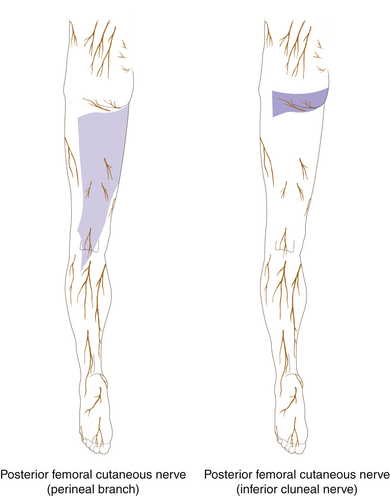
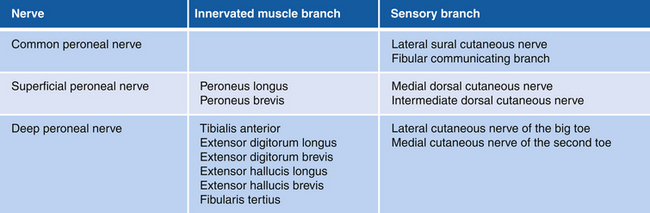
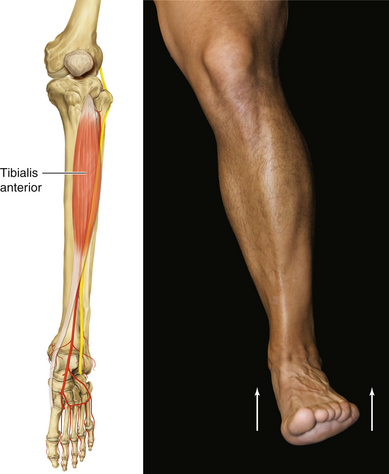
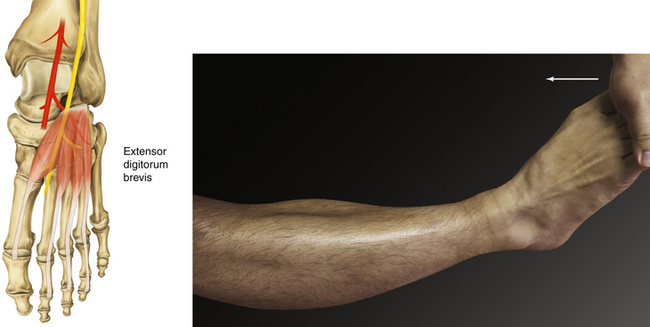
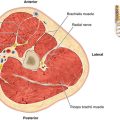
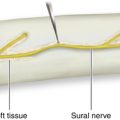
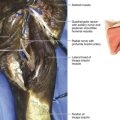
Chapter 13 Anatomy and Function in the Lower Extremity
Note: Unless otherwise noted, arrows in figures indicate the direction of patient motion.
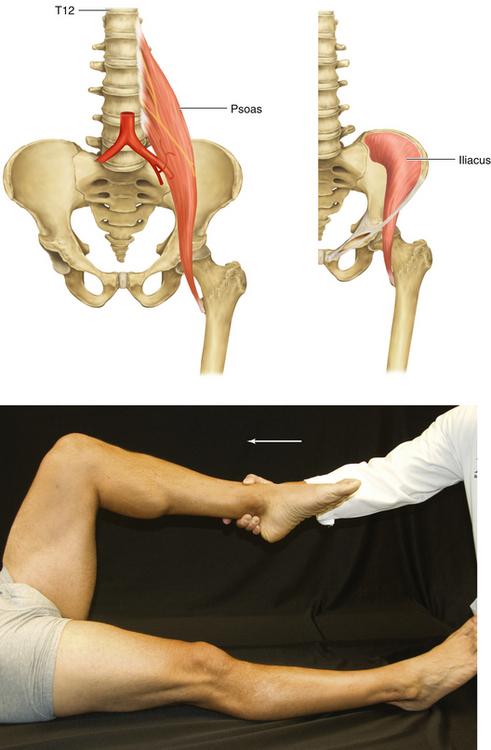
Figure 13-2 Iliopsoas: Psoas and Iliacus Muscles
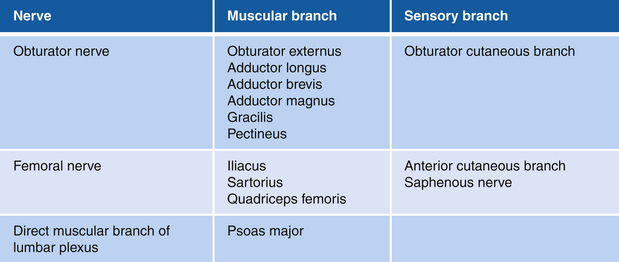
• Muscle attachments: Sides of T12 through L5 vertebrae to lesser trochanter of femur (psoas)
• Innervation: upper part of iliac fossa to lesser trochantor (iliacus)
• Function: Flexion of hip joint
• Physical examination: The patient lies supine with the leg flexed at the knee and hip and tries to flex the thigh against resistance.
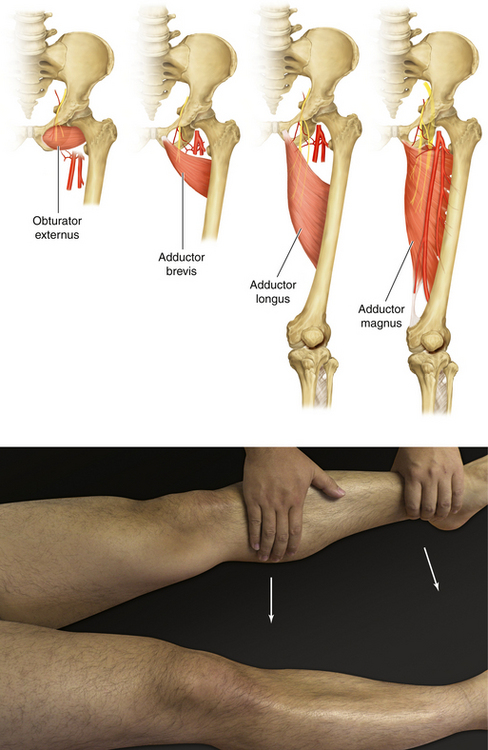
Figure 13-4 Hip Adductor Muscles: Obturator Externus, Adductor Brevis, Adductor Longus, and Adductor Magnus
• Physical examination: The patient lies supine with the leg extended at the knee and tries to adduct the hip joint against resistance.
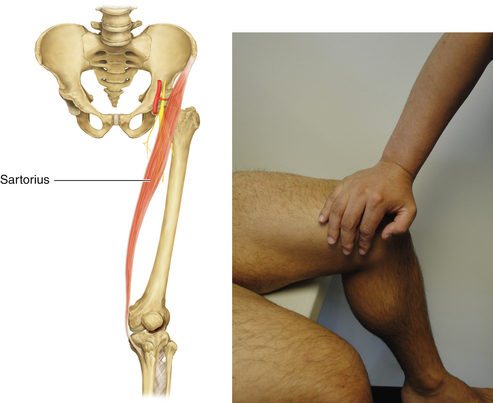
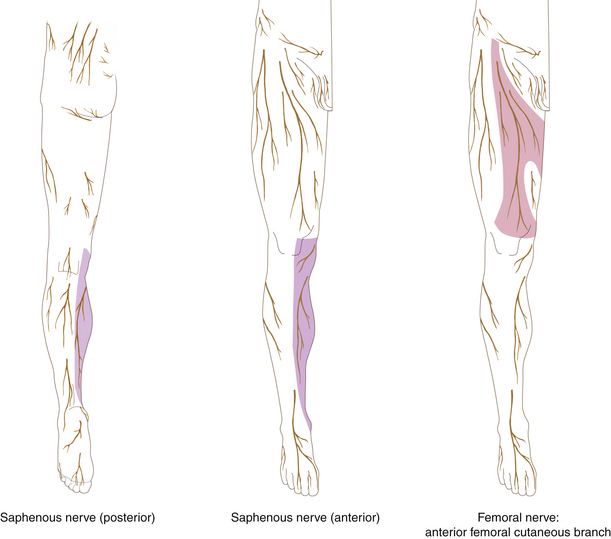
Figure 13-6 Sartorius Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Anterior superior iliac spine to tibia
• Innervation: Femoral nerve (L2 and L3)
• Function: Flexion and abduction of hip joint
• Physical examination: The patient sits in the “tailor’s position” (hip flexed and at maximal internal rotation, knee flexed) and attempts to flex the hip further against resistance applied at the medial surface of knee.
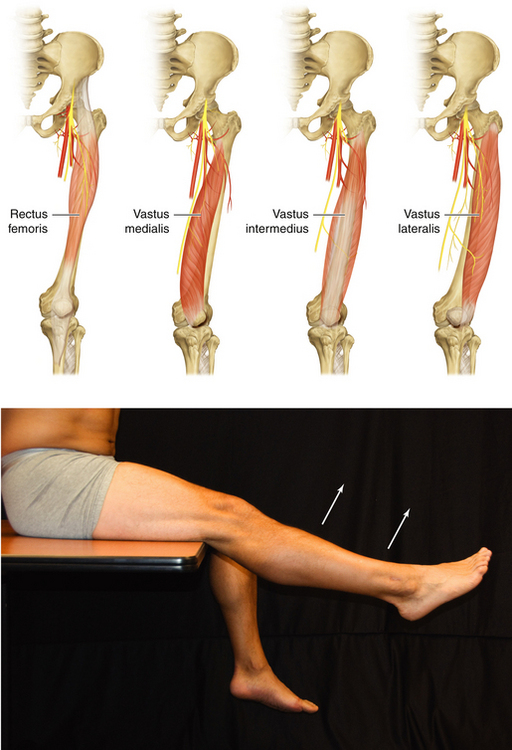
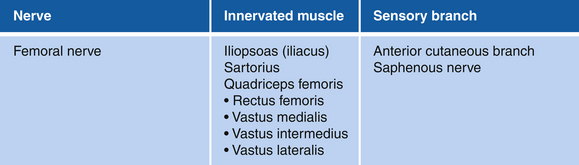
Figure 13-7 Quadriceps Femoris: Rectus Femoris, Vastus Medialis, Vastus Intermedius, and Vastus Lateralis Muscles
• Distal muscle attachments: Base of patella and by patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity
• Innervation: Femoral nerve (L2, L3, and L4)
• Function: Extension of knee joint
• Physical examination: With the leg flexed 90 degrees at the knee, the patient attempts to extend the knee against resistance.
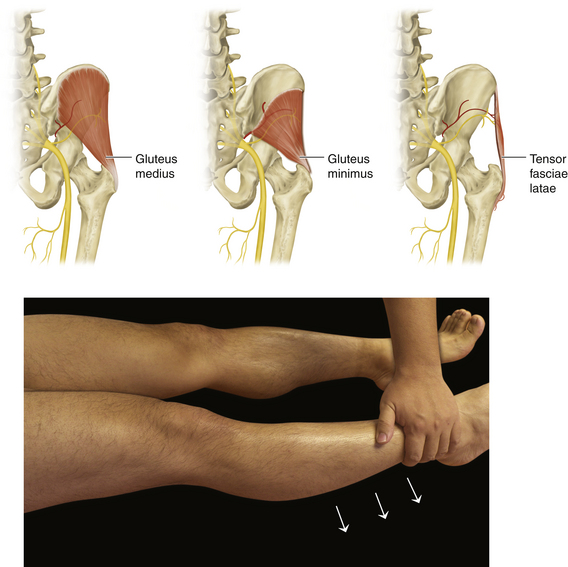
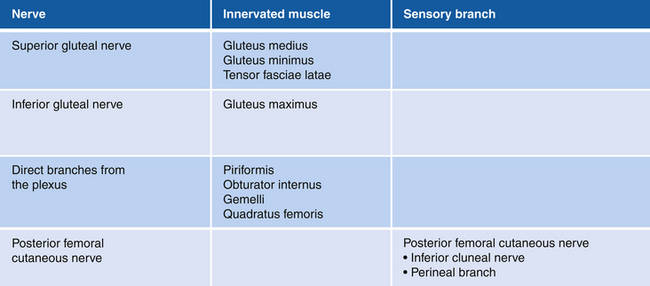
Figure 13-10 Gluteus Medius, Gluteus Minimus, and Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscles
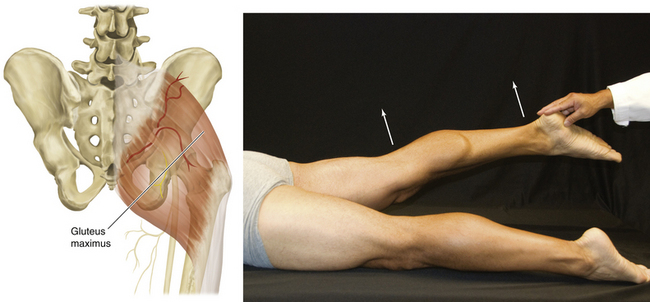
Figure 13-11 Gluteus Maximus Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Ilium, dorsal surface of sacrum and coccyx, and sacrotuberous ligament to gluteal tuberosity of femur and iliotibial tract
• Innervation: Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, and S2)
• Function: Extension of thigh and lateral rotation
• Physical examination: The patient lies prone with legs extended and tries to elevate the leg against resistance.
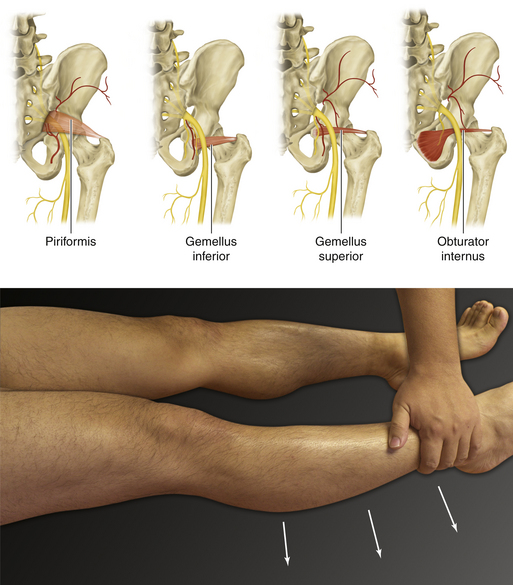
Figure 13-12 Piriformis, Gemellus Inferior, Gemellus Superior, and Obturator Internus Muscles
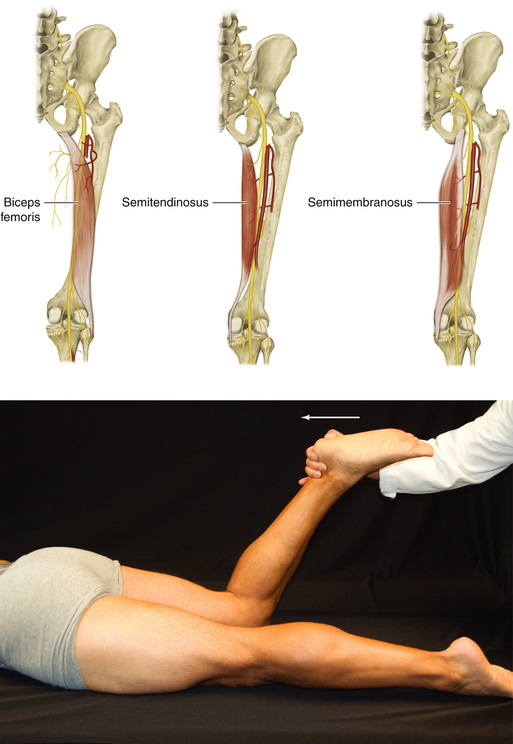
Figure 13-15 Hamstring Muscles: Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosus, and Semimembranosus
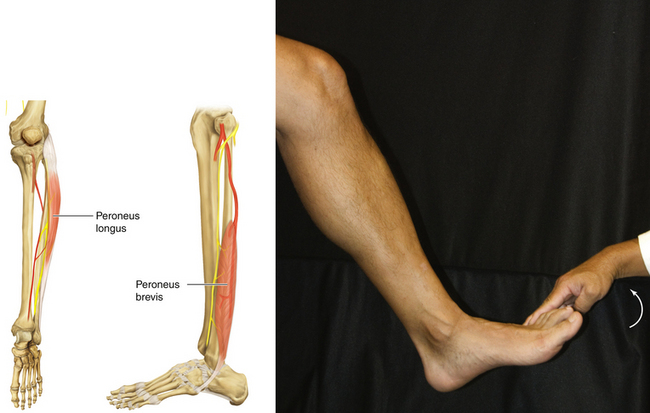
Figure 13-17 Peroneus Longus and Peroneus Brevis Muscles
• Muscle attachments: Head and surface of fibula to first metatarsal, medial cuneiform, and lateral tuberosity of fifth metatarsal
• Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, and S2)
• Function: Plantar flexion of talocrural joint and eversion of subtalar joint
• Physical examination: The patient tries to evert the foot against resistance.
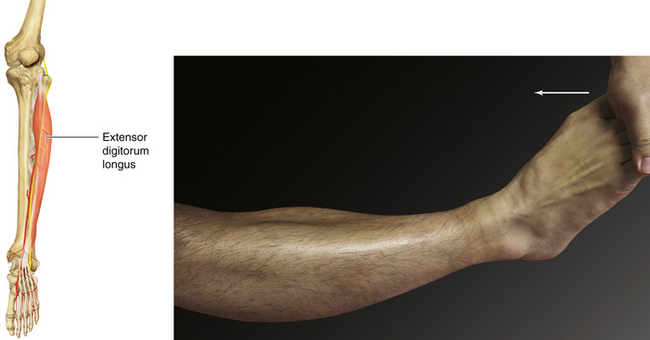
Figure 13-19 Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Lateral condyle of tibia and interosseous membrane to phalanges of lateral four digits
• Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve (L5 and S1)
• Function: Dorsiflexion of ankle joint and extension of metatarsophalangeal joints of the second through fifth toes
• Physical examination: The patient tries to extend the metatarsophalangeal joints against resistance.
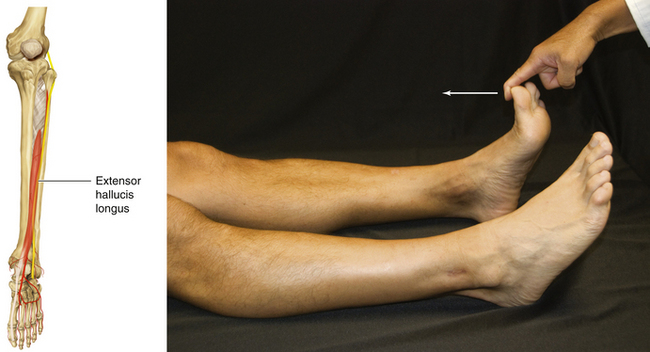
Figure 13-20 Extensor Hallucis Longus Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Fibula and interosseous membrane to distal phalanx of great toe
• Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve (L5 and S1)
• Function: Dorsiflexion of ankle joint and extension of metatarsophalangeal joint of big toe
• Physical examination: The patient tries to extend the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe against resistance.
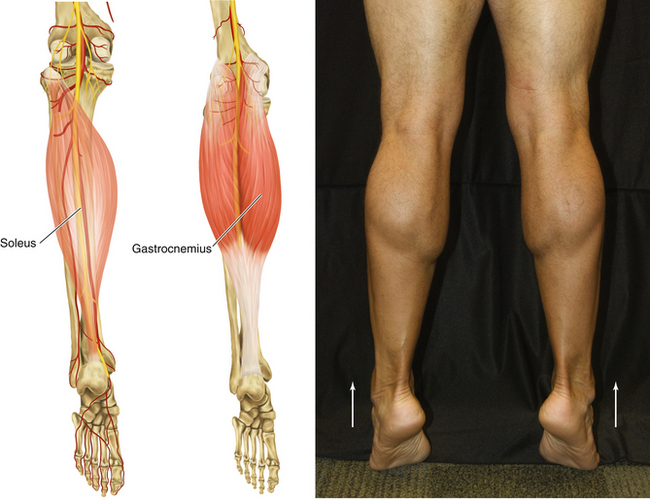
Figure 13-24 Triceps Surae: Soleus and Gastrocnemius Muscles
• Muscle attachments: Lateral condyle of femur, popliteal and posterior surfaces of femur, head of femur, soleal line, and medial border of tibia to posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
• Innervation: Tibial nerve (S1 and S2)
• Function: Plantar flexion of ankle joint
• Physical examination: The patient tries to plantar flex the ankle joint against resistance.
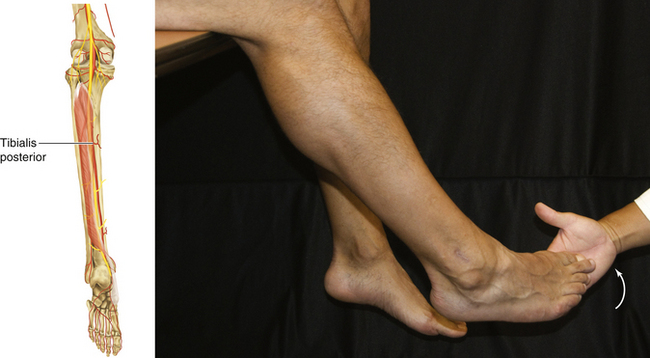
Figure 13-25 Tibialis Posterior Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Interosseous membrane and posterior surfaces of tibia and fibula to tuberosity of navicular, cuneiform, cuboid, and bases of second, third, and fourth metatarsals
• Innervation: Tibial nerve (L4 and L5)
• Function: Plantar flexion of ankle joint and inversion of subtalar joint
• Physical examination: The patient tries to invert the foot against resistance.
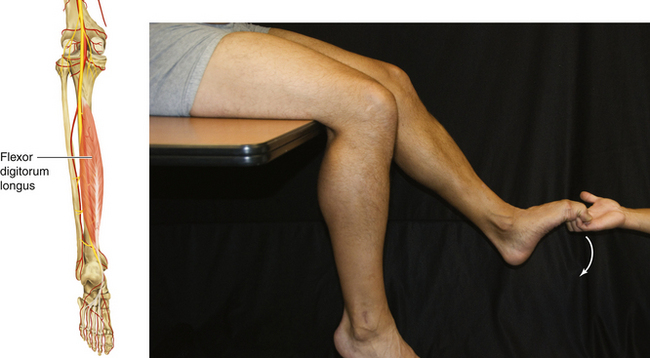
Figure 13-26 Flexor Digitorum Longus Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Posterior surface of tibia and, by a broad tendon to the fibula, to bases of distal phalanges of lateral four digits
• Innervation: Tibial nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Plantar flexion of metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the second through fifth toes
• Physical examination: The patient tries to flex the toes against resistance.
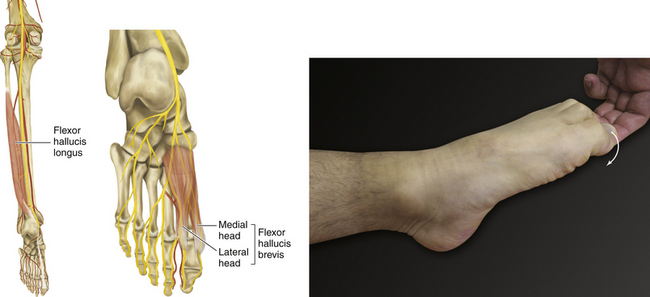
Figure 13-27 Flexor Hallucis Longus Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Posterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane to base of distal phalanx of great toe
• Innervation: Tibial nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Plantar flexion of great toe.
• Physical examination: The patient tries to flex the big toe against resistance.
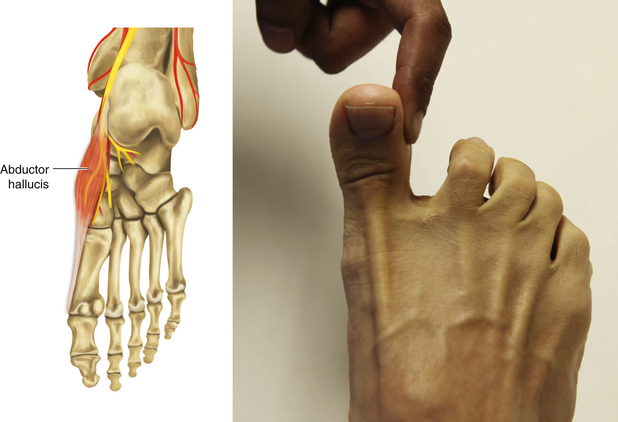
Figure 13-28 Abductor Hallucis Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Medial tubercle of tuberosity of calcaneus, flexor retinaculum, and plantar aponeurosis to base of proximal phalanx of first digit
• Innervation: Medial plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Flexion and medial abduction of first metatarsophalangeal joint of big toe
• Physical examination: The patient tries to abduct the big toe against resistance.
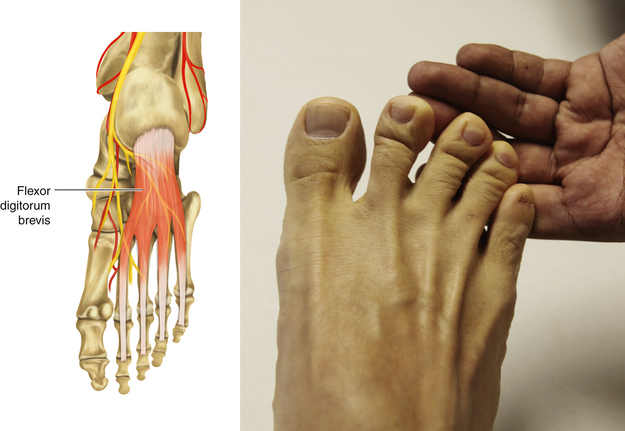
Figure 13-29 Flexor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Medial tubercle of tuberosity of calcaneus, plantar aponeurosis, and intermuscular septa to both sides of middle phalanges of lateral four digits
• Innervation: Medial plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Flexion of the metatarsophalangeal joint and proximal interphalangeal joints of the second through fifth toes
• Physical examination: The patient tries to plantar flex the lateral four toes against resistance.
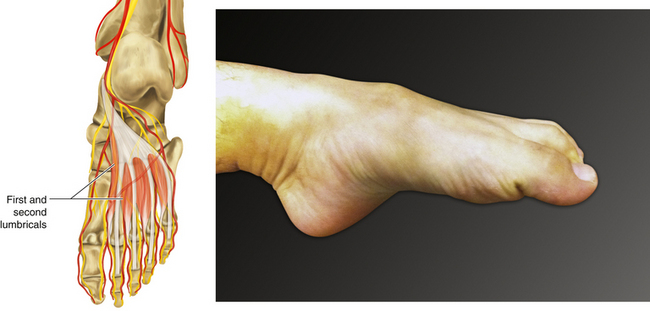
Figure 13-30 Lumbricals
• Muscle attachments: Tendons of flexor digitorum longus to medial aspect of expansion over lateral four digits
• Medial toe: Medial plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Lateral three toes: Lateral plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Flexion of metatarsophalangeal joints of the second through fifth toes, extension of interphalangeal joints of the second through fifth toes, and adduction of the second through fifth toes toward the big toe
• Physical examination: The patient tries to cup the sole of the foot.
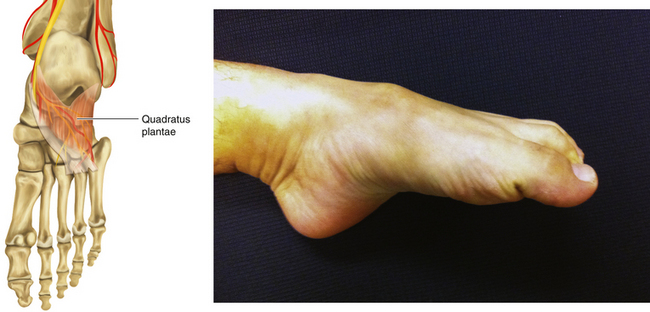
Figure 13-31 Quadratus Plantae Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Plantar surfaces of cuboid and lateral cuneiform to both sides of base of proximal phalanx of first digit
• Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Aiding the function of flexor digitorum longus
• Physical examination: The patient lies supine and tries to cup the sole of the foot.
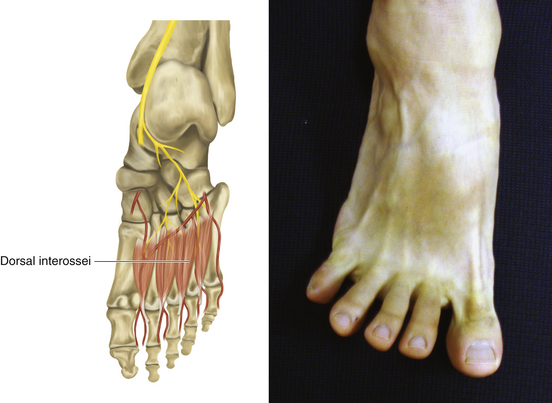
Figure 13-33 Dorsal Interossei
• Muscle attachments: Adjacent sides of metatarsals 1 through 5 to medial side of proximal phalanx of second digit (first) and lateral sides of second to fourth digits (second to fourth)
• Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Flexion of metatarsophalangeal joints of second to fourth toes, extension of interphalangeal joints of second to fourth toes, and abduction of third and fourth toes from second toe
• Physical examination: The patient tries to abduct the toes.
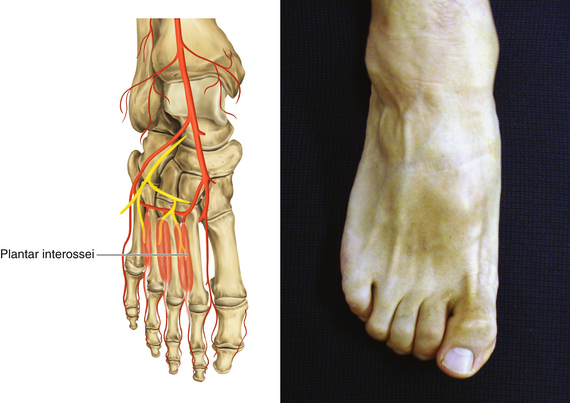
Figure 13-34 Plantar Interossei
• Muscle attachments: Bases and sides of metatarsals 3 through 5 to medial sides of bases of proximal phalanges of third to fifth digits
• Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Flexion of metatarsophalangeal joints of third to fifth toes, extension of interphalangeal joints of third to fifth toes, and adduction of third through fifth toes to second toe
• Physical examination: The patient tries to adduct the toes.
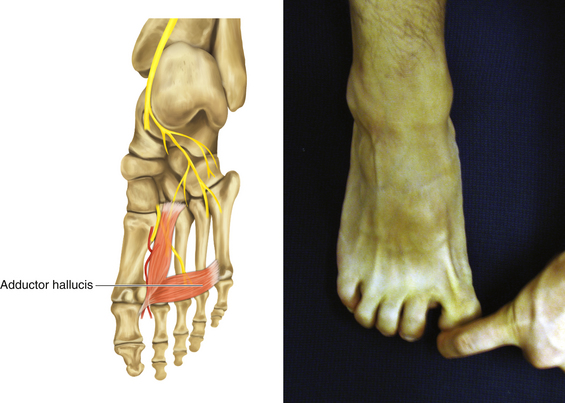
Figure 13-35 Adductor Hallucis Muscle
• Muscle attachments: Bases of metatarsals 2 to 4 (oblique head) and plantar ligaments of metatarsophalangeal joints (transverse head) to tendons of lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of first digit
• Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve (S2 and S3)
• Function: Flexion of the first metatarsophalangeal joint and adduction of the big toe
• Physical examination: The patient tries to adduct the big toe against resistance.