221 Anaemia
Patient 1
Salient features
Patient 2
Salient features
Examination
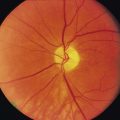
• Comment on the pallor of the face and conjunctiva, looking for the lemon-yellow hue of pernicious anaemia.
Questions
How would you investigate macrocytic anaemia?
• Vitamin B12 and red-cell folate and serum folate concentrations
• Serum ferritin, plasma iron and total iron-binding capacity (for associated iron deficiency)
• Gastric parietal cell and intrinsic factor antibodies
• Reticulocyte count (a high MCV could be present when the reticulocyte count is >50%)
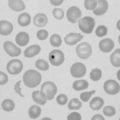
When is a peripheral smear useful in the evaluation of anaemia?
• Sickle cell disease: dactylitis or sudden splenic enlargement and pallor in a young child, or limb, abdominal or chest pain in an older child or adult
• Thrombocytopenia (e.g. petechiae or abnormal bruising) or neutropenia (e.g. unexpected or severe infection)
• Lymphoma or other lymphoproliferative disorder (lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly): enlargement of the thymus (a mediastinal mass on radiology) or other lymphoid organs, skin lesions suggestive of infiltration, bone pain and systemic symptoms such as fever, sweating, itching and weight loss
• Myeloproliferative disease: splenomegaly, plethora, itching or weight loss
• Disseminated non-haematopoietic cancer: weight loss, malaise, bone pain
• Disseminated intravascular coagulation
• Infectious mononucleosis or other viral infection or inflammatory or malignant disease: general ill health, often with malaise and fever
• Bacterial or parasitic disease
• Acute or recent-onset renal failure or unexplained renal enlargement
• Retinal examination reveals haemorrhages, exudates, signs of hyperviscosity, optic atrophy