Most other toxins result in ↓ density due to steatohepatitis ± hepatocellular necrosis
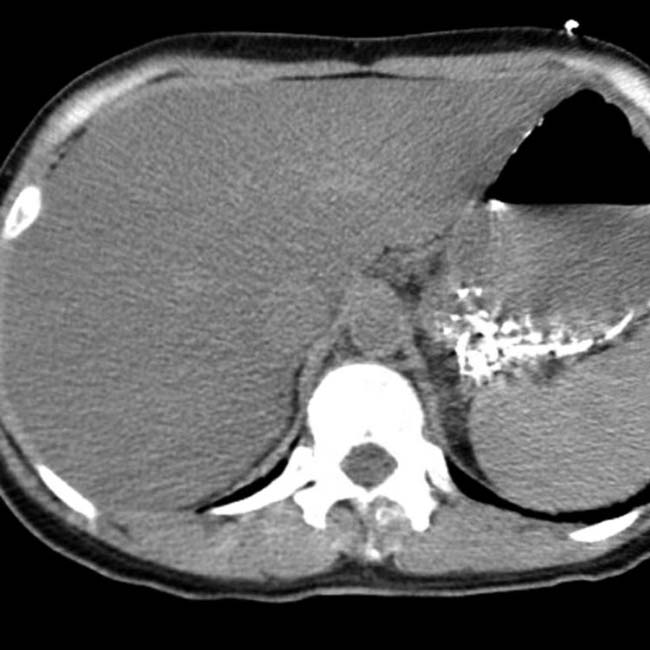

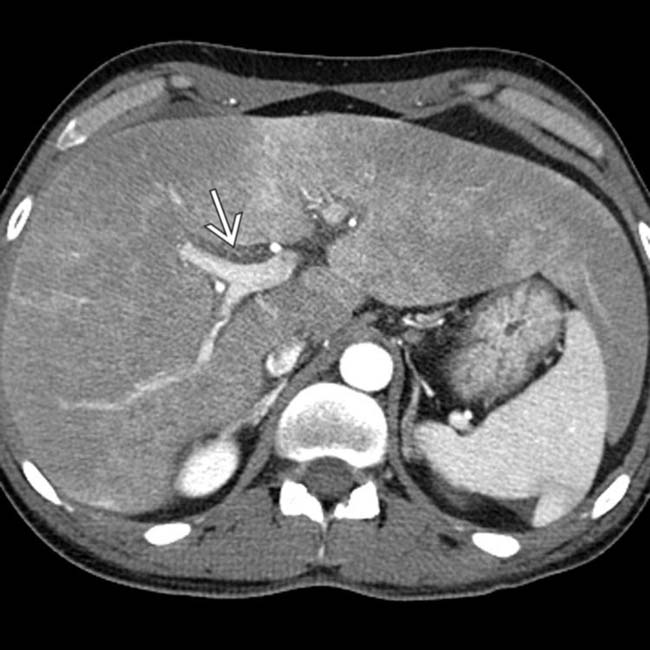
 . This was attributed to the combined toxic effects of alcohol abuse and acetaminophen used to treat a hangover.
. This was attributed to the combined toxic effects of alcohol abuse and acetaminophen used to treat a hangover.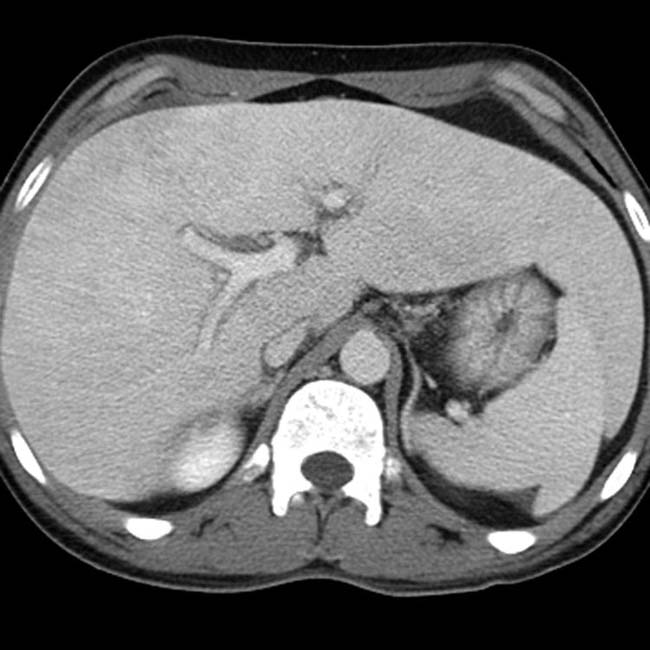
 .
.
 , a bad prognostic sign in the setting of acute toxic hepatic injury.
, a bad prognostic sign in the setting of acute toxic hepatic injury.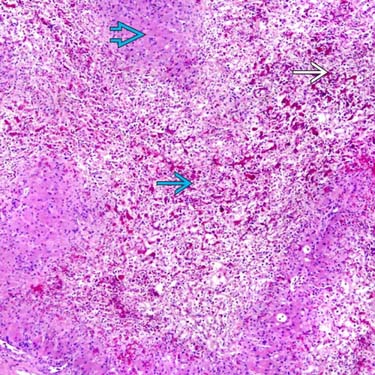
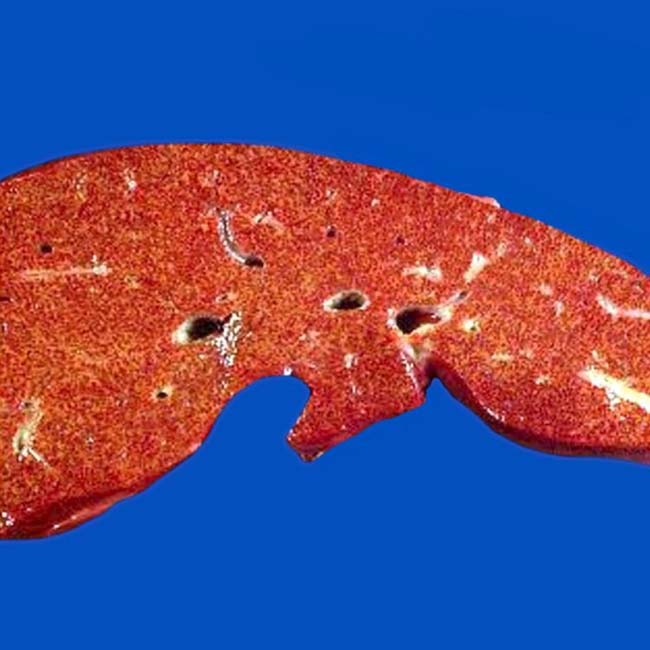
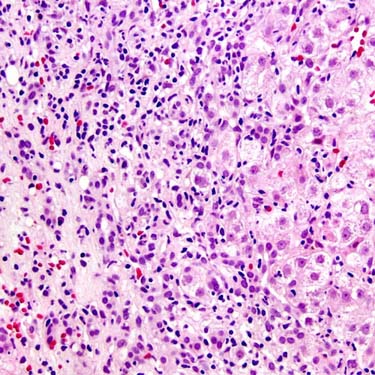
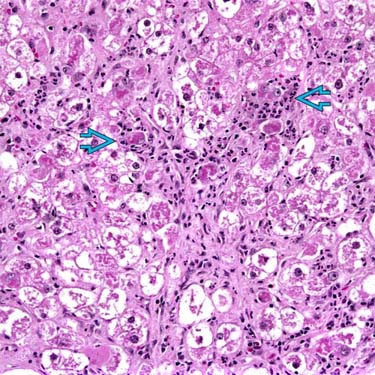
 , congestion
, congestion  , and lack of inflammation with sparing of periportal hepatocytes
, and lack of inflammation with sparing of periportal hepatocytes  are typical of acetaminophen toxicity but can also be seen in acute ischemia and acute Budd-Chiari syndrome. (Courtesy S. Kakar, MD.)
are typical of acetaminophen toxicity but can also be seen in acute ischemia and acute Budd-Chiari syndrome. (Courtesy S. Kakar, MD.)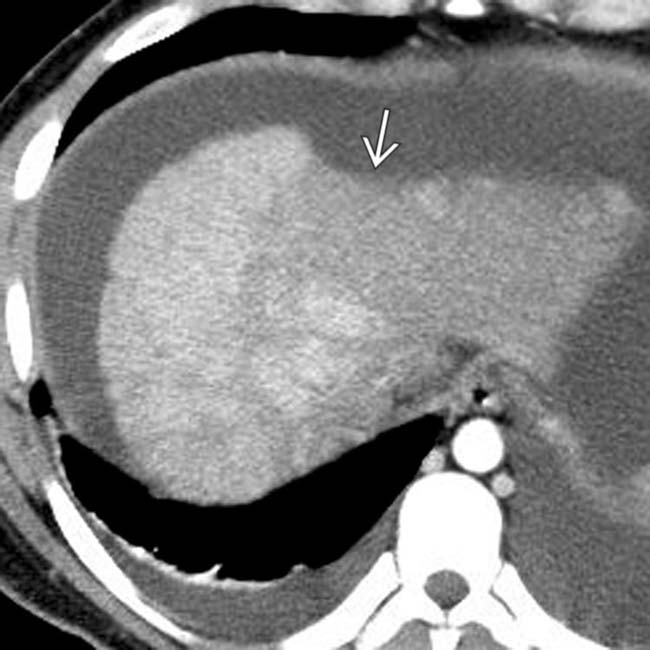
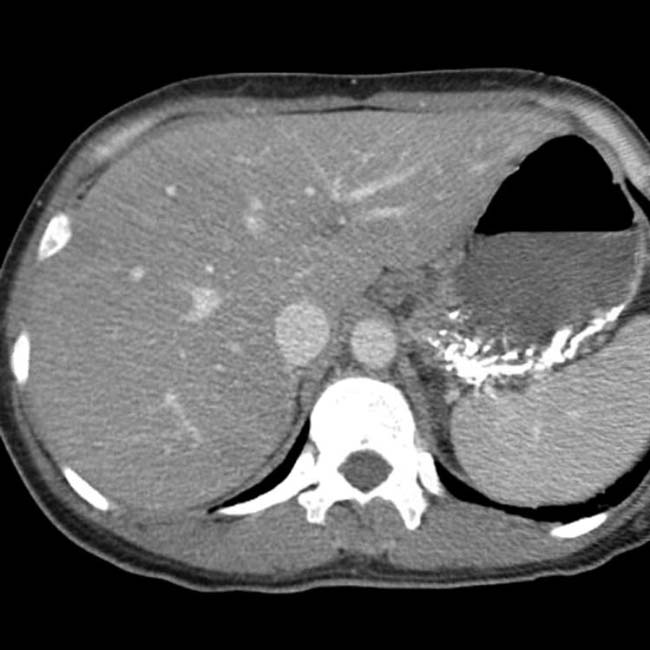
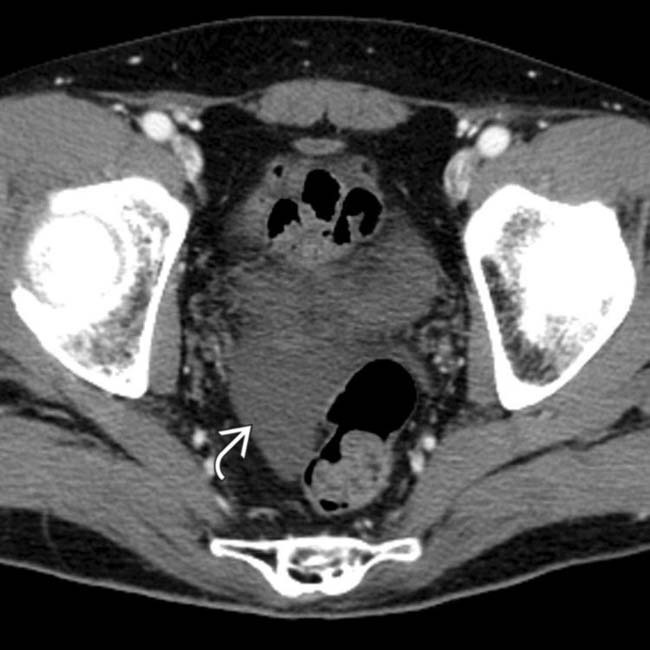
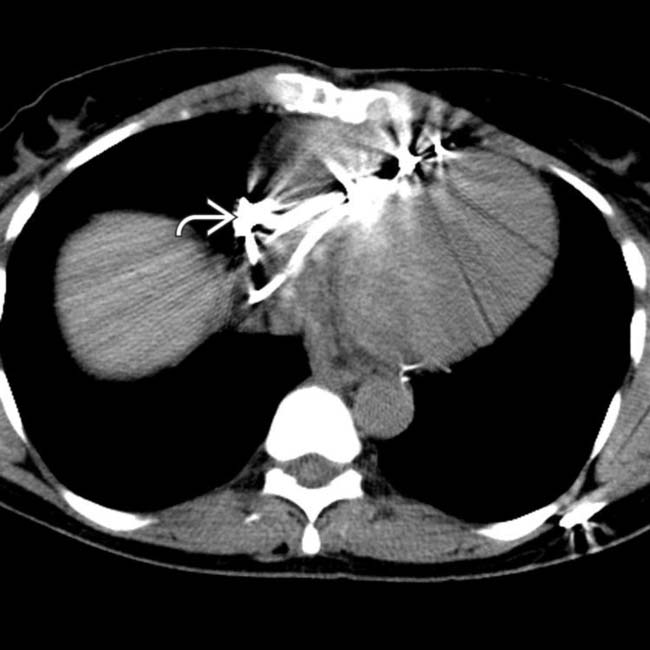
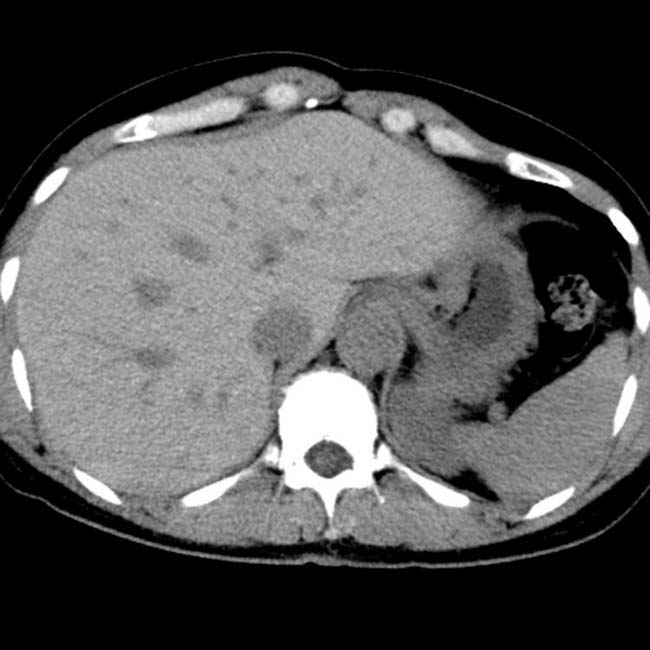
 . A large amount of ascites and pleural effusions are also noted. These are ominous findings, usually associated with death or requiring urgent transplantation.
. A large amount of ascites and pleural effusions are also noted. These are ominous findings, usually associated with death or requiring urgent transplantation.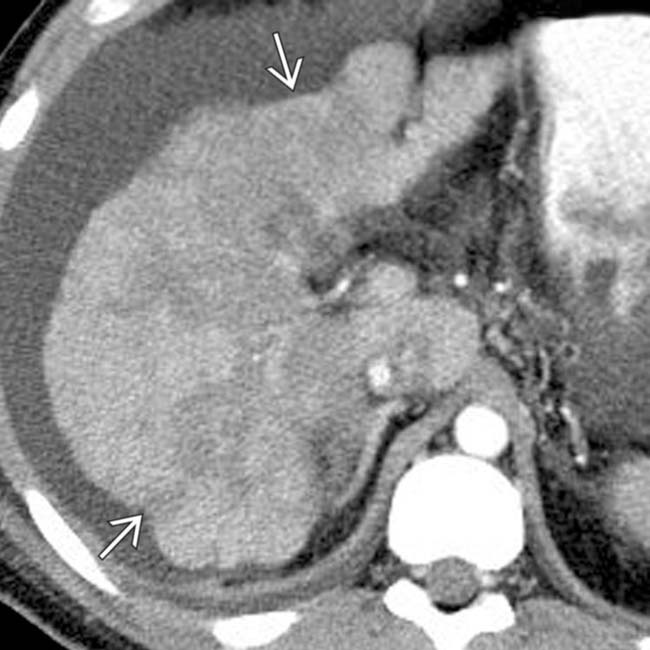
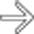 and ascites. The patient died of acute hepatic failure.
and ascites. The patient died of acute hepatic failure.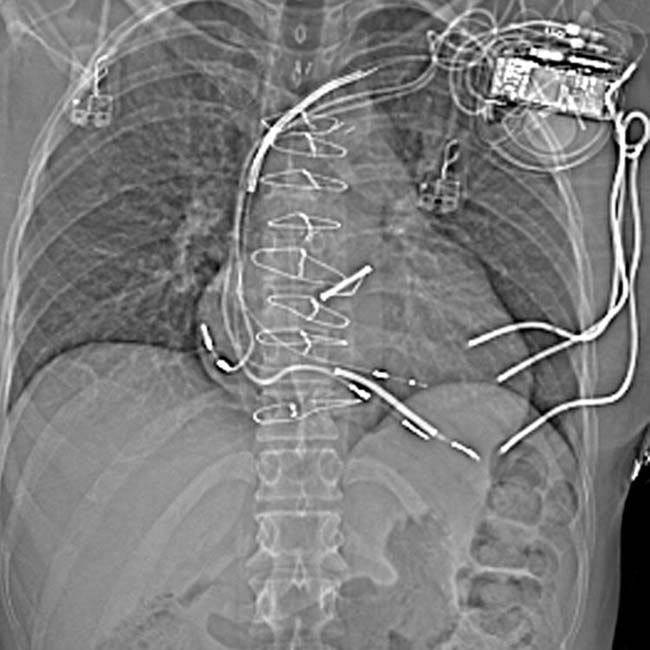




























 .
.
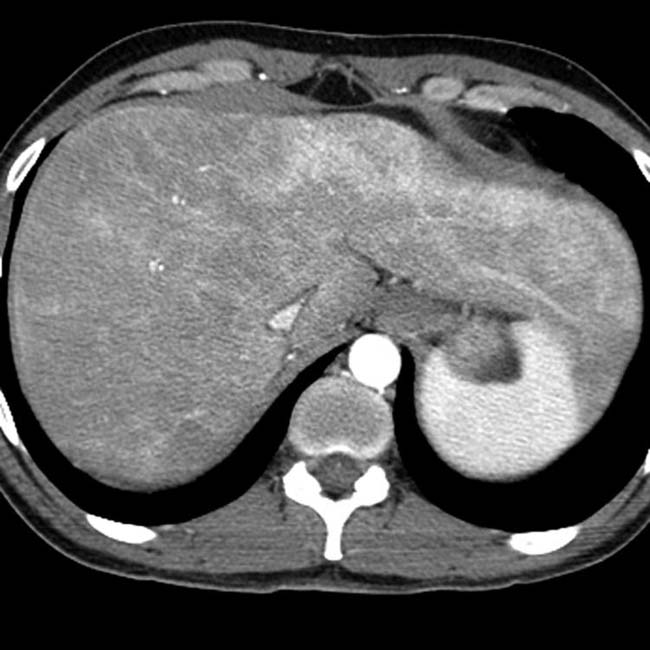
 . This is a frequent feature of amiodarone toxicity. Steatosis may or may not be present.
. This is a frequent feature of amiodarone toxicity. Steatosis may or may not be present. 


