Acute renal failure
Aetiology
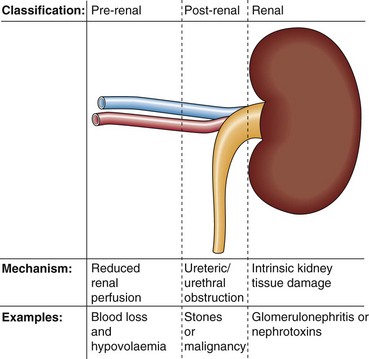
Kidney failure or uraemia can be classified as (Fig 18.1):
 Pre-renal: the kidney fails to receive a proper blood supply.
Pre-renal: the kidney fails to receive a proper blood supply.
 Post-renal: the urinary drainage of the kidneys is impaired because of an obstruction.
Post-renal: the urinary drainage of the kidneys is impaired because of an obstruction.
 Renal: intrinsic damage to the kidney tissue. This may be due to a variety of diseases, or the renal damage may be a consequence of prolonged pre-renal or post-renal problems.
Renal: intrinsic damage to the kidney tissue. This may be due to a variety of diseases, or the renal damage may be a consequence of prolonged pre-renal or post-renal problems.
Diagnosis
Biochemical findings in pre-renal uraemia include the following:
 Serum urea and creatinine are increased. Urea is increased disproportionately more than creatinine because of its reabsorption by the tubular cells, particularly at low urine flow rates. This leads to a relatively higher serum urea concentration than creatinine, which is not so readily reabsorbed.
Serum urea and creatinine are increased. Urea is increased disproportionately more than creatinine because of its reabsorption by the tubular cells, particularly at low urine flow rates. This leads to a relatively higher serum urea concentration than creatinine, which is not so readily reabsorbed.
 Metabolic acidosis: because of the inability of the kidney to excrete hydrogen ions.
Metabolic acidosis: because of the inability of the kidney to excrete hydrogen ions.
 Hyperkalaemia: because of the decreased glomerular filtration rate and acidosis.
Hyperkalaemia: because of the decreased glomerular filtration rate and acidosis.
Acute tubular necrosis
 acute blood loss in severe trauma
acute blood loss in severe trauma
 specific renal disease, such as glomerulonephritis
specific renal disease, such as glomerulonephritis
 nephrotoxins, such as the aminoglycosides, analgesics or herbal toxins.
nephrotoxins, such as the aminoglycosides, analgesics or herbal toxins.
It may be difficult to decide the reason for a patient’s oliguria. The biochemical features that distinguish pre-renal uraemia from intrinsic renal damage are shown in Table 18.1.
Table 18.1
Biochemical features in the differential diagnosis of the oliguric patient
| Biochemical feature | Pre-renal failure | Intrinsic renal damage |
| Urine sodium | <20 mmol/L | >40 mmol/L |
| Urine/serum urea | >10 : 1 | <3 : 1 |
| Urine/plasma osmolality | >1.5 : 1 | <1.1 : 1 |
Management
Important issues in the management of the patient with ARF include:
 Correction of pre-renal factors, if present, by replacement of any ECF volume deficit. Care should be taken that the patient does not become fluid overloaded. In cardiac failure, inotropic agents may be indicated.
Correction of pre-renal factors, if present, by replacement of any ECF volume deficit. Care should be taken that the patient does not become fluid overloaded. In cardiac failure, inotropic agents may be indicated.
 Treatment of the underlying disease (e.g. to control infection).
Treatment of the underlying disease (e.g. to control infection).
 Biochemical monitoring. Daily fluid balance charts provide an assessment of body fluid volume. Serum creatinine indicates the degree of impairment of the GFR and the rate of deterioration or improvement. Serum potassium should be monitored closely.
Biochemical monitoring. Daily fluid balance charts provide an assessment of body fluid volume. Serum creatinine indicates the degree of impairment of the GFR and the rate of deterioration or improvement. Serum potassium should be monitored closely.
 Dialysis. Indications for dialysis include a rapidly rising serum potassium concentration, severe acidosis, and fluid overload.
Dialysis. Indications for dialysis include a rapidly rising serum potassium concentration, severe acidosis, and fluid overload.
Recovery
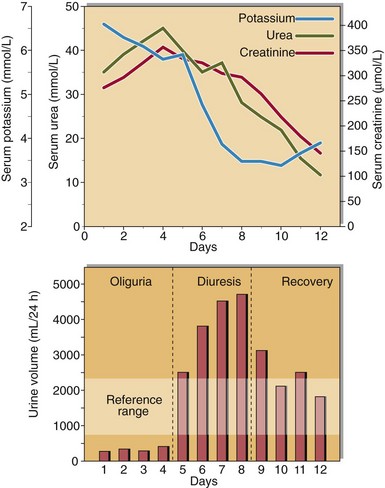
There may be three distinct phases in the resolving clinical course of a patient with acute renal failure (Fig 18.2). An initial oliguric phase, where glomerular impairment predominates, is followed by a diuretic phase when urine output is high, as glomerular function slowly improves but tubular function remains impaired. During a recovery phase, complete renal function may return. Careful clinical and biochemical monitoring is necessary throughout the course of the patient’s illness.