61 Abnormal gait
Salient features
Examination
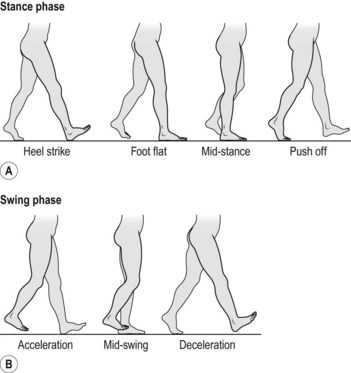
There are several types of abnormal gait. Keep in mind the phases and pathogenesis of gait (Fig. 61.1):
1 Heel strike: the lateral calcaneus makes contact with the ground and the muscles, tendons and ligaments relax, providing for optimal energy absorption.
2 Midstance: the foot is flat and is able to adapt to uneven terrain, maintain equilibrium and absorb the shock of touchdown; the calcaneus is just below the ankle, keeping the front and back of the foot aligned for optimal weight bearing.
3 Heel rise: the calcaneus lifts off the ground, the foot pronates, the muscles, tendons and ligaments tighten, and the foot regains its arch.