Chapter 42 A FAMILY HISTORY OF LIVER DISEASE
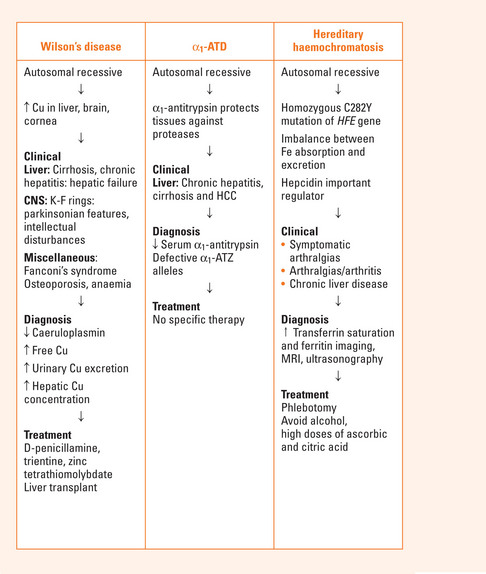
WILSON’S DISEASE
Clinical features
Hepatic
Diagnosis
Liver biopsy: hepatic Cu concentration >250 μg/g dry tissue (normal less than 50 μg/g).
Treatment
Trientine: second-line therapy. Less potent Cu chelator. Sideroblastic anaemia a major side effect.
Zinc: used mainly in presymptomatic patients as maintenance therapy and in combination therapy.
Liver transplantation: transplant recipients have an excellent long-term prognosis because the underlying biochemical defect is corrected.
ALPHA1-ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY (A1-ATD)
Clinical manifestations
Liver disease
Liver disease encompasses chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. α1-ATD should be considered in any adult who presents with the above diseases of unknown aetiology. α1-ATD is usually diagnosed early in life (4–8 weeks of life) presenting as persistent jaundice with raised liver transaminases and bilirubin.
Investigations: serum concentrations of α1-AT and detection of defective α1-ATZ alleles.
HEREDITARY HAEMOCHROMATOSIS
Hereditary haemochromatosis (HH) is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder. Most adult patients are homozygous for the C282Y mutation of the HFE gene (C282Y: C282Y). A small but significant percentage of HH patients have the mutation C282Y:H63D termed the compound heterozygote state (see Chapter 37).
Clinical presentation
The most common presenting symptoms are:
Investigations
| Inherited | Acquired |
|---|---|
Treatment
Phlebotomy at weekly intervals with regular monitoring of haemoglobin and haematocrit values. The target ferritin level should be 25–50 mg/L. Once Fe stores have been mobilised, phlebotomy 3 or 4 times per year may be adequate.
High doses of ascorbic and citric acid and dietary supplements containing Fe should be avoided.
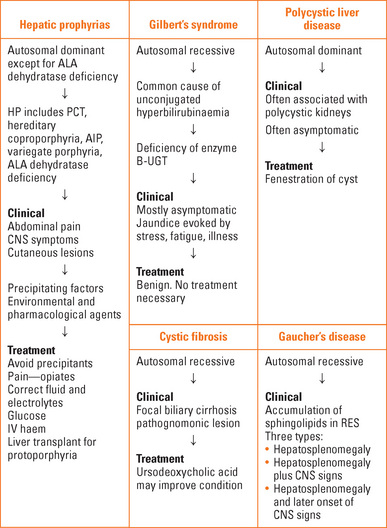
HEPATIC PORPHYRIAS
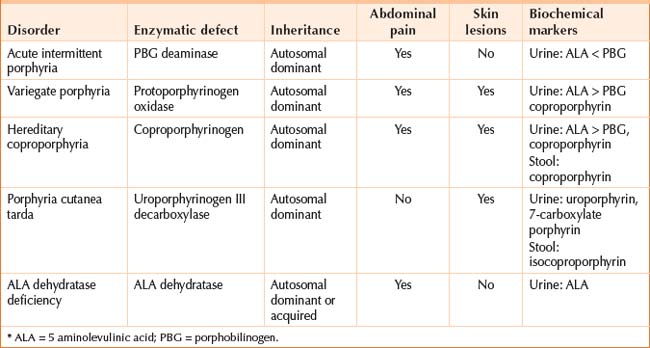
The hepatic porphyrias are: acute intermittent porphyria, variegate porphyria, hereditary coproporphyria, porphyria cutanea tarda, ALA dehydratase porphyria (Table 42.2).
Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria and erythropoietic protoporphyria involve the liver and bone marrow.
Clinical features
Acute porphyrias
CYSTIC FIBROSIS (CF)
GAUCHER’S DISEASE
POLYCYSTIC LIVER DISEASE
GILBERT’S SYNDROME
Pathogenesis
There is a defect in the hepatic uptake of bilirubin by the hepatocyte and a partial defect in conjugation of bilirubin. There is a reduction in the enzyme bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 (B-UGT), the enzyme responsible for formation of conjugated bilirubin in the hepatocyte. This is from a mutation in the gene encoding B-UGT (in the promoter region upstream to exon-1) that reduces production. Gilbert’s syndrome arises in those homozygous for the variant promoter.
Ferenci P. Wilson’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:726-733.
Lazaridis KN, Petersen GM. Genomics, genetic epidemiology and genomic medicine. Clin Gastroentrol Hepatol. 2005;3:320-328.
Stoller JK, Aboussouan LS. α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Lancet. 2005;365:2225-2236.
Zoller H, Cox T. Haemochromatosis: genetic testing and clinical practice. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:945-958.