with antiseptic so that they cannot drain.
9. Apply a splint if appropriate to restrict motion.
10. If the wound is of the high-risk type (see following features) or treatment is hours away, administer a prophylactic antibiotic as listed in Appendix J. High-risk wounds have the following features:
a. Location: hand; scalp or face in infants; over a major joint (possible perforation); through-and-through wound of cheek
b. Type of wound: puncture; tissue crush; carnivore bite over a vital structure (artery, nerve, or joint)
c. Patient risk factor: older than age 50 years; asplenic; chronic alcoholic; immunosuppressed; diabetic; peripheral vascular insufficiency; receiving chronic corticosteroid therapy; prosthetic or diseased cardiac valve; prosthetic or seriously diseased joint
Wound Infection
The causative organisms in a wound infection after an animal bite are most often Staphylococcus or Streptococcus, but anaerobic infection may occur. Less common pathogens, such as Pasteurella or Eikenella, are usually sensitive to and effectively treated with the antibiotics discussed in Appendix J.
Specific Animal Considerations
1. If a dog’s large teeth cause facial or scalp wounds in a small child, particularly an infant, be alert for the possibility of an underlying skull or facial bone fracture.
2. For a bite made by a large dog or any other animal with large teeth, when the bite is close to a major vessel, examine the wound for absent or diminished pulse, sensory or motor deficit, large or expanding hematoma, or extremely active bleeding. Any of these may indicate an arterial injury that will require immediate evacuation to a center equipped with vascular imaging and surgeons.
Porcupine
1. Be aware that porcupine quills not only penetrate human skin but also can migrate up to 25 cm (9.8 inches). The quills are barbed with spongy cores, allowing them to absorb body fluid and expand, which makes removal even more difficult.
2. Pull the quill straight out. If the quill is deeply penetrated, make a small nick in the skin to allow egress of the entrapped barb.
Skunk
1. The skunk sprays its victim with musk from anal sacs. The musk causes skin irritation, keratoconjunctivitis, temporary blindness, nausea, and occasionally seizures and loss of consciousness. The chief component of the musk is butyl mercaptan.
2. Neutralize the butyl mercaptan with a strong oxidizing agent such as sodium hypochlorite in a 5.25% solution (household bleach), further diluted 1 : 5 or 1 : 10 in water. Then cleanse the area with tincture of green soap, followed by a dilute bleach rinse. Tomato juice as a shampoo has been advocated for deodorizing hair, which should then be washed and can be mildly bleached or cropped short.
Avoiding and Mitigating Animal Attacks
To avoid animal attacks and bites:
1. Do not leave young children alone with wild or potentially biting animals.
2. Never pet an unfamiliar dog, especially if it is tied up or confined.
3. Avoid sudden movements around animals.
4. Do not try to take food or favored objects away from animals.
5. Never try to separate fighting animals unless you are well protected; instead, use a bucket of water or a hose.
6. Do not invade the territory of nursing animals or animals with young offspring.
7. Do not corner or threaten animals, unless in a purposeful defensive gesture (such as when under attack by a cougar).
8. Know which animals you might encounter and their likely behaviors when frightened, hungry, irritated, and threatened, and how they will respond to your behaviors for the purposes of pacification, intimidation, and defense.
9. After handling food, wash hands before touching a hungry animal.
Bear Attack Prevention and Risk Reduction
1. Avoid camping along bear travel corridors or at feeding sites.
2. Use proper food storage to render human food unavailable to bears.
3. Avoid campsites littered with human refuse.
4. Reduce food odors by cooking and eating at a site away from the sleeping area. Do not sleep in clothes worn while cooking or eating.
5. Do not leave garbage or food buried or poured into the ground at the campsite.
6. Keep sleeping bags at least partially unzipped to facilitate a quick exit.
7. Sleep in a tent. Equip each tent with a flashlight. Consider equipping yourself with pepper spray.
Avoiding an Encounter
1. Make noise so that the bear knows a person is present. Bear bells may not be sufficiently loud.
2. Remain alert to the terrain and environment in bear country. An “upwind bear” is more likely to be surprised by you, as is one in heavy forestation, near loud rushing water, in the rain, or in fog.
3. Avoid ripened berry patches, streams with spawning fish, and elk calving grounds. A collection of ravens may indicate carrion and the presence of feeding bears.
4. If you see bear signs (e.g., tracks, scratchings, droppings, or a prey carcass), suspect that a bear is in the vicinity.
5. Do not approach bears or any wild animals too closely for a better view or photograph.
Avoiding an Attack
1. Allow the bear to know that you are human and not a prey species. Once the bear sees you, step out away from any visual obstruction and make it clear that you are a human. If you attempt to hide, you may confuse the bear. Speak in a calm voice to allow the bear to identify you.
2. Do not make sudden movements or yell out.
3. Do not stare directly at the bear. Look to the side or stand sideways to the bear. Never turn your back to any wild carnivore.
If a Grizzly Bear Attacks
1. Do not run, try to climb a tree, fight, or scream.
2. Drop to the ground, and protect the head and neck by interlocking the hands behind the head (ear level) and flexing the head forward, either in the fetal position or flat on the ground face down (Fig. 42-1). If a curious bear turns you supine, continue rolling to face down position.

FIGURE 42-1 Curling into the fetal position to defend against a grizzly bear attack. (Courtesy Marilynn G. French.)
3. Do not hold out an arm to ward off the attack.
4. Never try to look at the bear during an attack.
5. After the attack, minimize any perceived threat, and stay down until you are sure the bear has left the area.
6. When you believe the bear has left the area, peek around while moving as little as possible, try to determine which way the bear went, and then pick the best option for leaving the area.