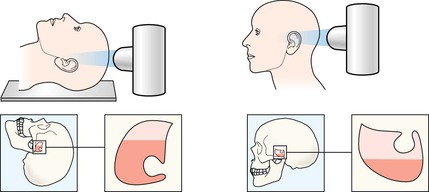
Adult skull
Following an apparently mild head injury requests for skull radiography (SXR) will occur very infrequently1–9. Compelling evidence that CT should be the examination of choice was initially based on a meta-analysis of 20 head injury surveys7. SXR series may still be requested, perhaps in remote locations where imaging facilities are limited.
Analysis: false positive diagnoses
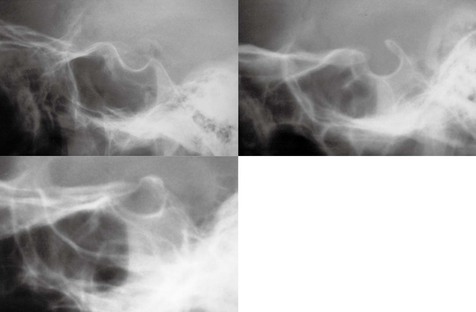
Most difficulties with interpretation arise because a normal appearance can be mistaken for an abnormality. These false positive diagnoses can be reduced by being familiar with the following.
▪ The normal sutures and accessory sutures (pp. 36–39). Specifically, the position and appearance of:
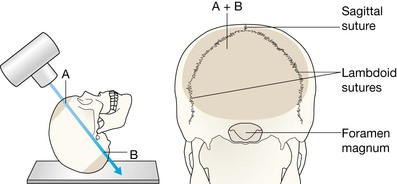
□ the three large sutures: the lambdoid, coronal and sagittal;
□ the other smaller sutures around the mastoid bones.
▪ The metopic suture (p. 38). The most common accessory suture persisting in some adults.
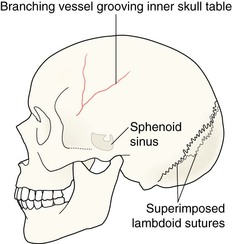
▪ Vascular impressions. Specifically:
□ the sites of the most common vessel grooves/markings;
□ the radiographic features (p. 52) that help to distinguish between a fracture and a vessel marking.
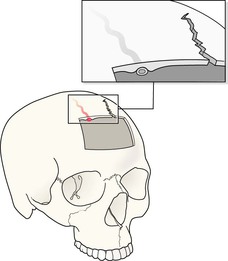
Analysis: recognising a fracture
In practice, the detection of a SXR abnormality is easy. There are really only three findings/abnormalities that indicate that a fracture is present—and one of these is very rare. The radiographs need to be checked/inspected in a systematic manner.
Step 1
Scrutinise the area on the radiograph which corresponds to the site of injury. Vary the windowing if necessary.