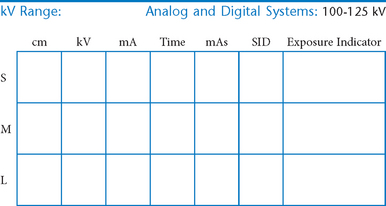
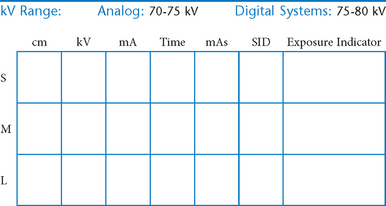
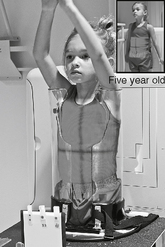Abdomen and Common Contrast Media Procedures
• Shielding and positioning landmarks
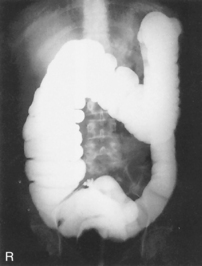
• Barium distribution and body positions
 AP supine and AP erect critique
AP supine and AP erect critique
 Lateral and dorsal decubitus critique
Lateral and dorsal decubitus critique
 AP supine and erect abdomen critique
AP supine and erect abdomen critique
 R and L lateral decubitus (double contrast)
R and L lateral decubitus (double contrast)
 AP/PA axial (butterfly position)
AP/PA axial (butterfly position)
 Lateral decubitus and AP/PA axial critique
Lateral decubitus and AP/PA axial critique
 AP and posterior oblique critique
AP and posterior oblique critique
 Posterior obliques and lateral
Posterior obliques and lateral
Abdomen and Common Contrast Media Procedures
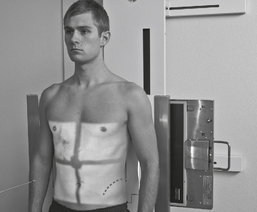
Shielding and Positioning Landmarks
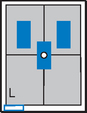
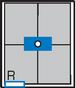
Gonadal Shielding
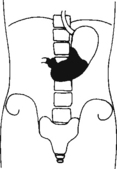
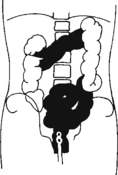
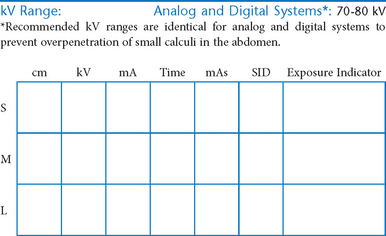
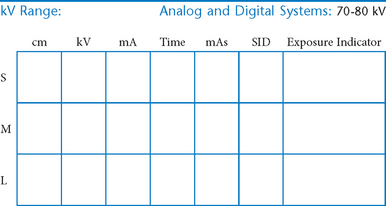
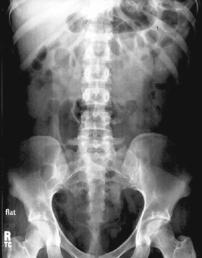
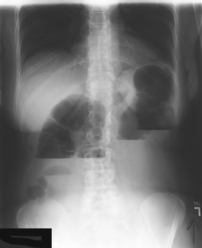
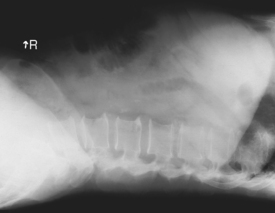
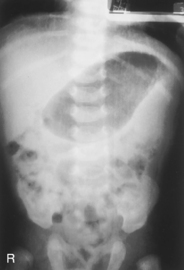
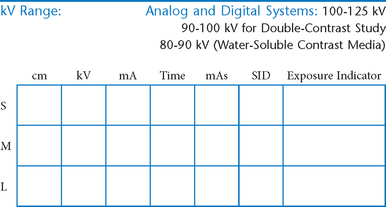
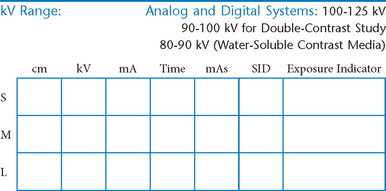
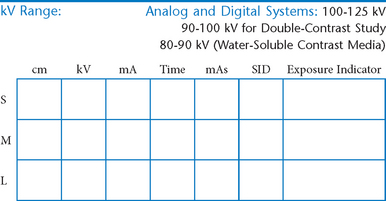
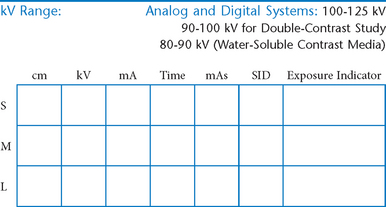
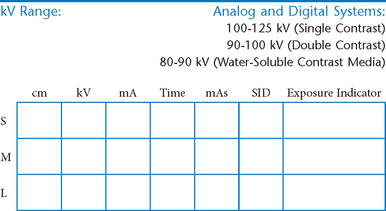
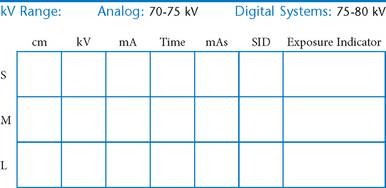
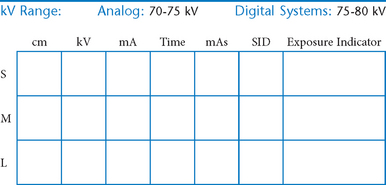
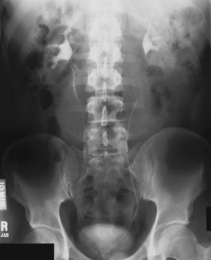
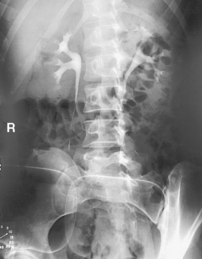
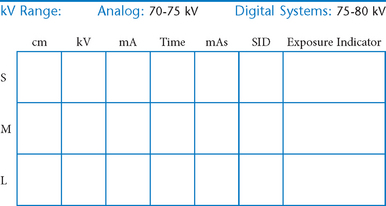
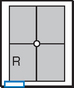
AP Abdomen (KUB)*
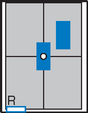
Position
• Supine, legs extended, arms at sides
• Midsagittal plane aligned and centered to centerline
• Ensure no rotation (ASISs equal distance from tabletop)
• Center of IR to level of iliac crests, ensuring that upper margin of symphysis pubis is included on lower IR margin. (A large hypersthenic patient may require that the IR be placed crosswise with a second IR centered higher.)
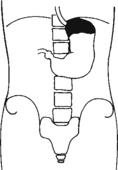
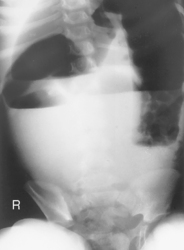
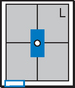
Erect AP Abdomen*
AP Supine and AP Erect Abdomen
Abdomen*
• Arrow marker to include upside
• Patient should be on side a minimum of 5 minutes before exposure; 10 to 20 minutes is preferred.
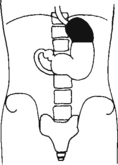
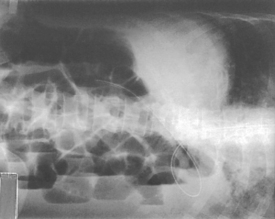
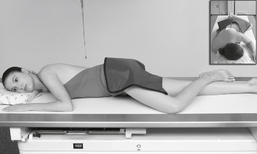
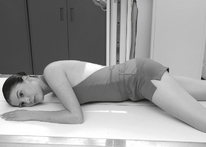
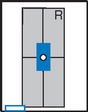
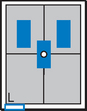
Position
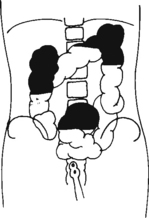
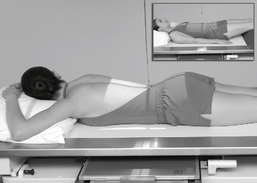
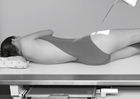
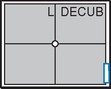
• Patient on side (on decubitus board or support to elevate downside abdomen), knees partially flexed, arms up near head
• Adjust patient and stretcher so center of IR and table (and CR) is approximately 2″ (5 cm) above level of iliac crest (to include diaphragm)
• Adjust height of IR to ensure that upside of abdomen is included for possible free air
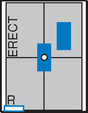
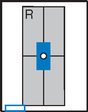
Abdomen*
Position
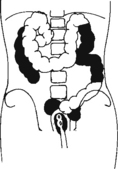
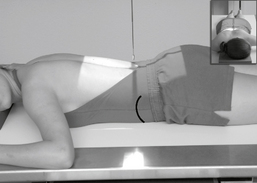
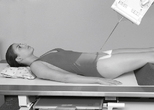
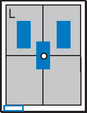
• Patient supine (on decubitus board or support to elevate posterior abdomen), side against table, arms above head
• Secure stretcher (lock wheels)
• Center of IR and table (and CR) at level of iliac crest (2″ above iliac crest to include diaphragm)
• Adjust height of IR to align midcoronal plane to centerline of IR
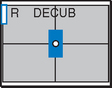
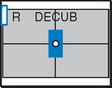
Lateral and Dorsal Decubitus Abdomen
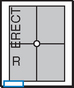
AP Pediatric Abdomen (KUB)*
AP Erect Pediatric Abdomen*
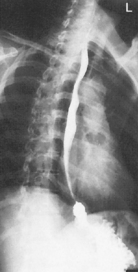
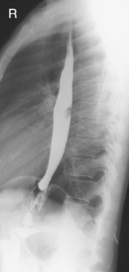
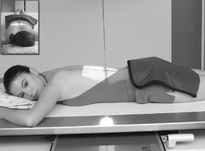
Esophagogram—RAO*
Esophagogram—Lateral*
Esophagogram—AP (PA)*
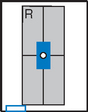
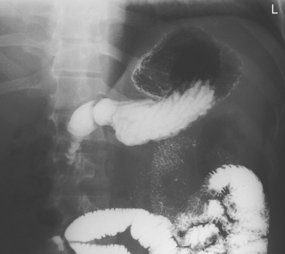
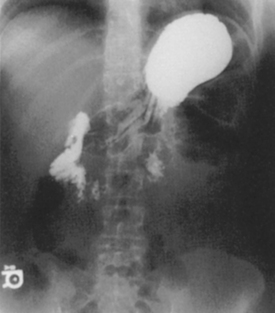
Upper GI—PA*
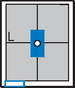
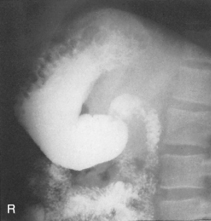
Upper GI—RAO*
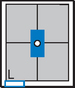
Upper GI—Lateral*
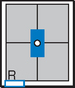
Upper GI—AP*
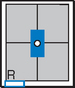
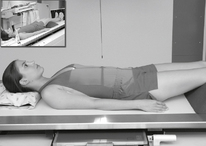
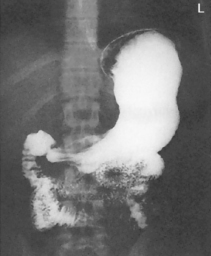
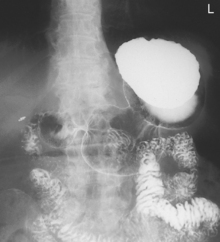
Fig. 9-31 AP supine Trendelenburg, upper GI (stomach) (Trendelenburg position best demonstrates hiatal hernia).
Lateral and AP Upper GI
Upper GI—LPO*
Small Bowel Series—PA*
A common routine includes images at 15- or 30-minute intervals until barium reaches ileocecal valve.
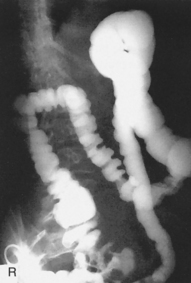
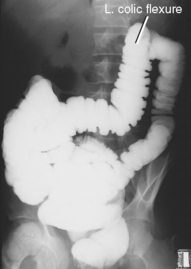
Barium Enema—PA or AP*
PA (AP) Barium Enema
Barium Enema—RAO and LAO*
Oblique Barium Enema
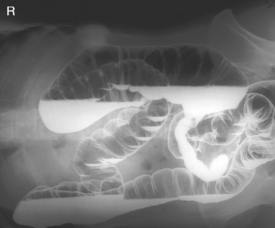
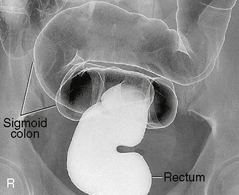
Barium Enema—Lateral Rectum (Ventral Decubitus)*
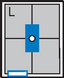
Alternative ventral decubitus projection is often performed for double-contrast studies.
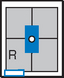
Barium Enema—Lateral Decubitus*
Both right and left lateral decubitus are commonly taken as part of a double-contrast series.
Lateral Decubitus and AP/PA Axial Barium Enema
Intravenous Urogram*
Intravenous Urogram*
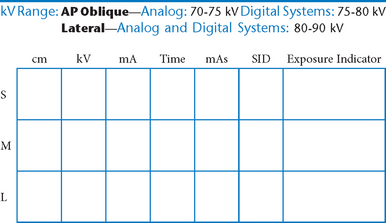
AP and Posterior Oblique IVU
Evaluation Criteria
Intravenous Urogram*
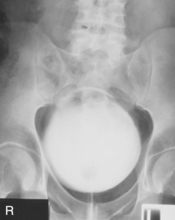
Cystogram—AP*
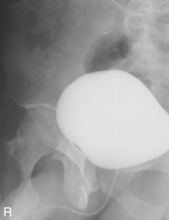
Cystogram—Posterior Obliques*
(RPO, LPO, and Optional Lateral)
Note: Cystogram routine may not include a lateral because of high gonadal dose.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 116.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 119.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 118.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 120.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 644.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 645.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 478.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 479.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 480.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 483.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 482.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 484.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 486.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 485.
*More rotation for hypersthenic patients
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 513.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 515.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 516 and 517.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 519.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 520.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 523.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 554.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 556.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 557.

 AP supine (KUB) (R)
AP supine (KUB) (R) AP erect (S)
AP erect (S) Lateral decubitus (S)
Lateral decubitus (S) Dorsal decubitus (S)
Dorsal decubitus (S) AP supine (R)
AP supine (R) AP erect (R)
AP erect (R) Lateral decubitus (S)
Lateral decubitus (S)
 AP supine (R)
AP supine (R) AP erect (R)
AP erect (R) Lateral decubitus (S)
Lateral decubitus (S) AP supine (KUB) (R)
AP supine (KUB) (R) AP erect (S)
AP erect (S) RAO
RAO Lateral
Lateral RAO and lateral critique
RAO and lateral critique AP (PA)
AP (PA) PA
PA RAO
RAO PA and RAO critique
PA and RAO critique Lateral
Lateral AP
AP Lateral and AP critique
Lateral and AP critique LPO
LPO LPO critique
LPO critique PA
PA PA (AP)
PA (AP) PA (AP) critique
PA (AP) critique Anterior/Posterior oblique
Anterior/Posterior oblique Oblique critique
Oblique critique Lateral rectum
Lateral rectum AP/PA (scout and series)
AP/PA (scout and series) Posterior obliques
Posterior obliques AP erect (postvoid)
AP erect (postvoid) AP
AP AP and posterior oblique critique
AP and posterior oblique critique