Chapter 15 ACUTE DIARRHOEA
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The symptoms of acute diarrhoea vary according to the portion of the intestine that is involved in the disease process. Infectious diarrhoea is often associated with symptoms of nausea, vomiting and abdominal cramps.
AETIOLOGY
Infectious and non-infectious causes may be responsible for acute diarrhoea (Table 15.1).
| Bacteria |
Infectious causes include bacteria, viruses and protozoa.
Bacteria
Viruses
Viruses cause the vast majority of all cases of acute diarrhoea.
ASSESSMENT
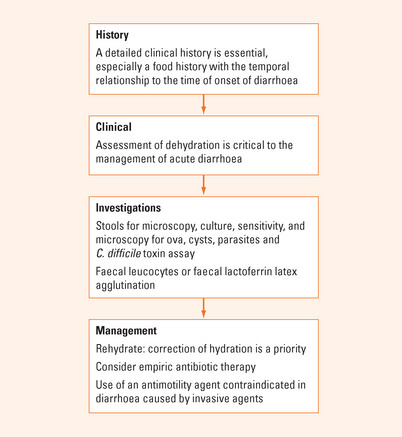
Assessment of the severity of dehydration is critical in the management of acute diarrhoea. Features suggestive of severe dehydration and subsequent need for hospital admission and intravenous fluid replacement include tachycardia, >20 mmHg decrease in systolic blood pressure, postural hypotension, poor skin turgor, severe dry mucosa and sunken eye balls. Other indications for consideration of hospital admission include stool frequency (>8/day), fever, significant constitutional symptoms, large amount of bloody diarrhoea, immunocompromised host, infants or the elderly.
Clostridium difficile should be suspected after recent antibiotic use or hospitalisation.
INVESTIGATIONS
Stool culture
Specifically request cultres for Yersinia, enterohaemolytic E. coli (EHEC), viruses and Vibrio.
TREATMENT
Persistent diarrhoea from suspected Giardia infection should be treated with metronidazole 250–750 mg three times daily for 7–10 days.
When an intestinal bacterium or protozoon is isolated, specific antibiotic therapy can be prescribed (Table 15.2).
TABLE 15.2 Recommendations for therapy against specific pathogens
| Organism | Recommendations for adults |
| Campylobacter species | Erythromycin 500 mg b.i.d. for 5 days |
| Salmonella (non-typhi species) | Not recommended in mild to moderate disease. |
| For severe disease, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim if susceptible or fluoroquinolone antibiotic for 5–7 days | |
| Shigella species | Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 160/800 mg respectively b.i.d. for 3 days (if susceptible) or fluoroquinolone antibiotic for 3 days |
| Escherichia coli Shiga toxin producing (O157:H7) | Supportive treatment only |
| Toxigenic Clostridium difficile | Offending antibiotic withdrawn if possible, treat with metronidazole 250 mg q.i.d. to 500 mg t.i.d. for 10 days |
| Cryptosporidium species | If severe, consider paromomycin, 500 mg t.i.d. for 7 days |
| Giardia | Metronidazole 250–750 mg t.i.d. for 7–10 days |
| Entamoeba histolytica | Metronidazole 750 mg t.i.d. for 5–10 days, plus either diiodohydroxyquin 650 mg t.i.d for 20 days or paromomycin 500 mg t.i.d. for 7 days |
b.i.d. = twice daily; q.i.d. = four times daily; t.d.s. = three times daily.
SUMMARY
Infectious diarrhoea is common worldwide. The majority of infections are self-limiting. A patient’s history is crucial as it may allow the early use of empiric antibiotic therapy (Figure 15.1). Clinical evaluation should identify if there is any evidence of volume depletion and oral rehydration solution can be started early to decrease the rate of hospitalisation. Stool cultures are often not required but should be considered in patients with severe illness, bloody diarrhoea or those with underlying inflammatory bowel disease in whom the distinction between a flare-up or coexisting infection needs to be excluded. Antimotility agents may be useful in symptomatic patients without evidence of fever or bloody stools.
Bouza E, Burillo A, Munoz P. Antimicrobial therapy of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Med Clin North Am. 2006;90:1141-1163.
Guerrant RL, Van Gilder T, Steiner TS. Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:331-350.
Manatsathit S, Dupont HL, Farthing M, et al. Guideline for the management of acute diarrhea in adults. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:S54-S71.
Musher DM, Musher BL. Contagious acute gastrointestinal infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2417-2427.
Thielman NM, Guerrant RL. Clinical practice. Acute infectious diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:38-47.