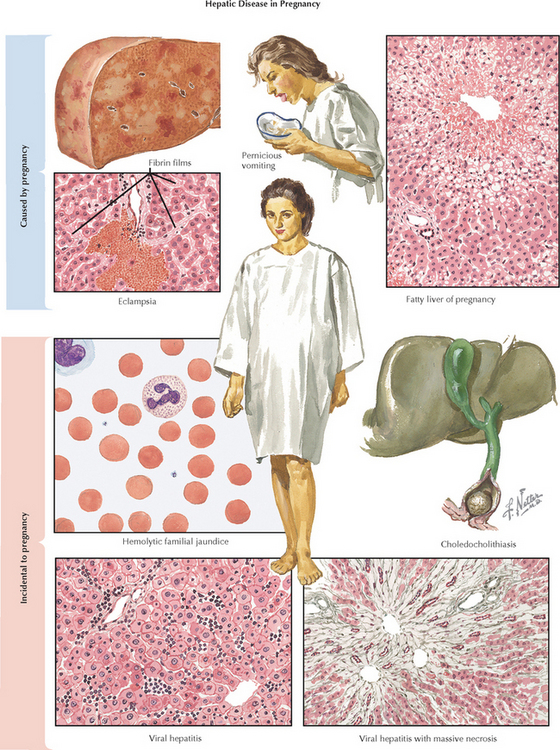
Chapter 196 Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
INTRODUCTION
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Signs and Symptoms
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
Workup and Evaluation
MANAGEMENT AND THERAPY
Nonpharmacologic
FOLLOW-UP
Fesenmeier MF, Coppage KH, Lambers DS, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy in 3 tertiary care centers. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:1416.
Ibdah JA, Okajima Y, Kang XS, et al. A fetal fatty-acid oxidation disorder as a cause of liver disease in pregnant women. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1723.
Pereira SP, O’Donohue J, Wendon J, et al. Maternal and perinatal outcome in severe pregnancy-related liver disease. Hepatology. 1997;26:1258.
Reyes H, Sandoval L, Wainstein A, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: a clinical study of 12 episodes in 11 patients. Gut. 1994;35:101.
Yang Z, Yamada J, Zhao Y, et al. Prospective screening for pediatric mitochondrial trifunctional protein defects in pregnancies complicated by liver disease. JAMA. 2002;288:2163-2166.
Barton JR, Sibai BM, Mabie WC, Shanklin DR. Recurrent acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;163:534.
Guntupalli SR, Steingrub J. Hepatic disease and pregnancy: an overview of diagnosis and management. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:S332.
Ibdah JA. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: an update on pathogenesis and clinical implications. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:7397.
Kaplan MM. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:367.
Ko H, Yoshida EM. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006;20:25.
Rajasri AG, Srestha R, Mitchell J. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP)—An overview. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2007;27:237.
Steingrub JS. Pregnancy-associated severe liver dysfunction. Crit Care Clin. 2004;20:763. xi.
Wolf JL. Liver disease in pregnancy. Med Clin North Am. 1996;80:1167.