Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis
Signs and Symptoms
1. Urticaria (hives), diffuse erythematous rash, and soft tissue edema present in up to 90% of patients
2. Wheezing, stridor, cough, chest tightness, hoarseness, dyspnea
3. Dysphagia, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
4. Hypotension and tachycardia (shock)
6. Edema involving the face, lips, tongue, pharynx, and larynx, producing an obstructed airway and respiratory arrest
7. Cardiovascular collapse with shock can occur rapidly, without any other antecedent symptoms.
8. In general, the more immediate the reaction after exposure to the inciting antigen, the more severe the degree of anaphylaxis.
9. Most anaphylactic reactions occur within 5 minutes to 2 hours after exposure to an inciting agent. The median time interval between onset of symptoms and respiratory or cardiac arrest is 5 minutes in medication-induced anaphylaxis, 15 minutes in stinging insect venom–induced anaphylaxis, and 30 minutes in food-induced anaphylaxis.
Treatment
1. In the event of anaphylactic shock, immediately administer epinephrine in the field.
a. Epinephrine 1 : 1000 (1 mg/mL solution) should be injected intramuscularly into the mid–anterolateral thigh (vastus lateralis muscle). Subcutaneous administration results in slower absorption and is less reliable.
b. The dose for an adult is 0.3 to 0.5 mL (0.3 to 0.5 mg), and for a child it is 0.01 mL/kg (0.1 mg/kg), not to exceed a total dose of 0.3 mL (0.3mg). Repeat in 5 to 15 minutes if relief is not complete.
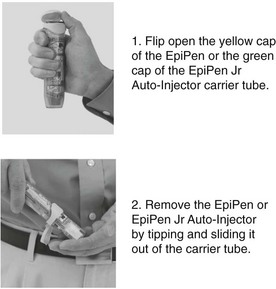
c. Epinephrine is available in a spring-loaded injectable cartridge that facilitates self-administration (EpiPen 0.3 mg [Figs. 26-1 and 26-2], Adrenaclick 0.3 mg, or Twinject 0.3 mg per dose adult dose). A child who weighs less than 30 kg (66 lb) should be injected with an EpiPen Jr 0.15 mg, Adrenaclick 0.15 mg, or Twinject 0.15 mg per dose.

FIGURE 26-2 How to use the auto-injector. (Image courtesy Dey Pharma, L.P., Basking Ridge, New Jersey).
d. If the reaction is life threatening and if the patient does not respond to intramuscular epinephrine, administer epinephrine intravenously. Mix 0.1 mL (0.1 mg) of 1 : 1000 aqueous epinephrine in 10 mL of normal saline (final dilution, 1 : 100,000) and infuse over 10 minutes. In an infant or child, the starting dose is 0.1 mcg/kg/min up to a maximum of 1.5 mcg/kg/min. This solution can also be injected through the venous plexus under the tongue if an intravenous line cannot be established.
e. There are no absolute contraindications to the use of epinephrine in the treatment of anaphylaxis, but caution is advised when treating a person older than age 50 years because epinephrine can produce cardiac ischemia and arrhythmias. The risk for death or serious disability from hypoxic encephalopathy as a result of inadequately treated anaphylaxis almost always outweighs other concerns.
f. In a refractory case in which the individual is not responsive to epinephrine (e.g., an individual on a β-blocker medication), administer glucagon 1 to 2 mg (adult dose) or 20 to 30 mcg/kg to a maximum of 1 mg (pediatric dose) intravenously over 5 minutes, or intramuscularly. Rapid administration of glucagon can induce vomiting; therefore protect the airway, for example, by placing the patient in the lateral recumbent position, if there is drowsiness or obtundation.
2. Place the individual in the Trendelenburg position, although this is of limited utility to support the blood pressure during shock.
3. Obtain and maintain the airway, administering oxygen as needed.
4. Administer an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 50 mg PO q4-6h for an adult; for children give 1 mg/kg PO q4-6h.
5. Consider adding a histamine2 blocker, such as cimetidine 400 to 800 mg PO.
6. Treat bronchospasm and wheezing with albuterol via a handheld, metered-dose inhaler with a spacer (adult dose: 200 to 400 mcg [4 to 8 full inhalations, depending on the preparation] q15-20min prn).
7. Administer a corticosteroid. If IV access is available, administer 125 mg methylprednisolone or 15 mg dexamethasone. If therapy is initiated orally, administer prednisone, 60 to 100 mg for adults and 2 mg/kg for children. Oral dexamethasone 8 to 16 mg adult dose and 0.15 to 0.6 mg/kg for children may also be used as an alternative to prednisone.
8. If a stinger remains after an insect sting, remove it by the most rapid means possible.
9. Note that in severe cases, endotracheal intubation may be necessary. Be sure to visualize the vocal cords with a rigid laryngoscope because of the distortion caused by laryngeal edema. If an airway cannot be obtained immediately, perform a cricothyrotomy (see Chapter 10); for a child under 12 years of age, perform a needle cricothyrotomy or tracheotomy if oral intubation is not successful.
10. After treatment, be prepared to transport the patient immediately for medical evaluation, because an anaphylactic reaction can recur as the effects of the epinephrine diminish.
11. If the reaction is limited to only pruritus and urticaria with no wheezing or facial swelling, administer antihistamines (see earlier) alone.
Allergic Rhinitis
Treatment
1. Nasal corticosteroids are the gold standard of treatment for allergic rhinitis. Several preparations are available; all are equally effective. An example is fluticasone (Flonase) 1 to 2 sprays in each nostril daily.
2. For more immediate relief of symptoms, administer an oral antihistamine (may be in combination with nasal corticosteroids), such as cetirizine (Zyrtec) 10 mg daily. The dose for children younger than 12 years of age is 2.5 to 10 mg daily.
3. In some individuals, addition of a decongestant, such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) 60 mg PO q4-6h, to the antihistamine may be helpful.
4. Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) are approved for use in allergic rhinitis. Montelukast and zafirlukast are two currently available oral LTRAs. The dose of montelukast for adults and adolescents 15 years of age and older is 10 mg at bedtime. Pediatric dose is 5 mg and 4 mg at bedtime for ages 6 to 14 years and 6 months to 5 years, respectively.